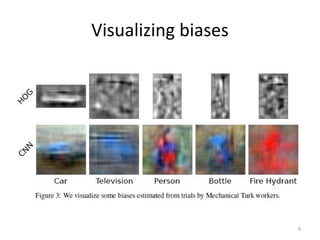
1) The document discusses a paper on improving visual recognition systems by leveraging human visual biases and generating images from random features.
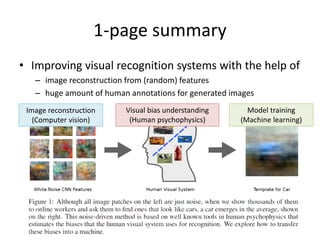
2) It describes estimating visual biases from human psychophysics experiments, then using those biases to reconstruct images from random features. The reconstructed images can then be used to train machine learning models.
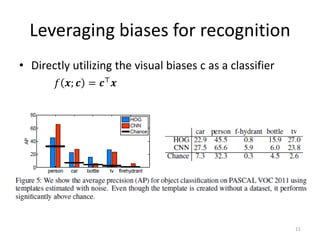
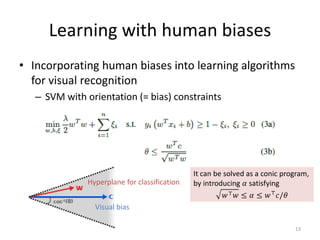
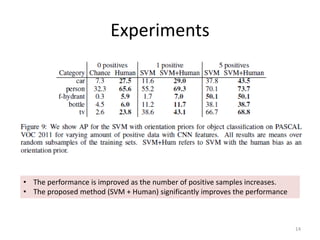
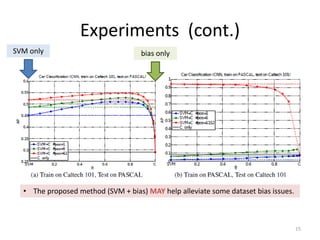
3) The document outlines experiments showing that incorporating estimated human visual biases into machine learning models, such as SVMs, can help improve visual recognition performance compared to models trained without biases.


![Visual biases in human visual systems
4
Canonical views
Preferred ways of
viewing objects
Gestalt law
Tendency to organize
visual elements into
unified groups
[Mezuman+ NPS12]
http://graphicdesign.spokanefalls.edu/tutorials/process/gestaltprinciples/gestaltprinc.htm](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bayes160304forpub-160305091622/85/NIPS2015-reading-Learning-visual-biases-from-human-imagination-4-320.jpg)
![Classification images
• Finding the internal template in human visual system
that discriminates 2 classes
5
[Ahumada Perception96]
𝑓𝑓 𝒙𝒙; 𝒄𝒄 = 𝒄𝒄⊤ 𝒙𝒙
𝒄𝒄 = 𝝁𝝁𝐴𝐴𝐴𝐴 + 𝝁𝝁𝐵𝐵𝐵𝐵 − 𝝁𝝁𝐴𝐴𝐴𝐴 + 𝝁𝝁𝐵𝐵𝐵𝐵
𝝁𝝁𝐴𝐴𝐴𝐴: Average of stimulus where
• The true class = A
• The predicted class = B](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bayes160304forpub-160305091622/85/NIPS2015-reading-Learning-visual-biases-from-human-imagination-5-320.jpg)
![Estimating biases in feature spaces
• No real images required
– robust to many issues in dataset bias
– It scales 6
Random feature
Feature inverse
Generated image
Is this television or not?
Yes
No
𝒄𝒄 = 𝝁𝝁𝑌𝑌𝑌𝑌𝑌𝑌 − 𝝁𝝁𝑁𝑁𝑁𝑁Approximate internal template of people
150,000 features
from standard Gaussian
• HOGgles
[Vondrick+ ICCV13] Amazon MT](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bayes160304forpub-160305091622/85/NIPS2015-reading-Learning-visual-biases-from-human-imagination-6-320.jpg)
![Reconstructing images from features
7
[Weinzaepfel+ CVPR11]
[Vondrick+ ICCV13]
[Kato+ CVPR14]
[Mahendran+ CVPR15]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bayes160304forpub-160305091622/85/NIPS2015-reading-Learning-visual-biases-from-human-imagination-7-320.jpg)
![HOGgles
• Paired dictionary learning
– Can be applied to other features such as CNN.
8
[Vondrick+ ICCV13]
𝒚𝒚𝑖𝑖
�𝒙𝒙𝑖𝑖
𝑽𝑽
𝑼𝑼](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bayes160304forpub-160305091622/85/NIPS2015-reading-Learning-visual-biases-from-human-imagination-8-320.jpg)