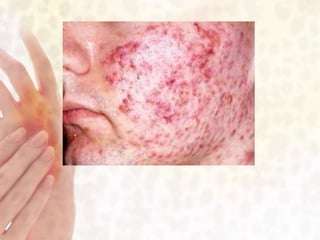
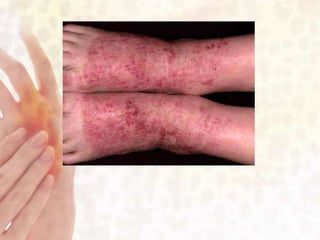
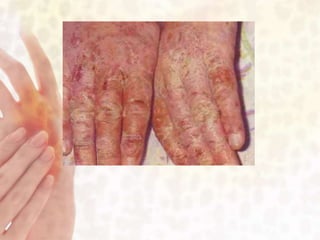
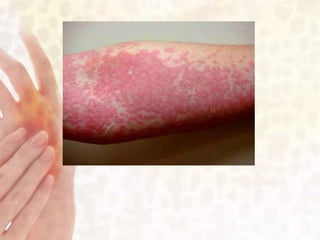
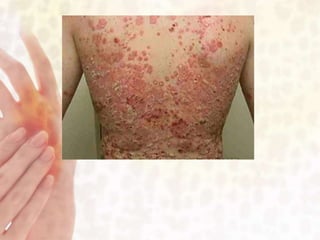
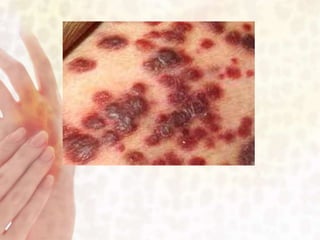
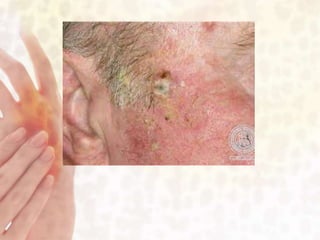
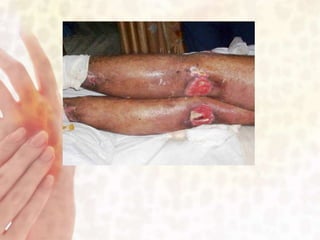
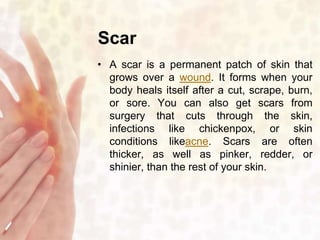
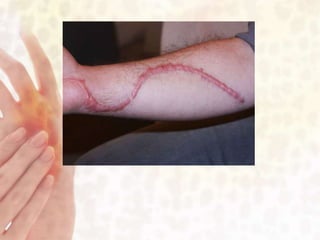
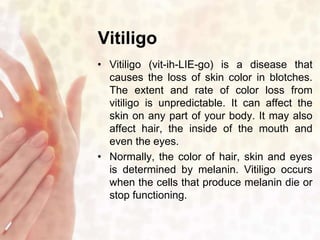
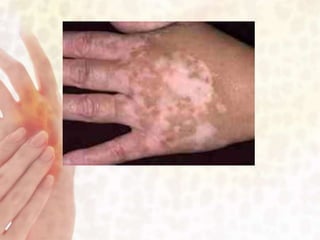
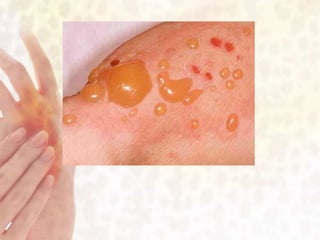
This document provides information on various non-contagious skin disorders and conditions, including acne, atopic dermatitis, contact dermatitis, hives, psoriasis, skin cancer, actinic keratosis, basal cell carcinoma, malignant melanoma, bedsores, scars, vitiligo, bullous pemphigoid and more. It describes the causes, symptoms and treatments for each condition at a basic level.