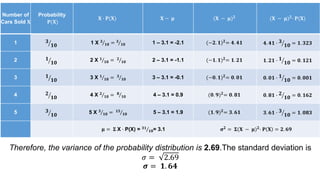
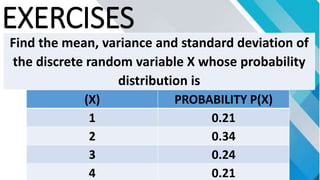
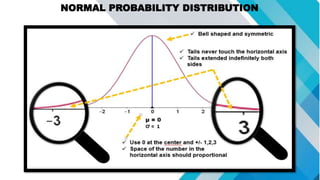
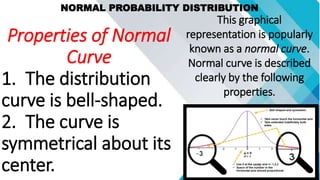
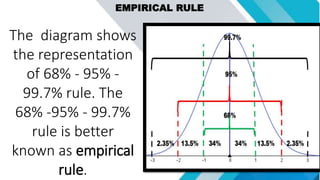
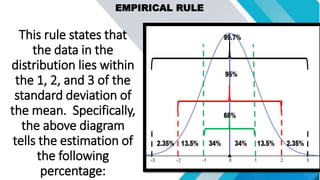
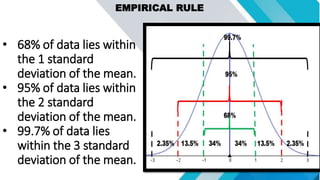
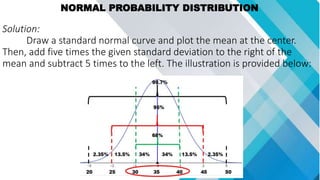
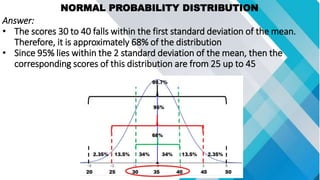
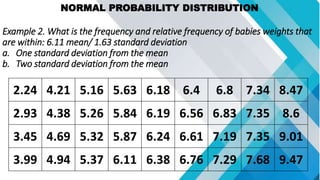
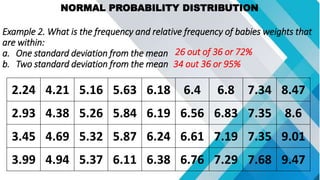
The document discusses concepts related to mean, variance, and standard deviation of discrete random variables. It provides examples of calculating the mean, variance, and standard deviation from probability distributions. It also covers the normal probability distribution and properties such as being bell-shaped and symmetrical about the mean.