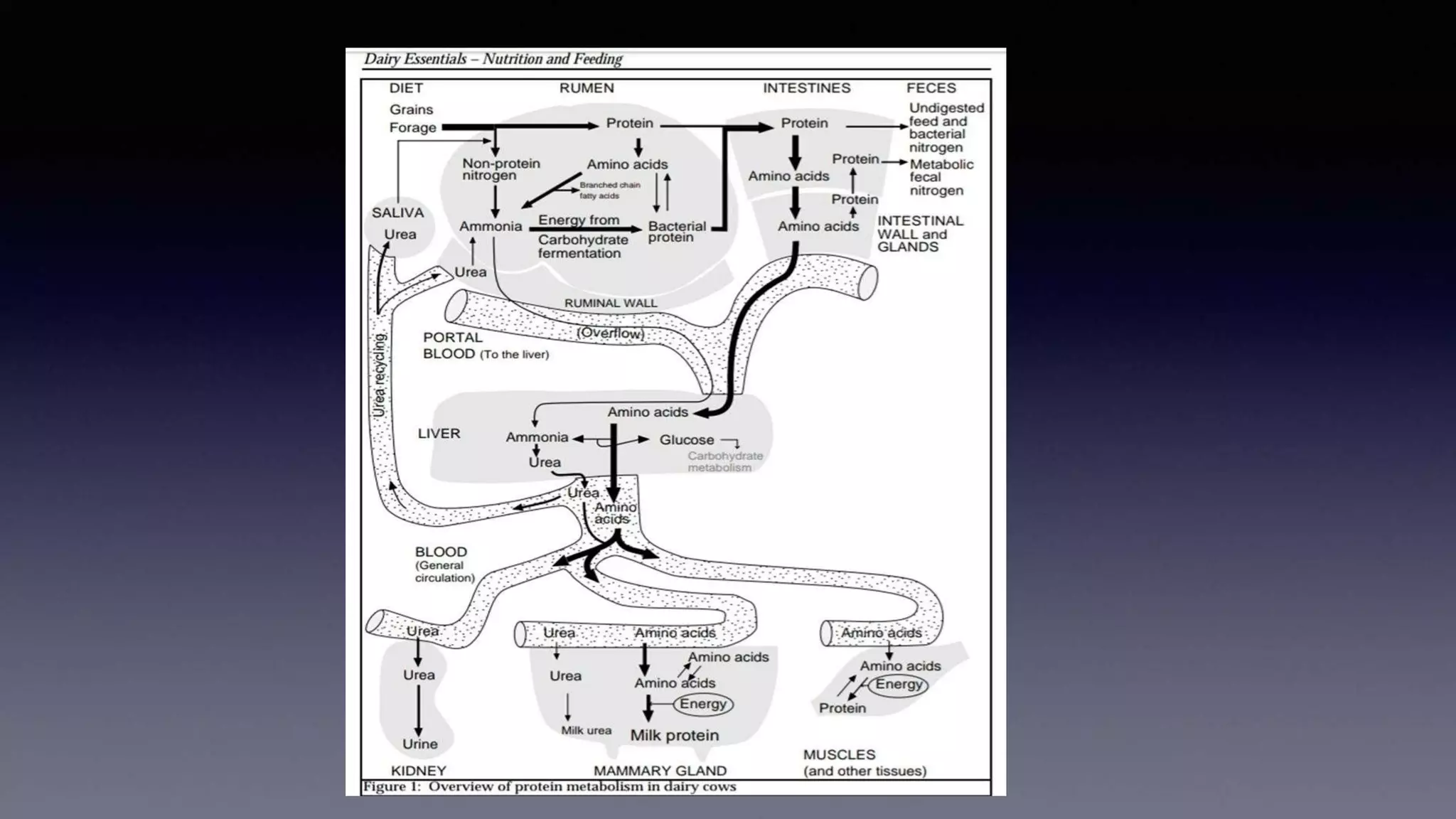
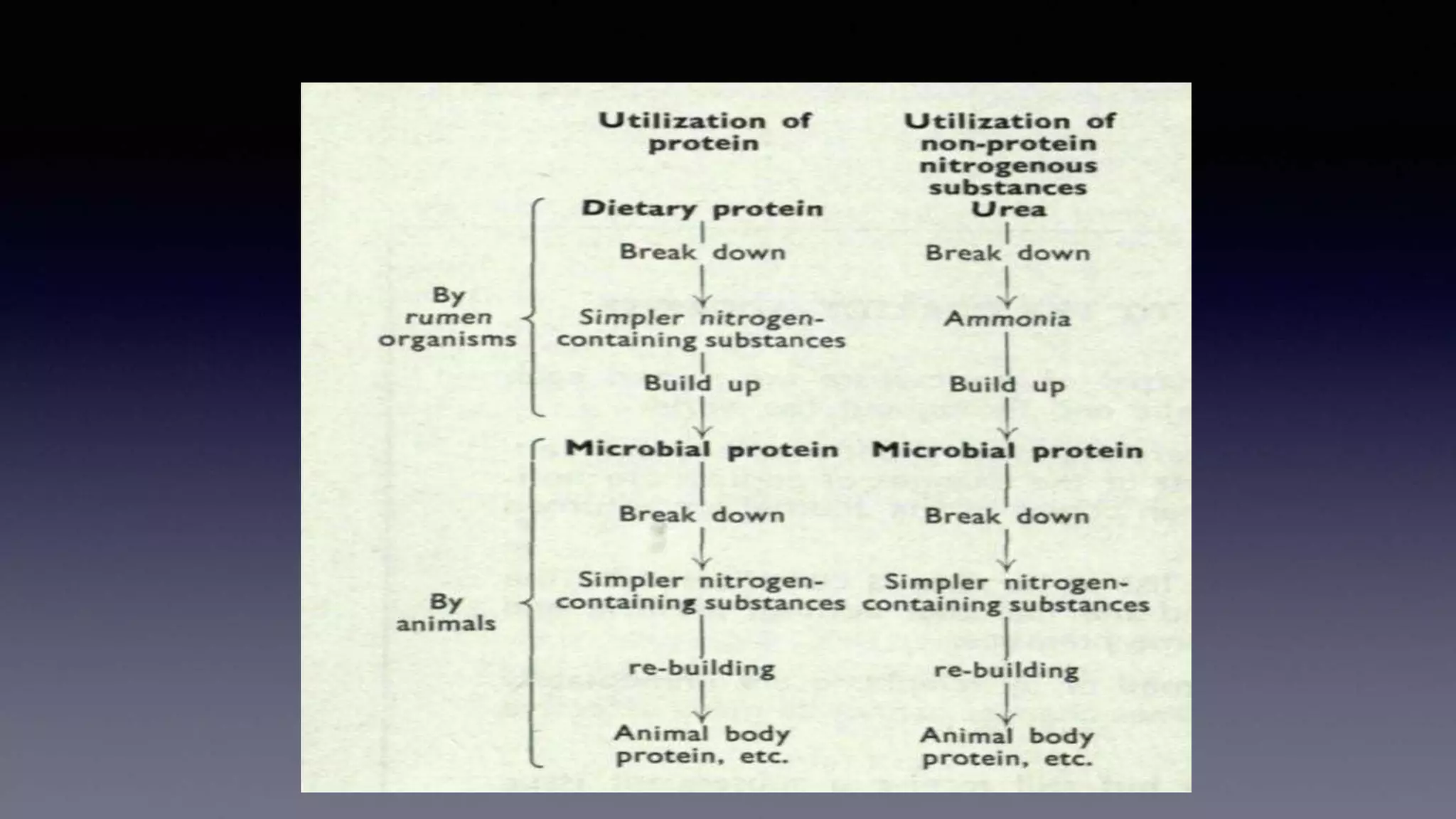
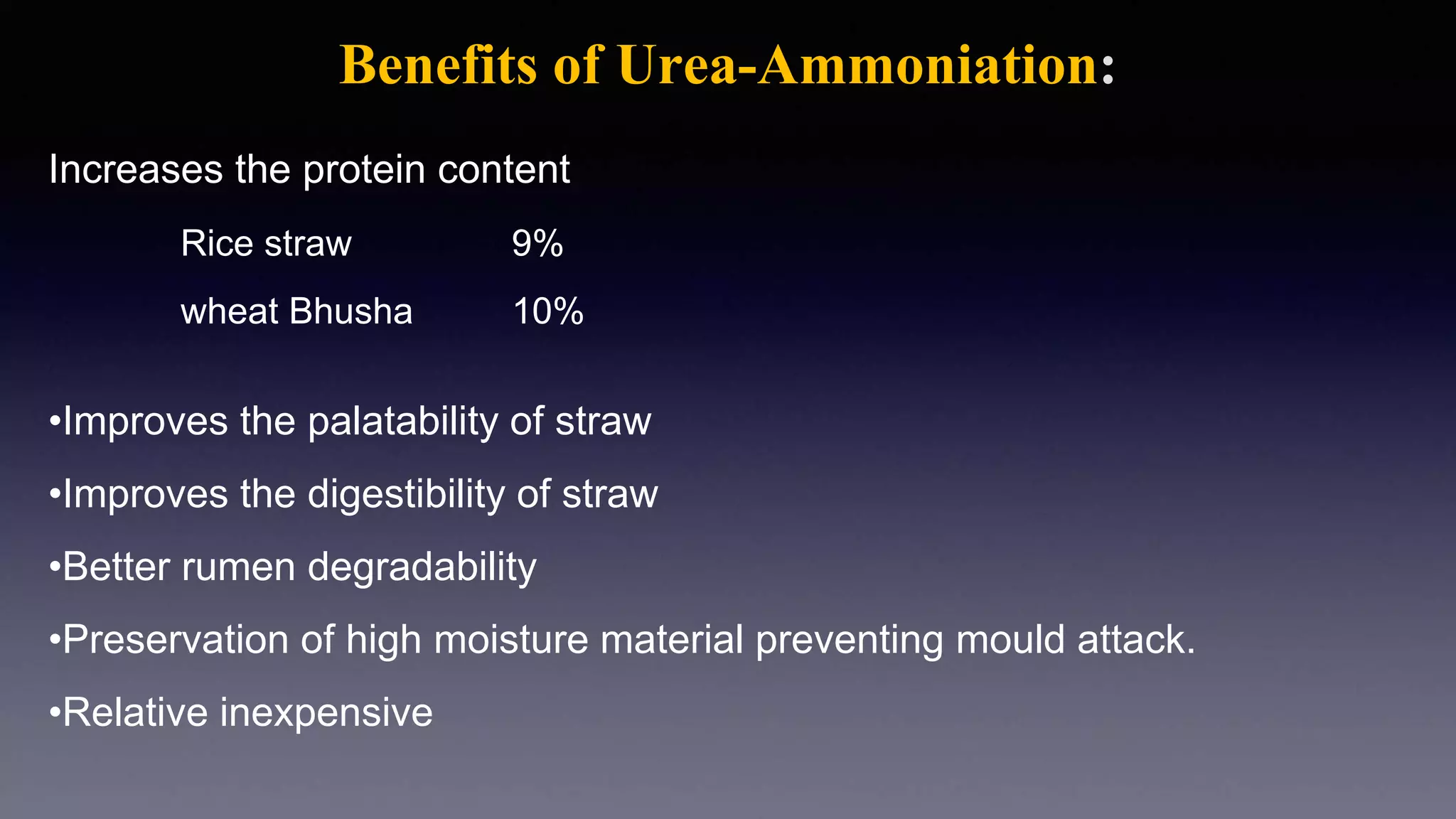
The document discusses non-protein nitrogen (NPN) compounds and their use in ruminant nutrition. It defines NPN as compounds that supply nitrogen other than in the form of protein, with urea being the most commonly used NPN compound. It explains that ruminants can metabolize dietary nitrogen into microbial protein in the rumen. NPN plays a role as an alternate nitrogen source for microbial protein synthesis. Guidelines are provided for supplemental NPN feeding, including gradual introduction and not exceeding 1% of the concentrate or 1/3 of total dietary protein. Potential toxicity from excess ammonia absorption is also discussed.