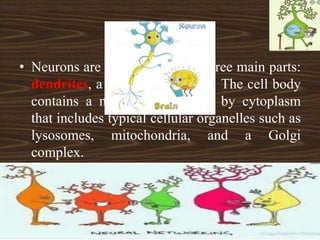
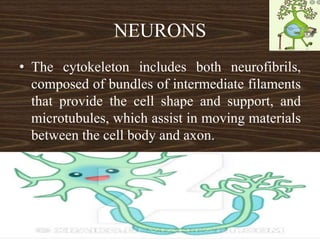
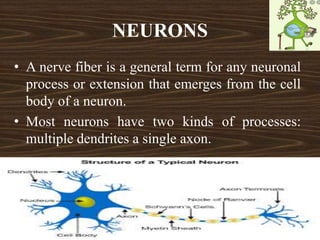
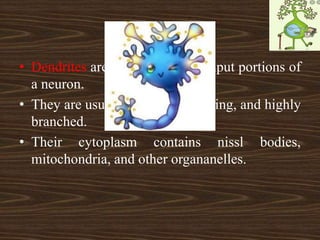
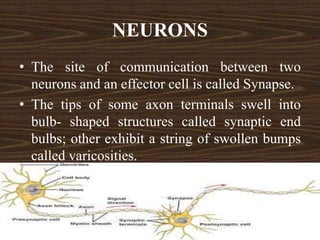
Nervous tissue consists of neurons and neuroglia cells. Neurons are composed of dendrites, a cell body, and an axon, and are responsible for functions like sensing, thinking, and muscle control. The cell body contains organelles and protein-producing structures. Dendrites receive signals and the axon transmits signals. Neuroglia provide support and nourishment to the neurons.