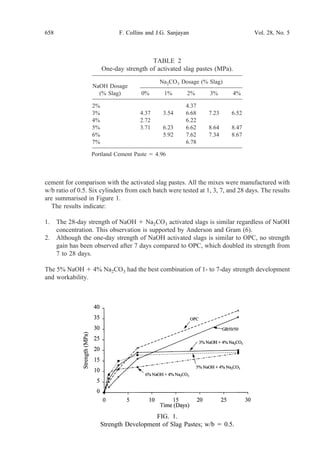
This document summarizes an investigation into activating blast furnace slag with sodium hydroxide (NaOH) and sodium carbonate (Na2CO3) to achieve equivalent one-day strength to ordinary Portland cement at normal curing temperatures of 23°C. The effects of varying dosages of NaOH and Na2CO3 on strength and workability of slag pastes, mortars, and concretes are reported. The results show that combinations of NaOH and Na2CO3 can achieve equivalent or higher one-day strength compared to Portland cement. However, strength gains beyond 7 days were lower than Portland cement. Additions of chemical admixtures improved workability but reduced early strength.