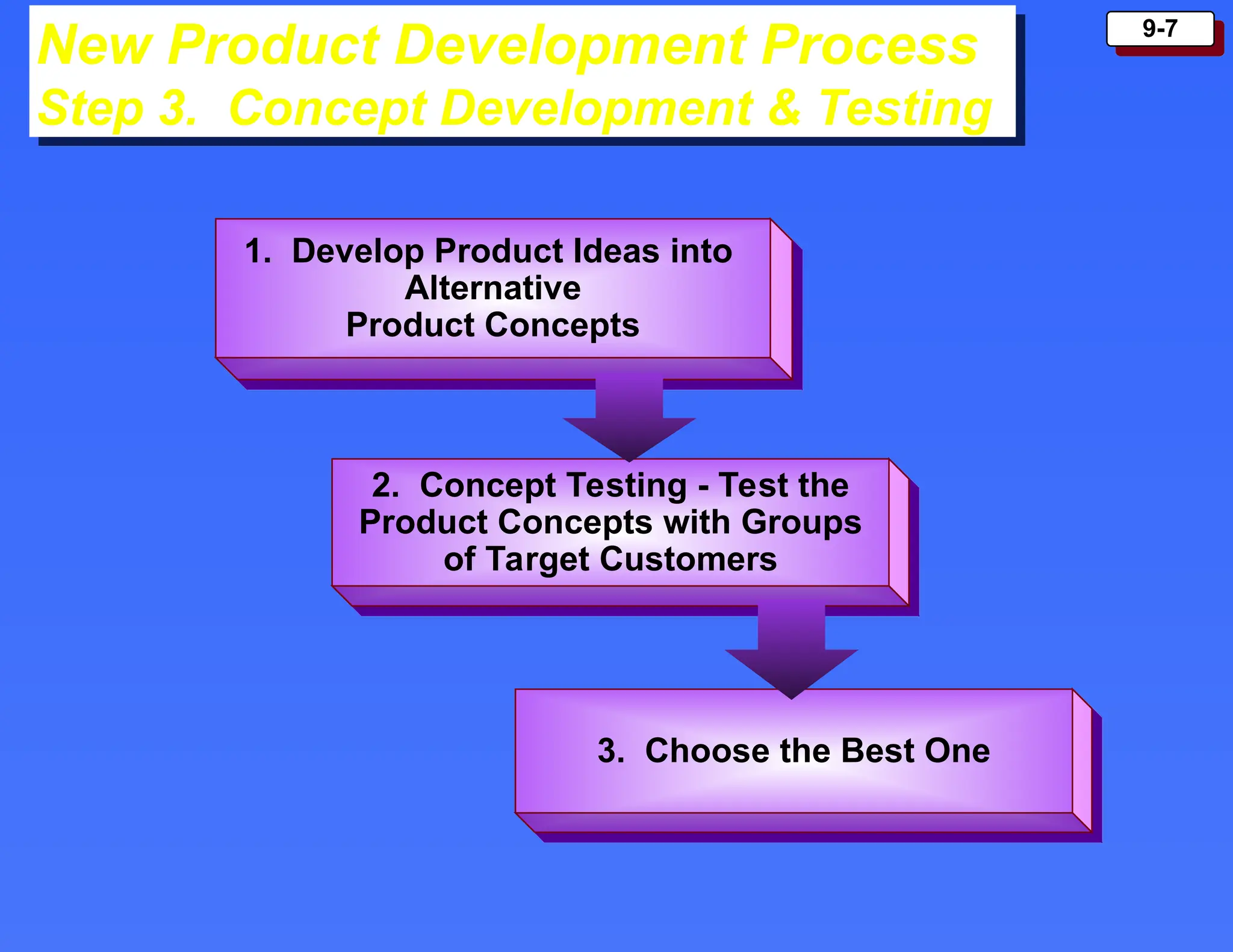
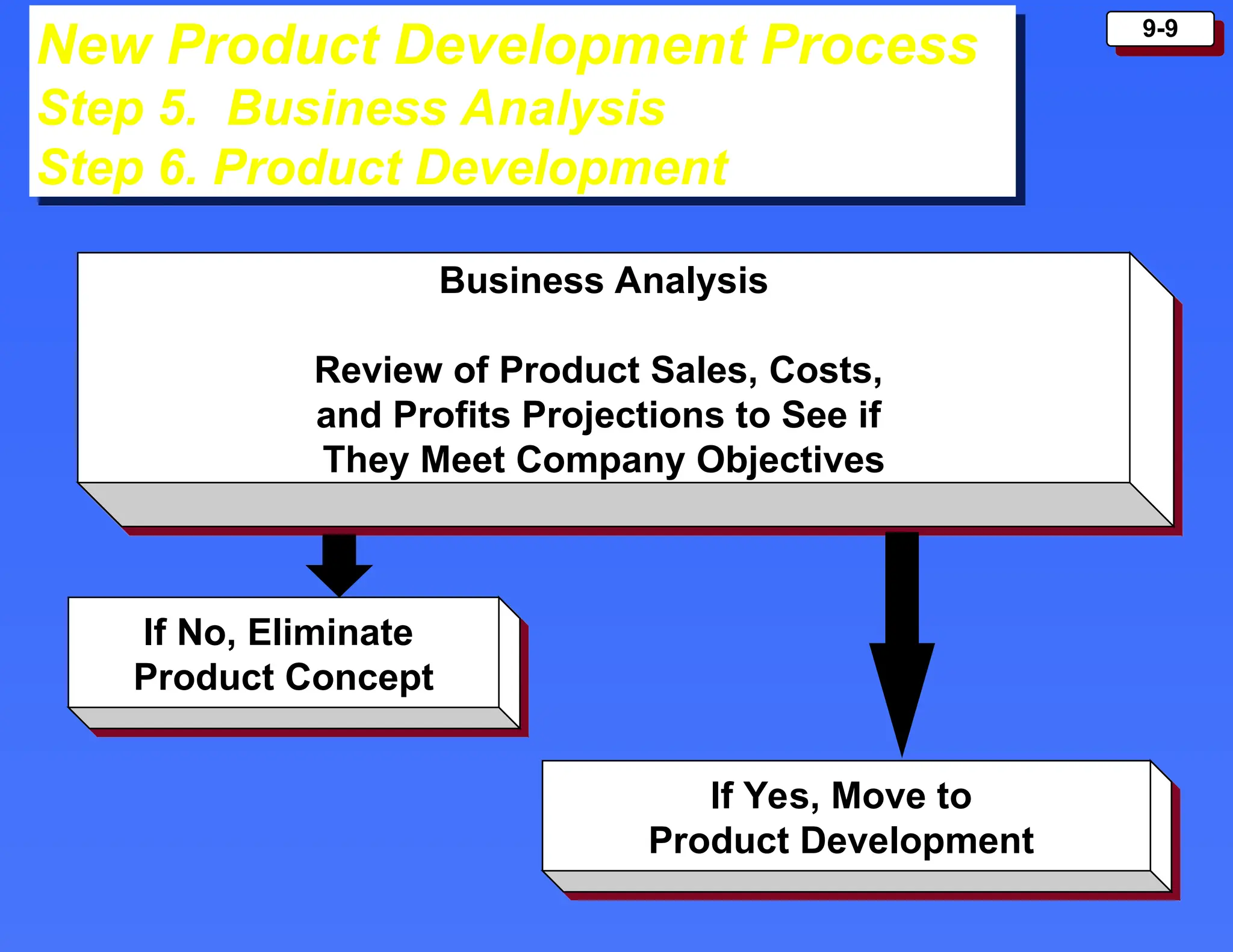
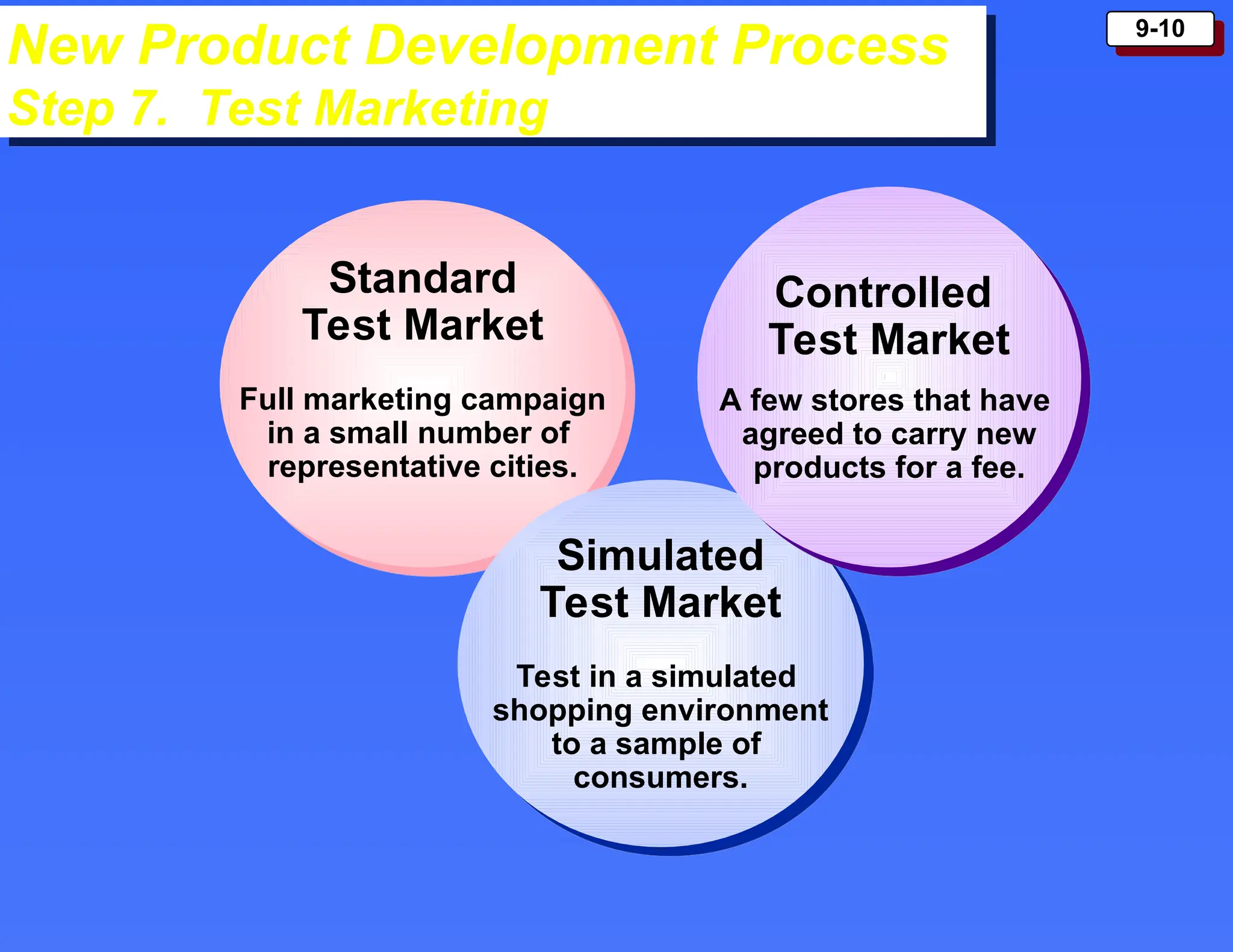
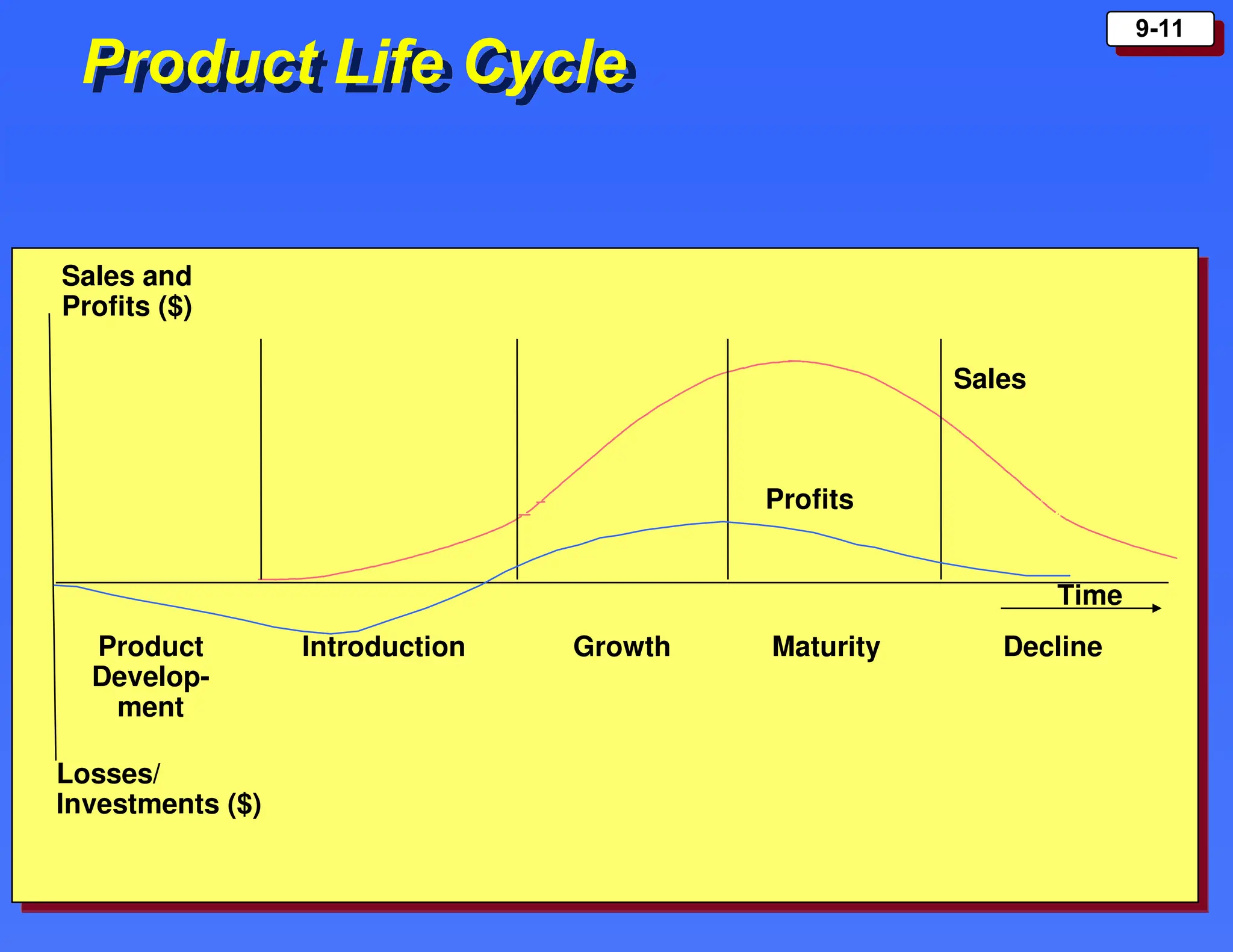
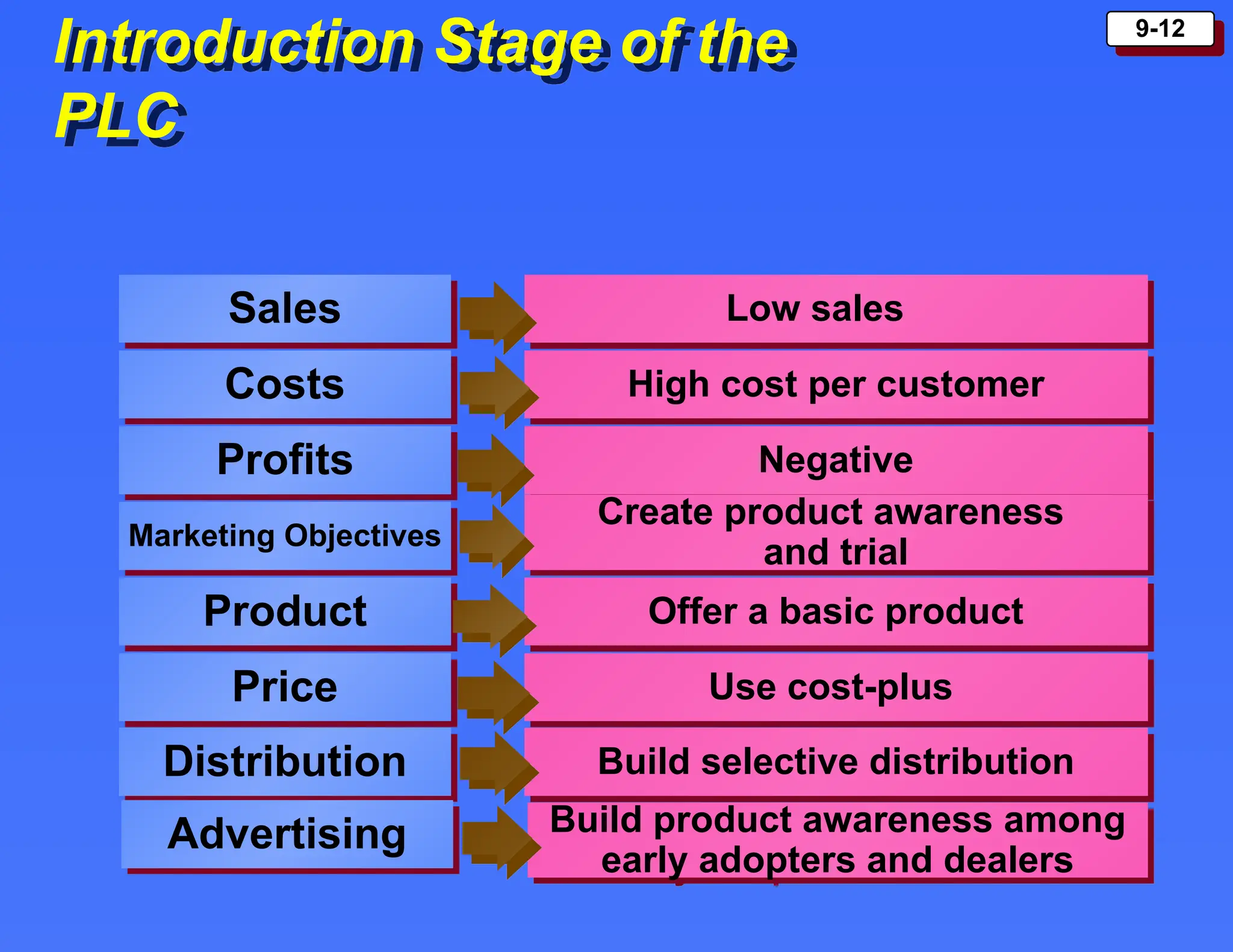
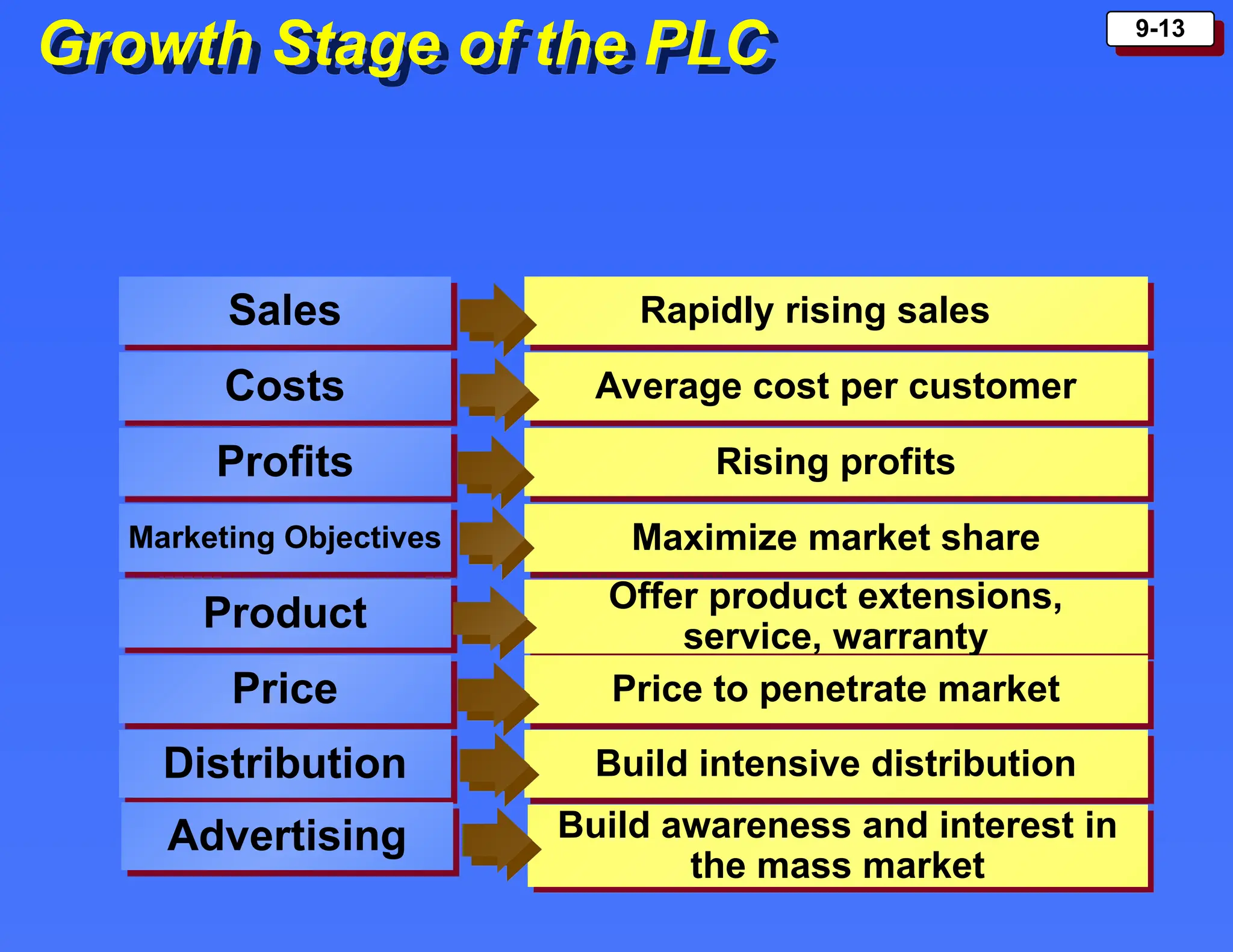
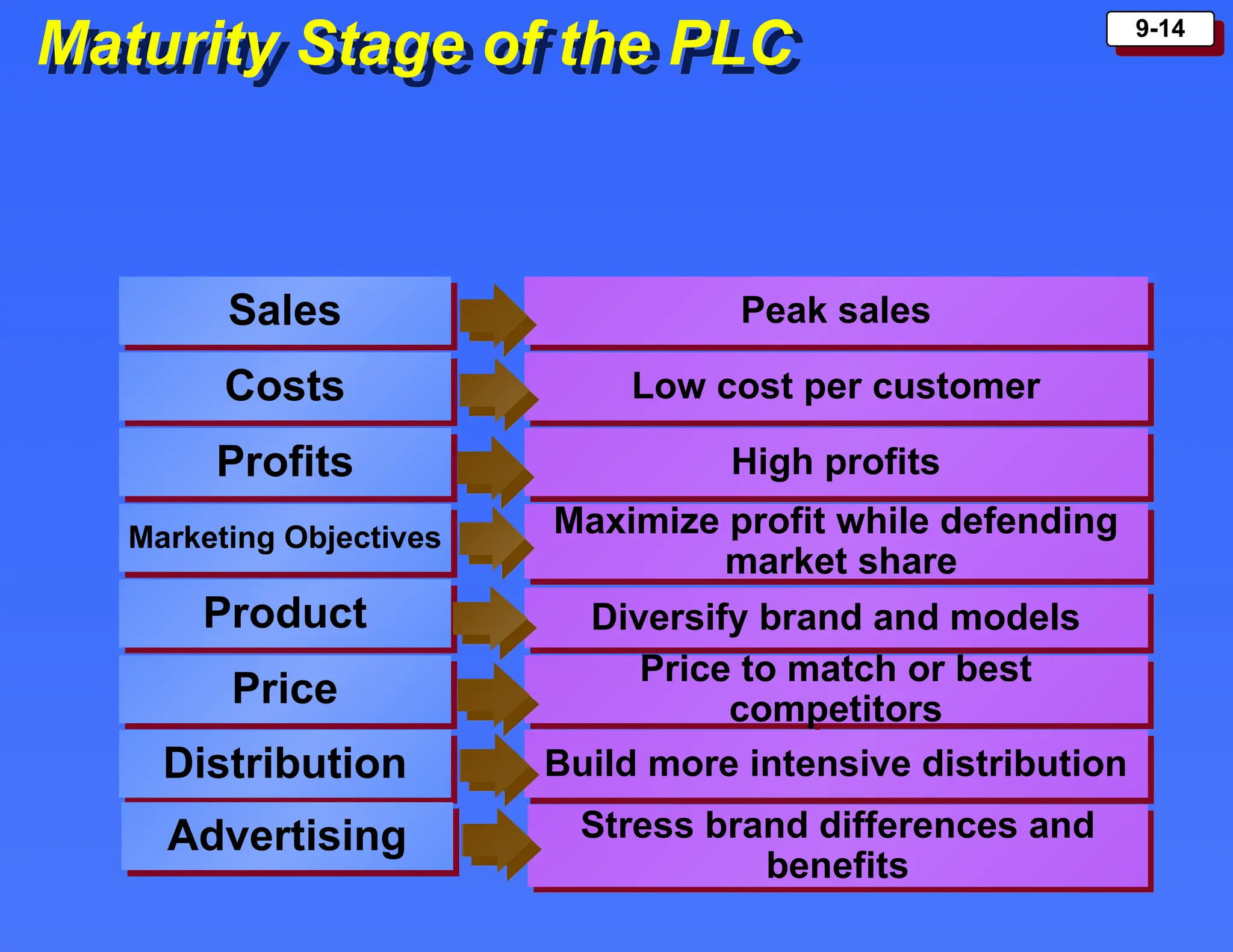
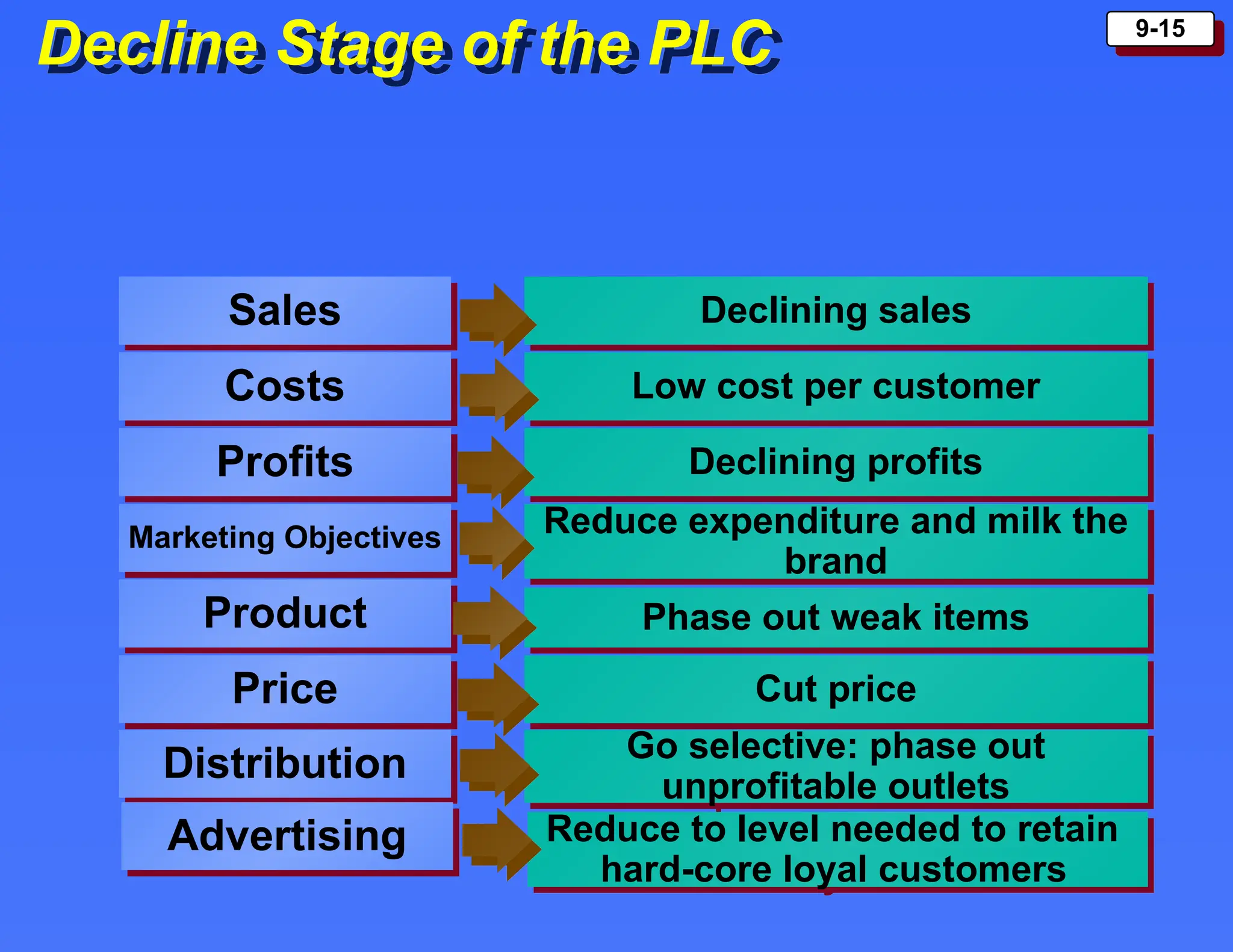
The document outlines the new product development process and factors contributing to new product failures, emphasizing the importance of understanding customer needs and competitive dynamics. It details a systematic approach to product development, including stages from idea generation to commercialization, along with strategies for managing the product life cycle, which comprises introduction, growth, maturity, and decline stages. Each stage has specific marketing objectives, pricing strategies, and distribution approaches to optimize sales and profitability.