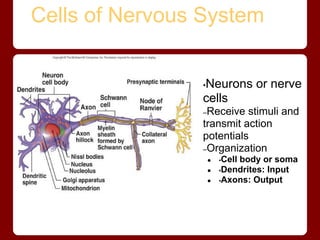
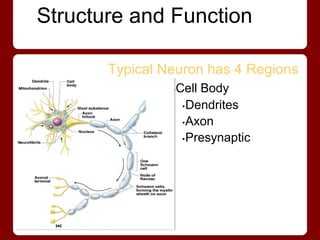
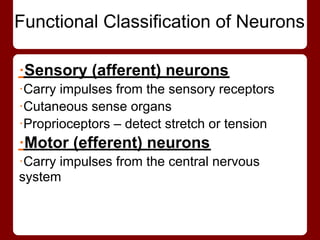
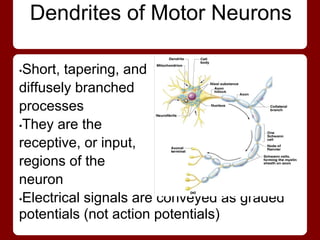
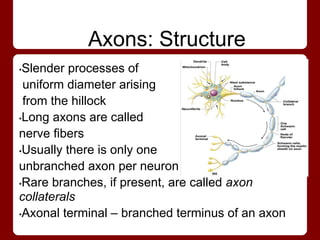
Neurons have four main regions - the cell body, dendrites, axon, and presynaptic terminals. The cell body contains the nucleus. Dendrites receive signals from other neurons and conduct them toward the cell body. The axon conducts signals away from the cell body, and presynaptic terminals transmit signals to other neurons. Neurons can be sensory/afferent neurons that carry signals from receptors to the CNS, or motor/efferent neurons that carry signals from the CNS to effectors. The myelin sheath surrounds long axons for protection, electrical insulation, and faster signal transmission.