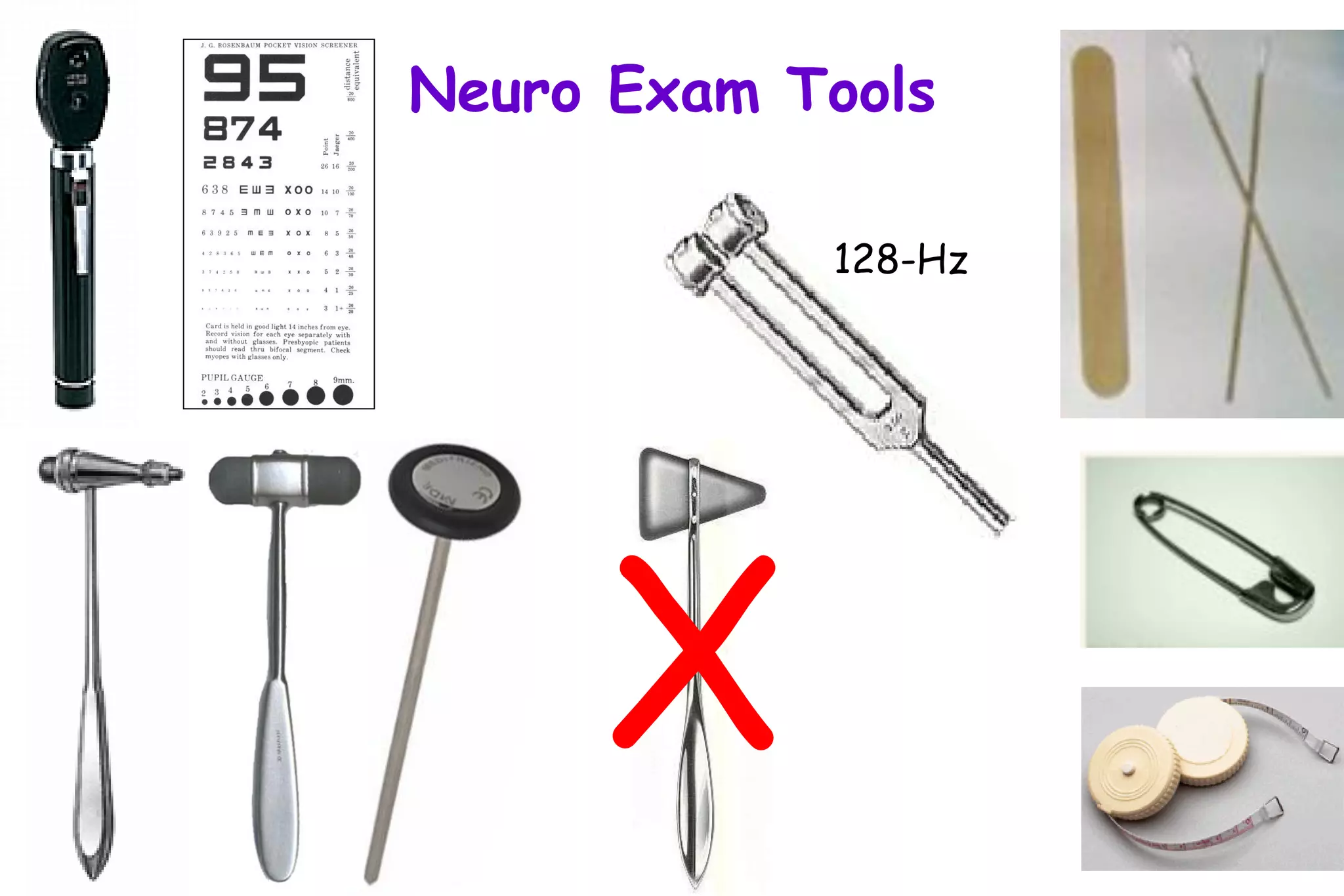
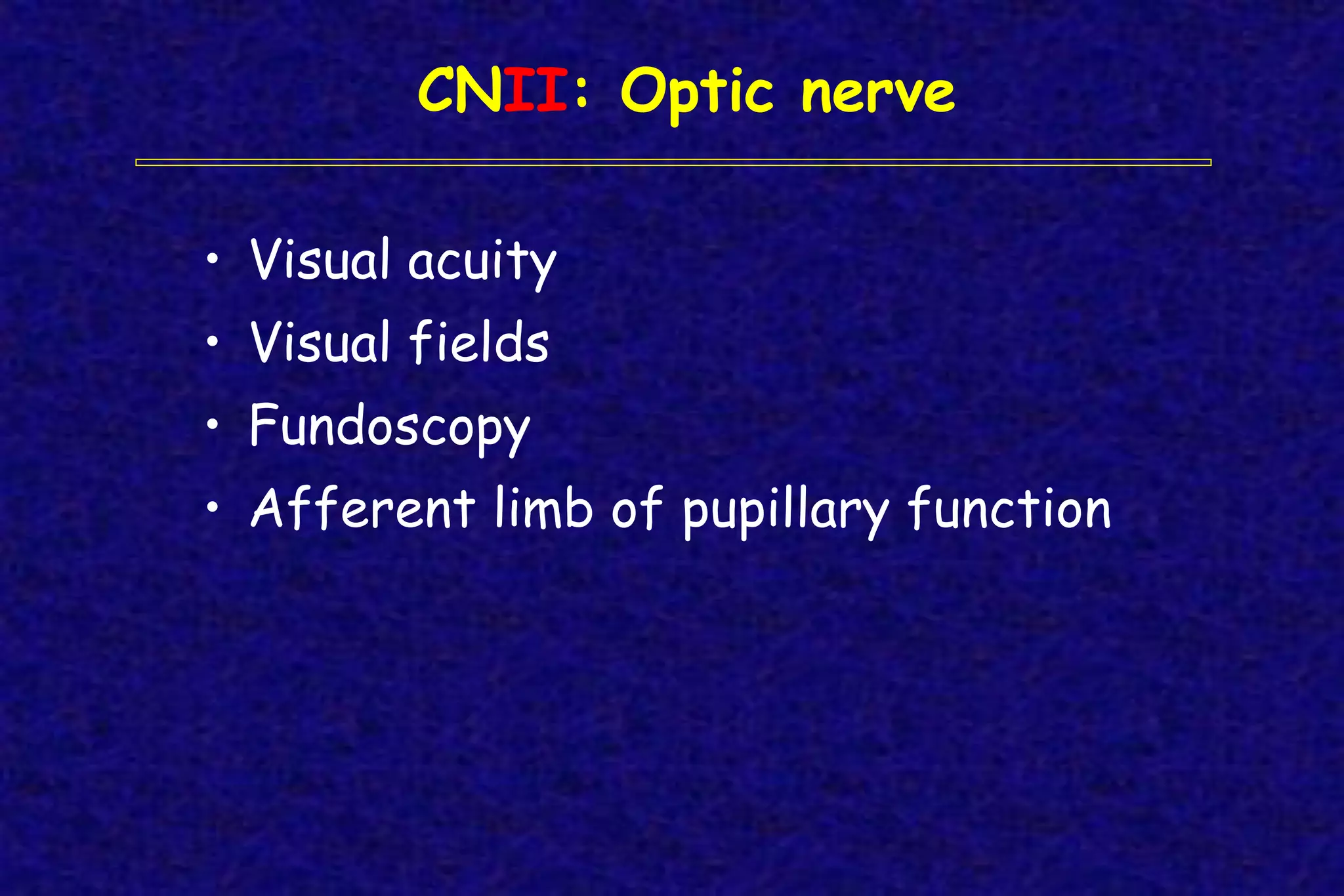
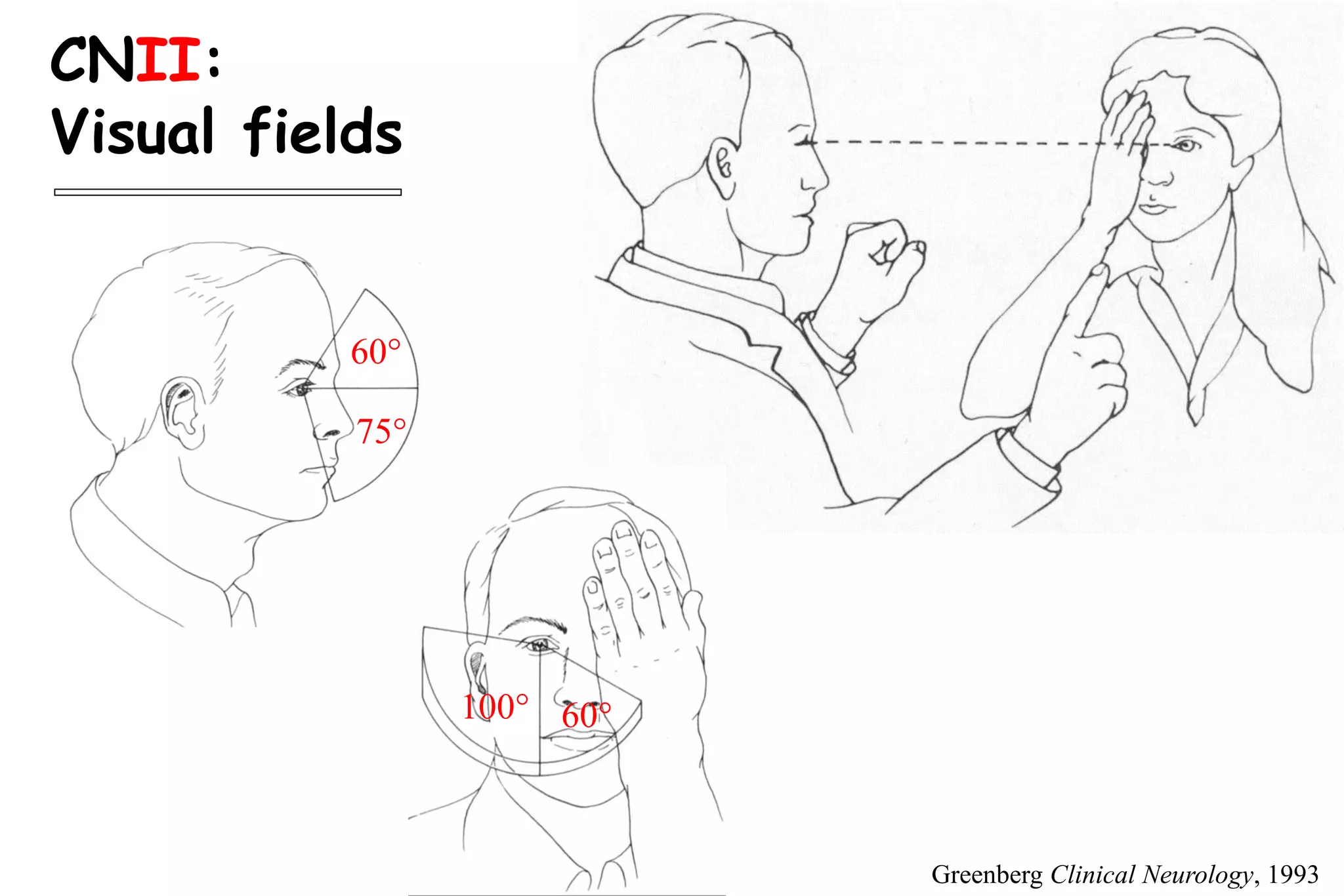
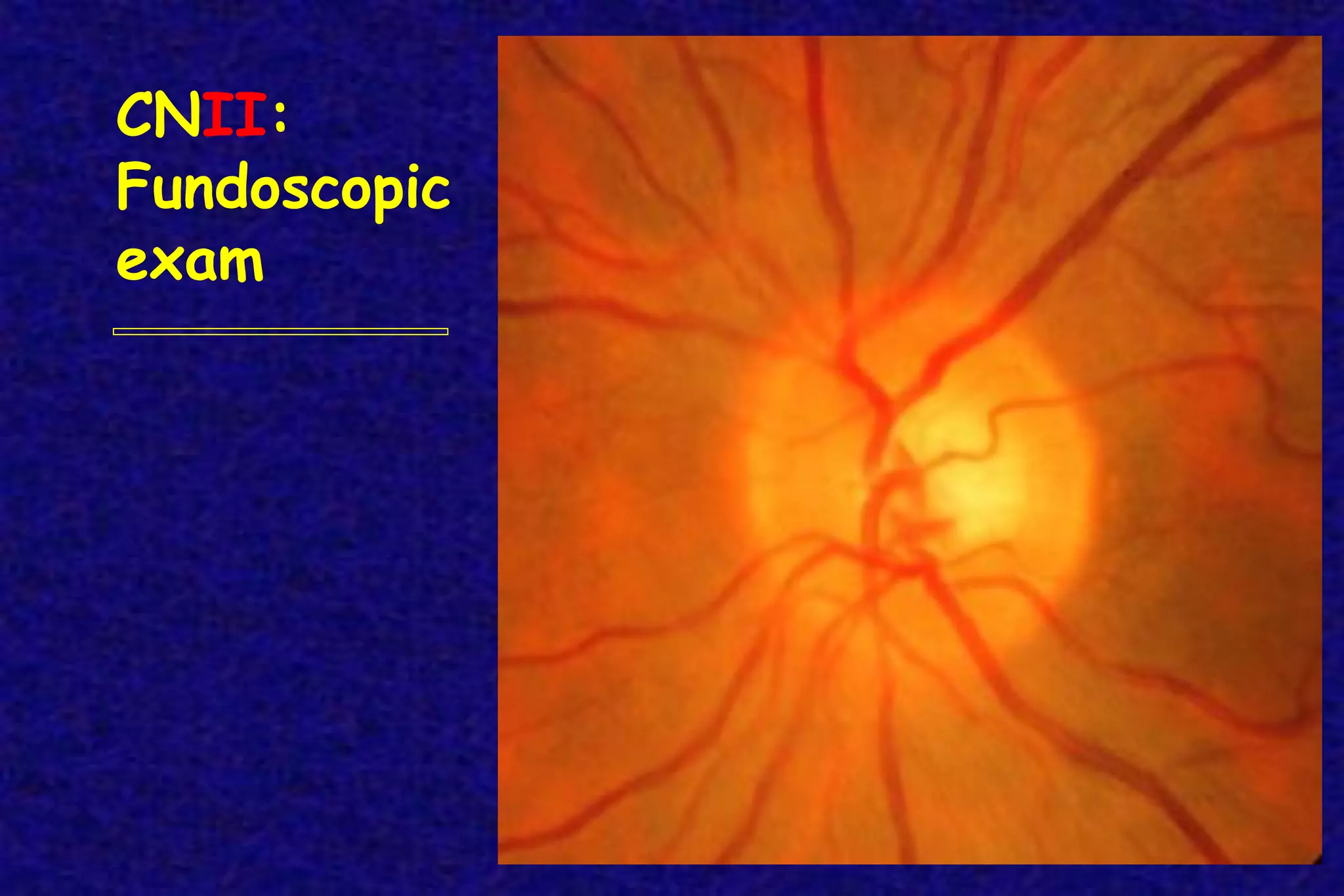
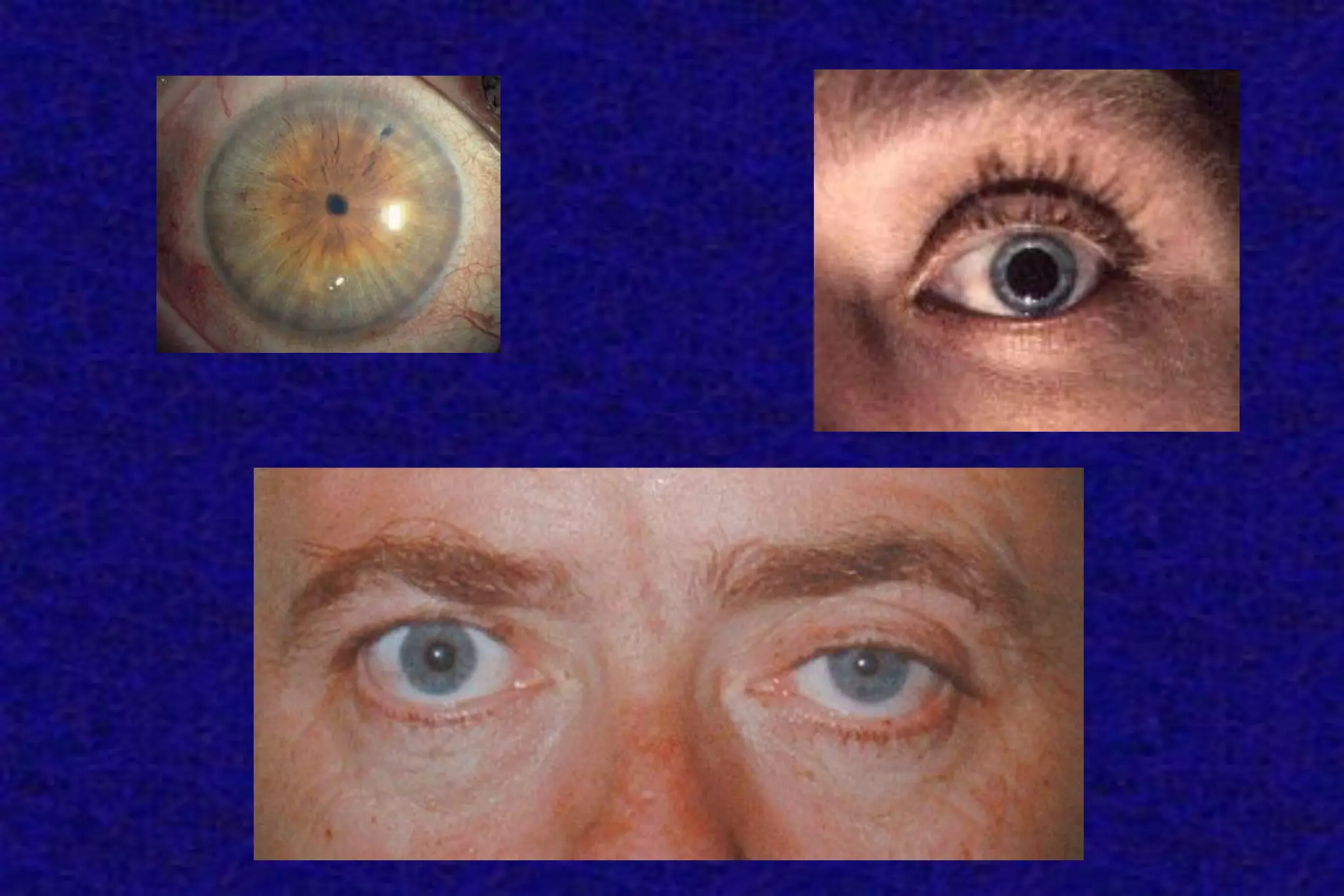
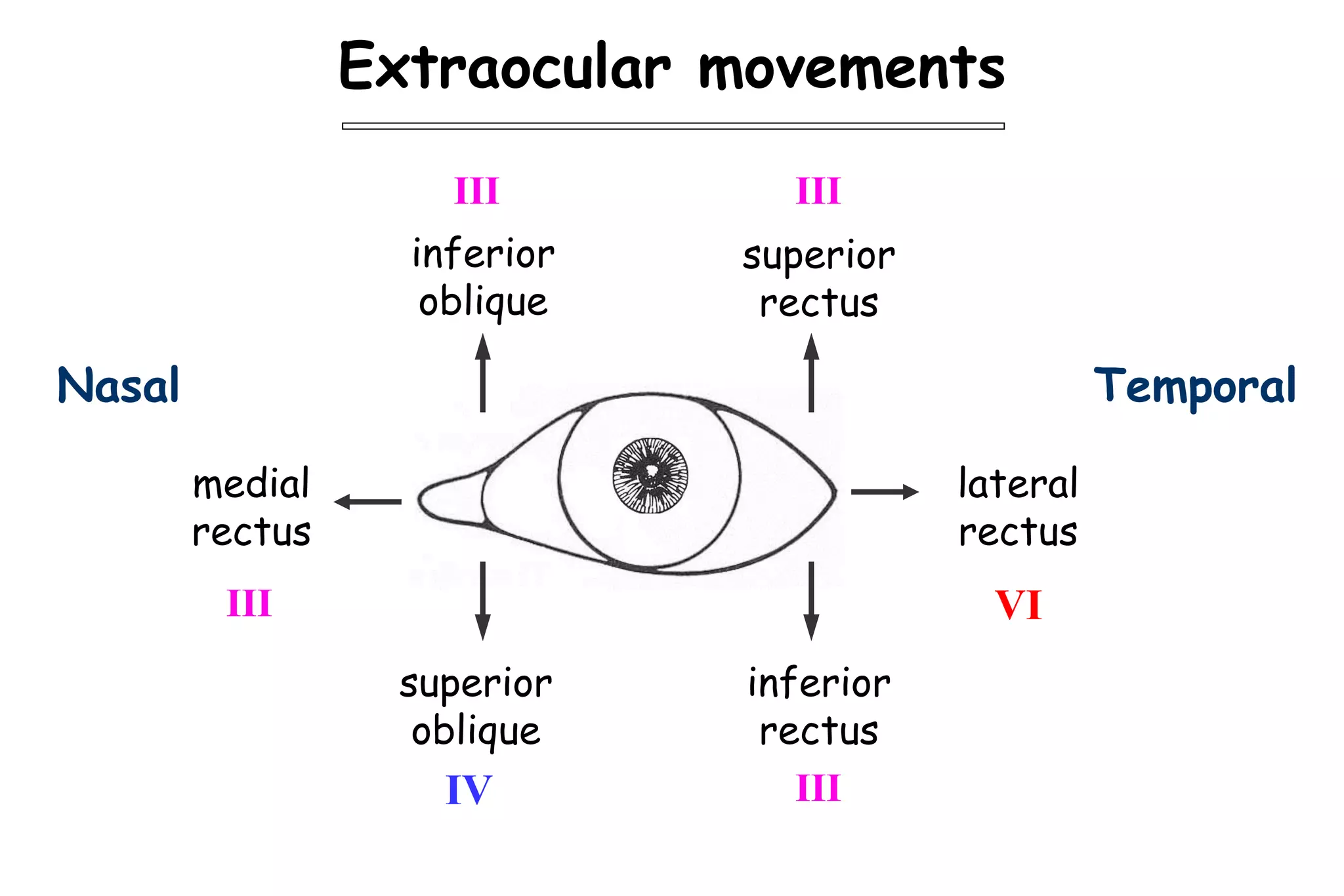
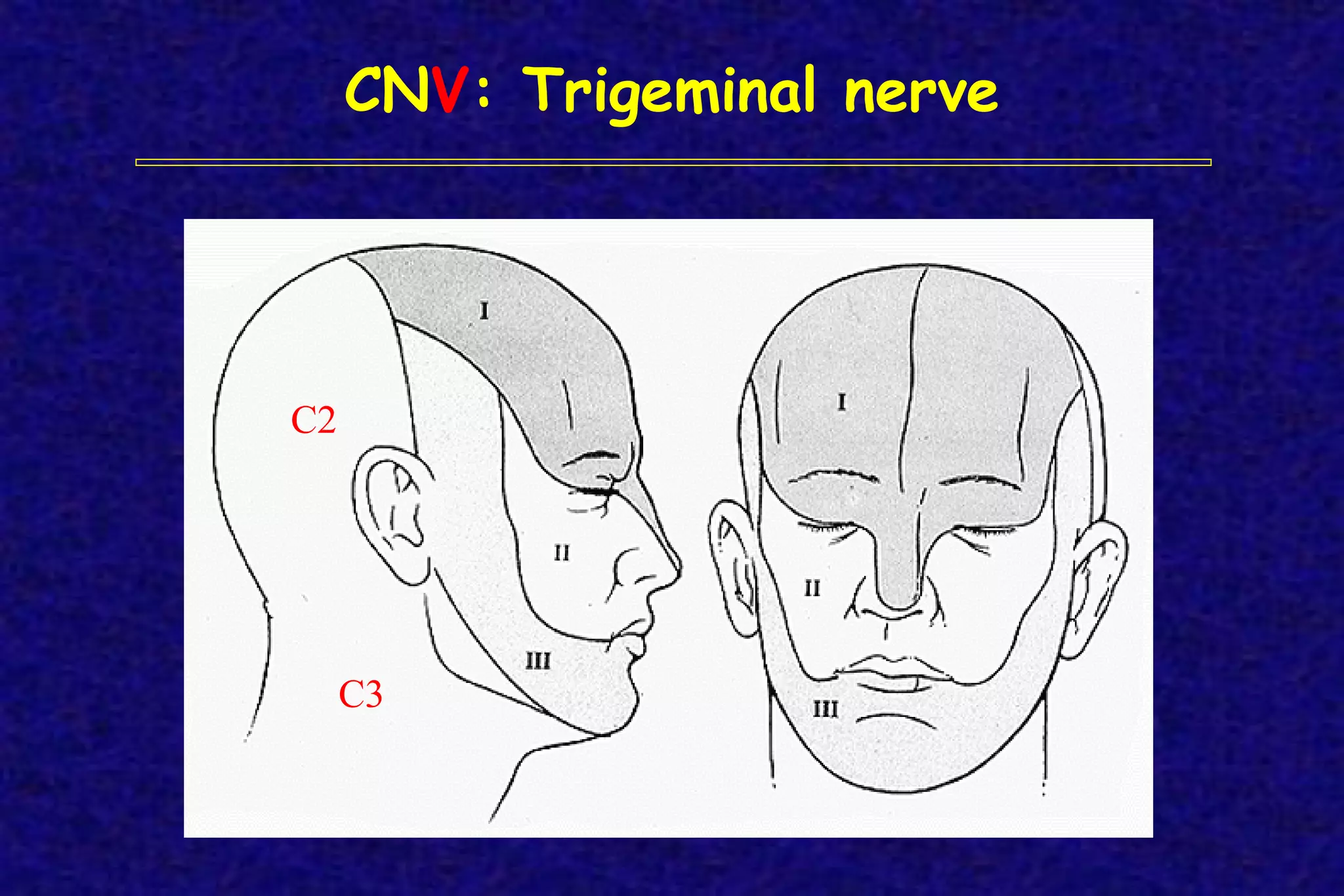
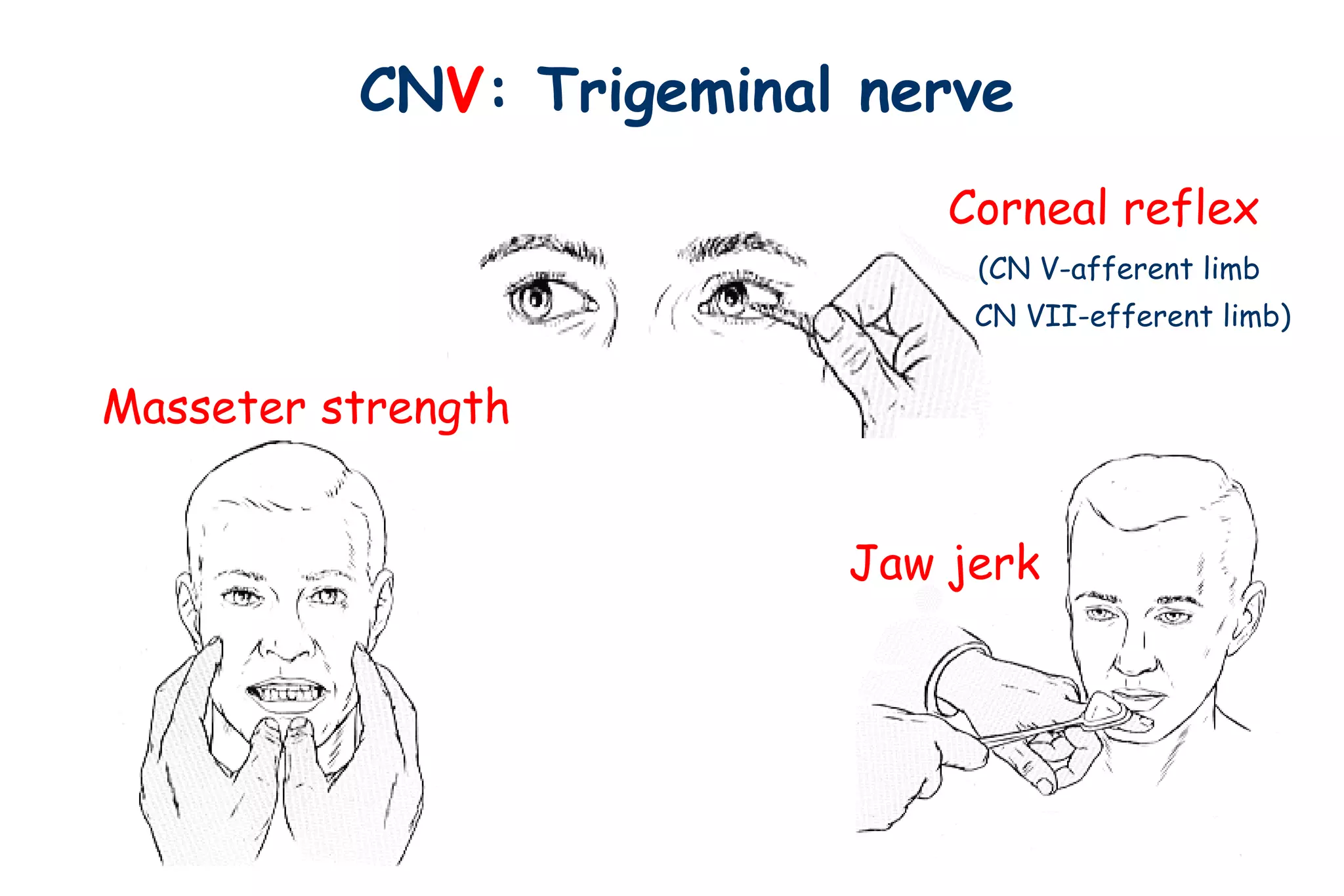
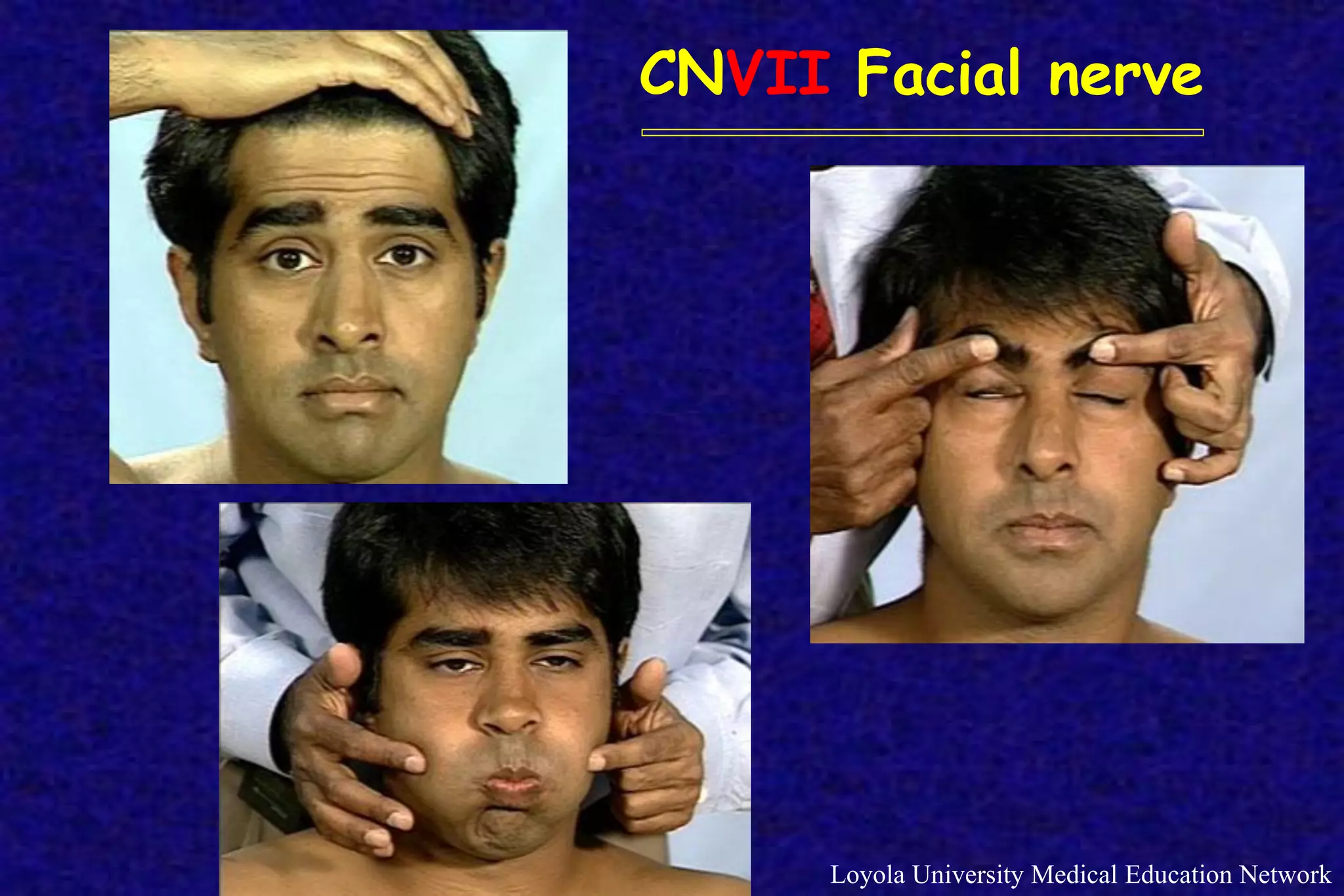
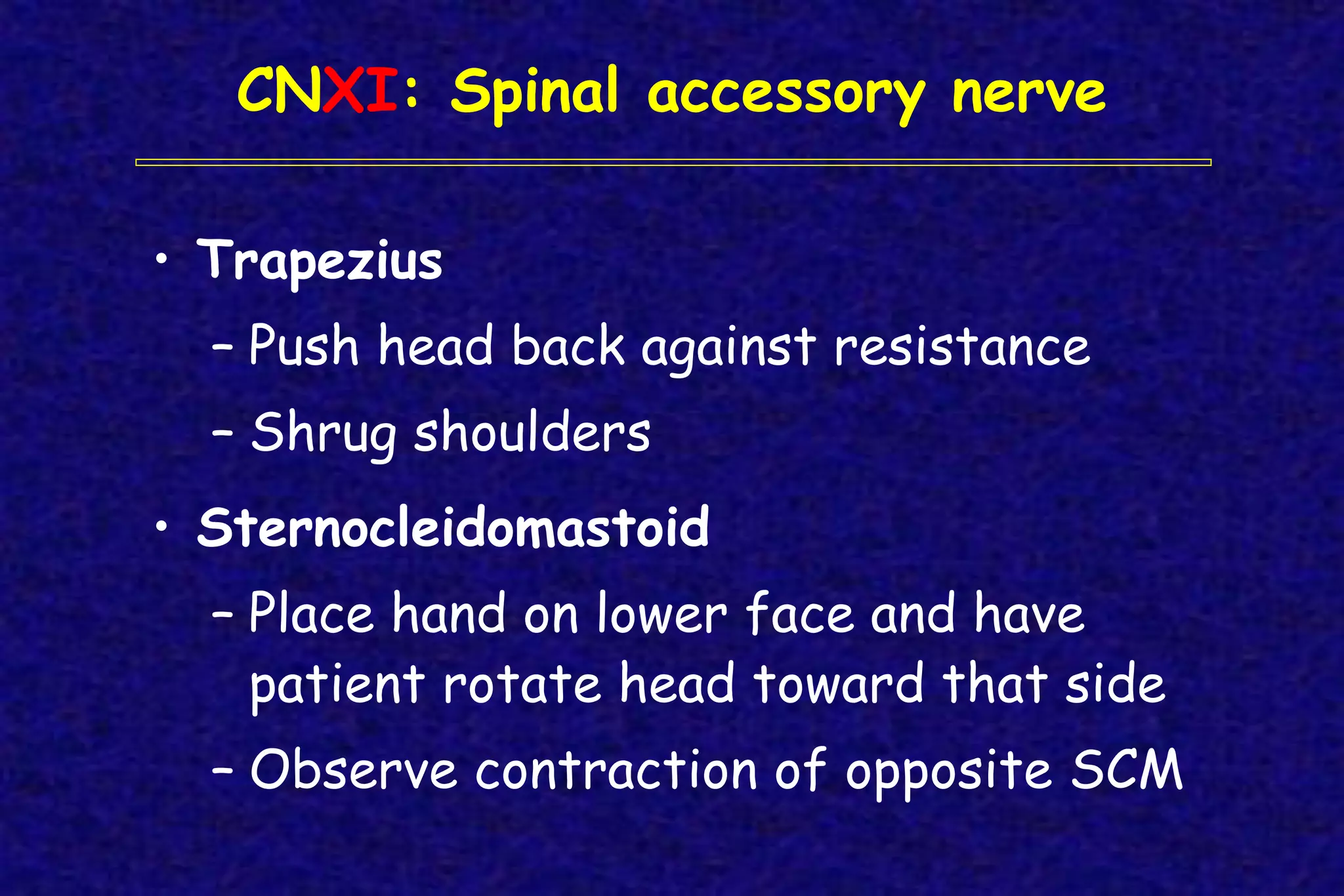
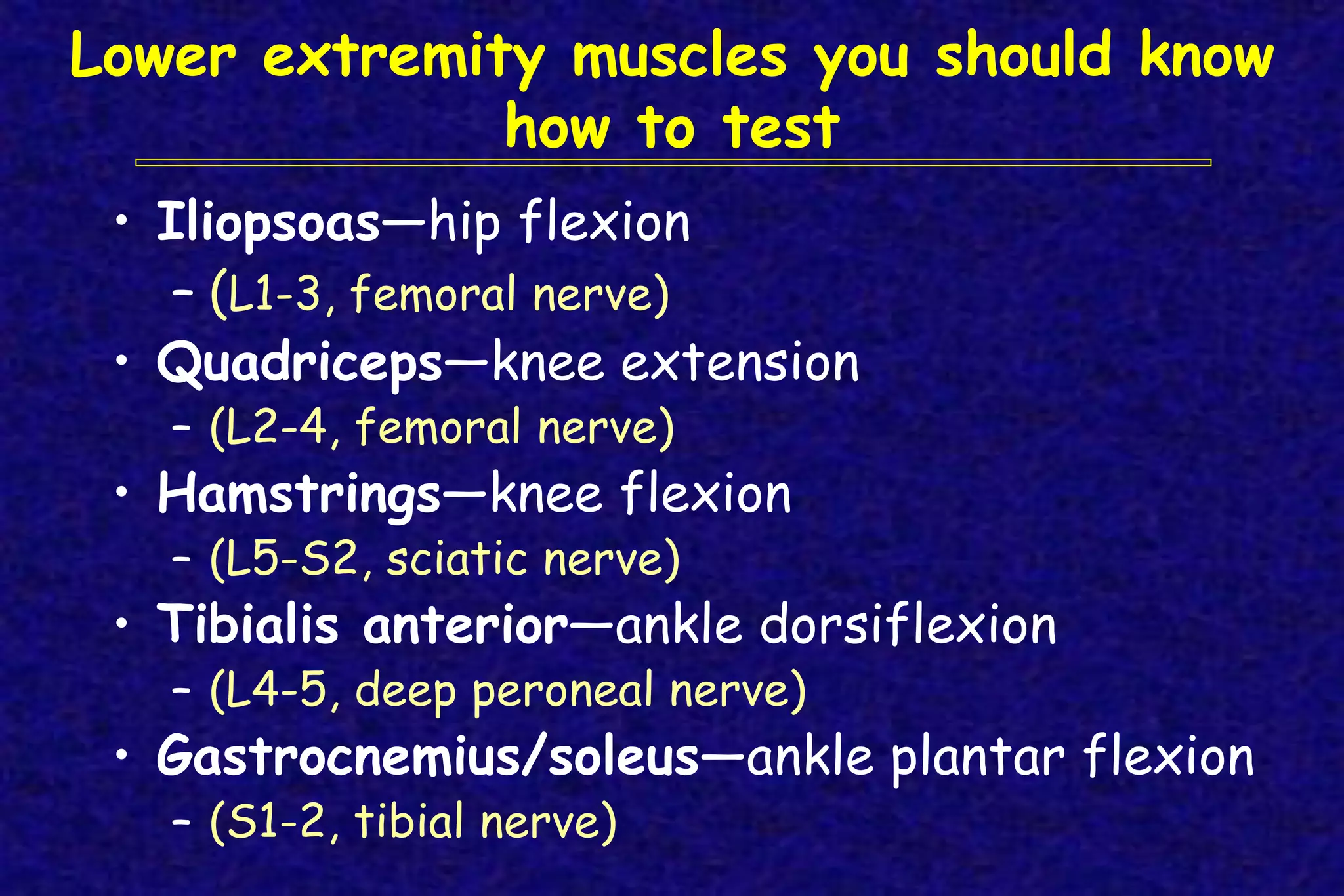
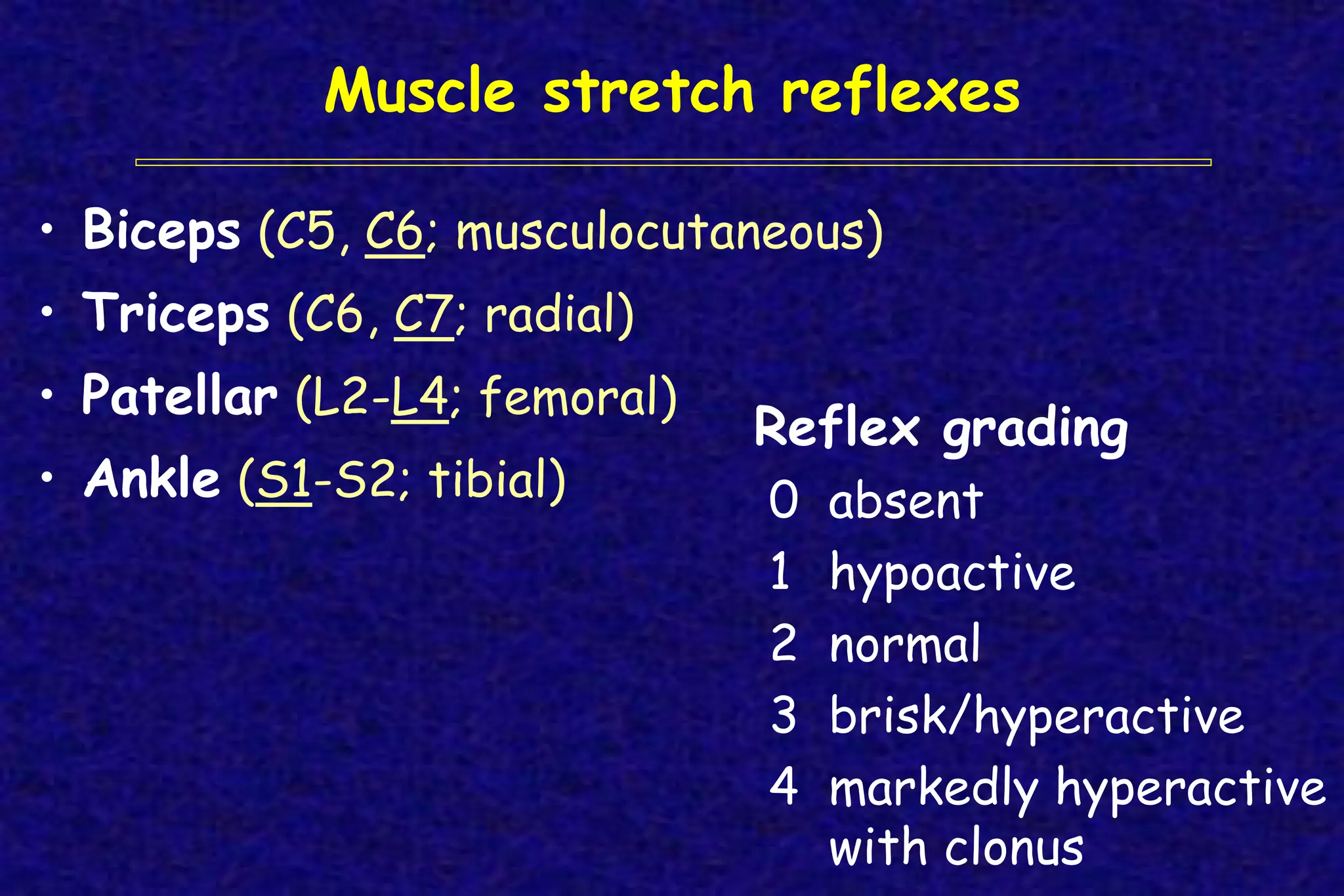
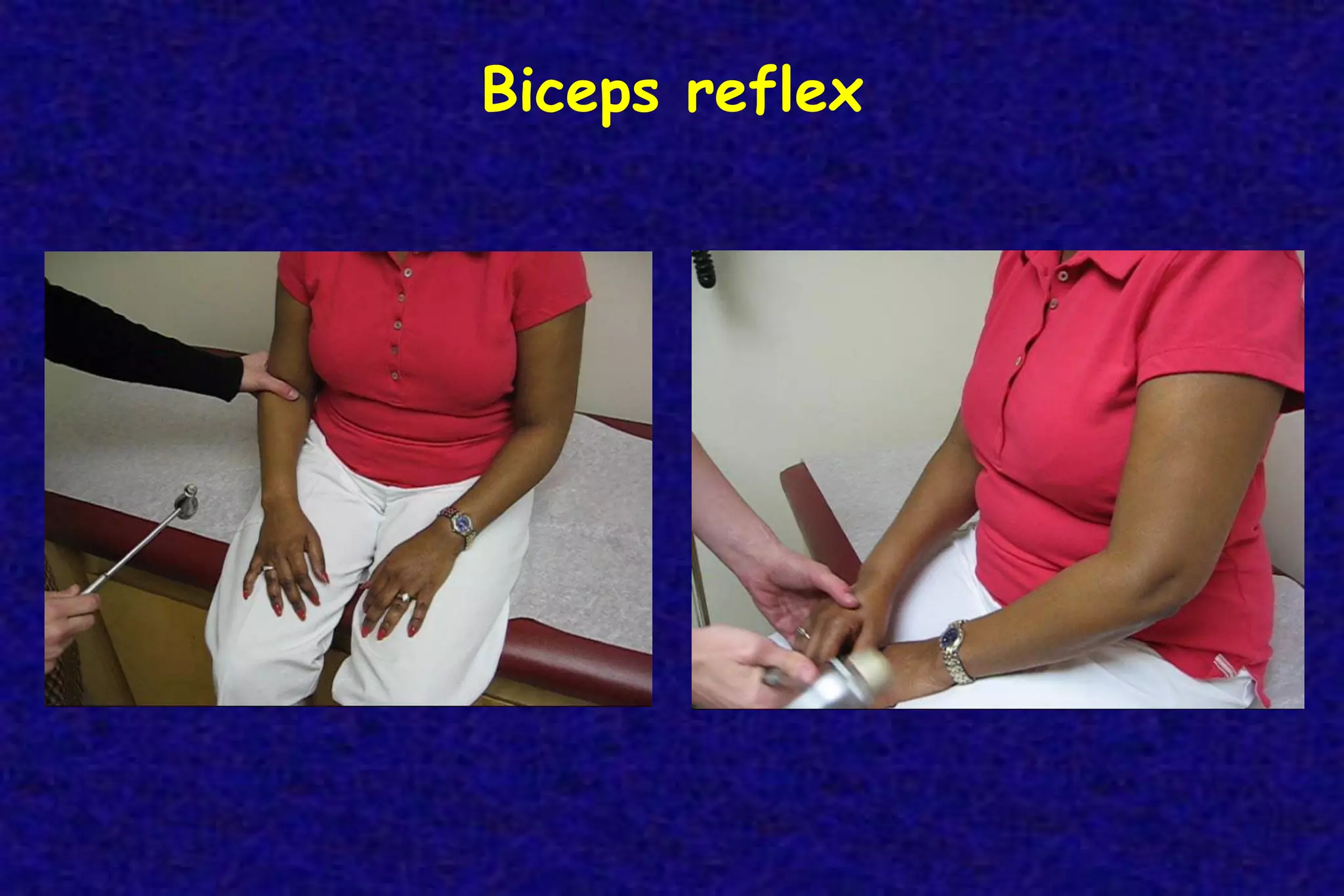
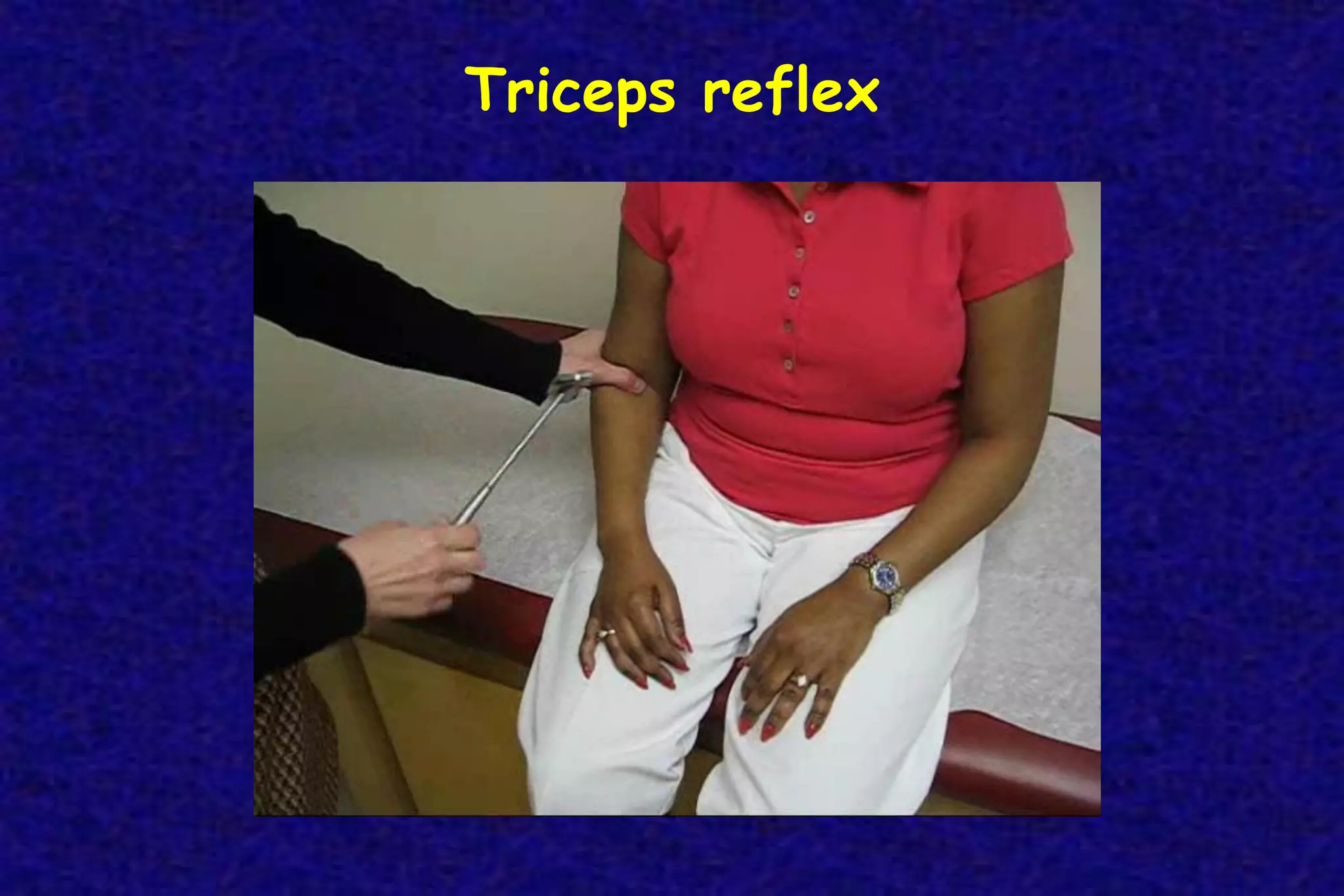
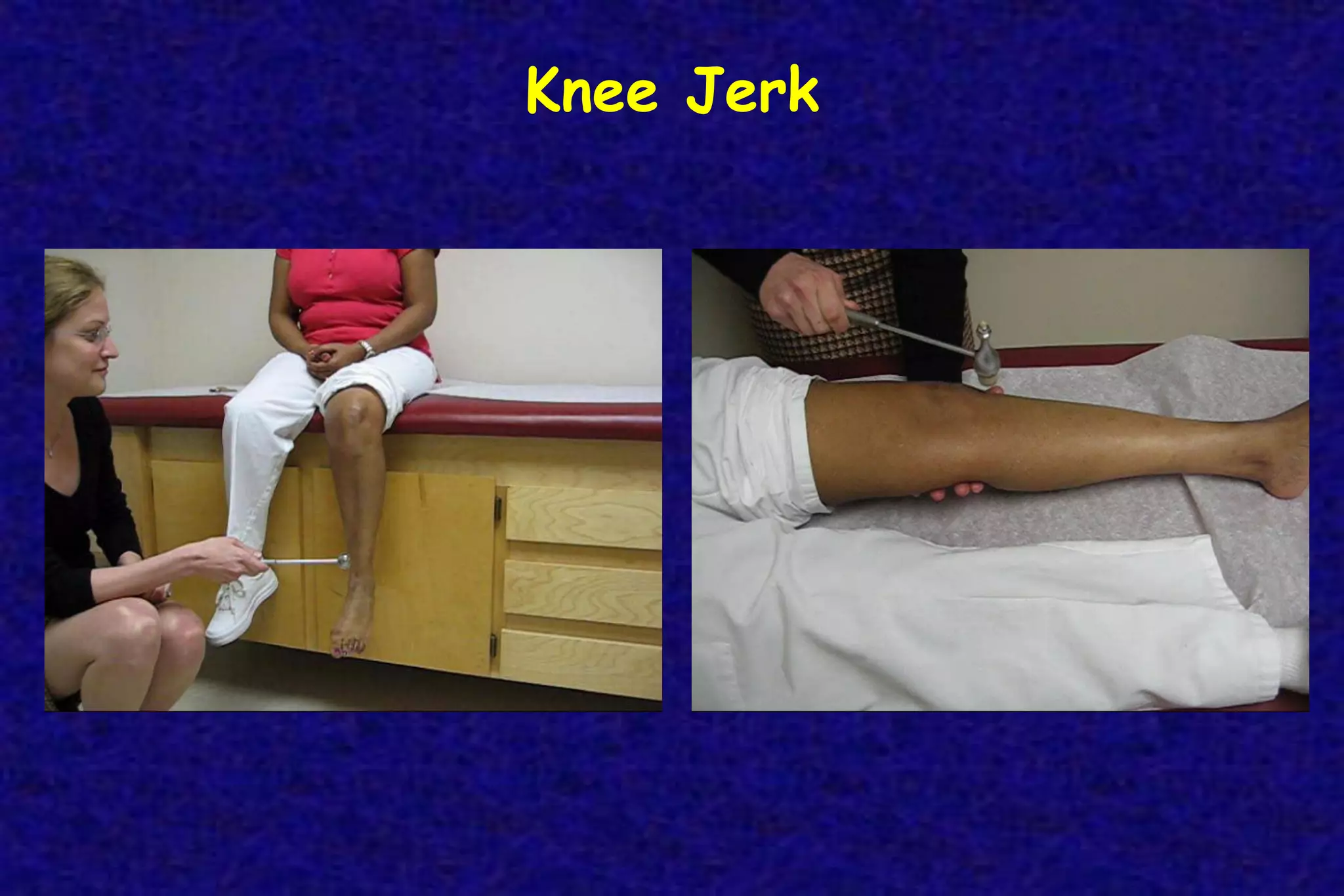
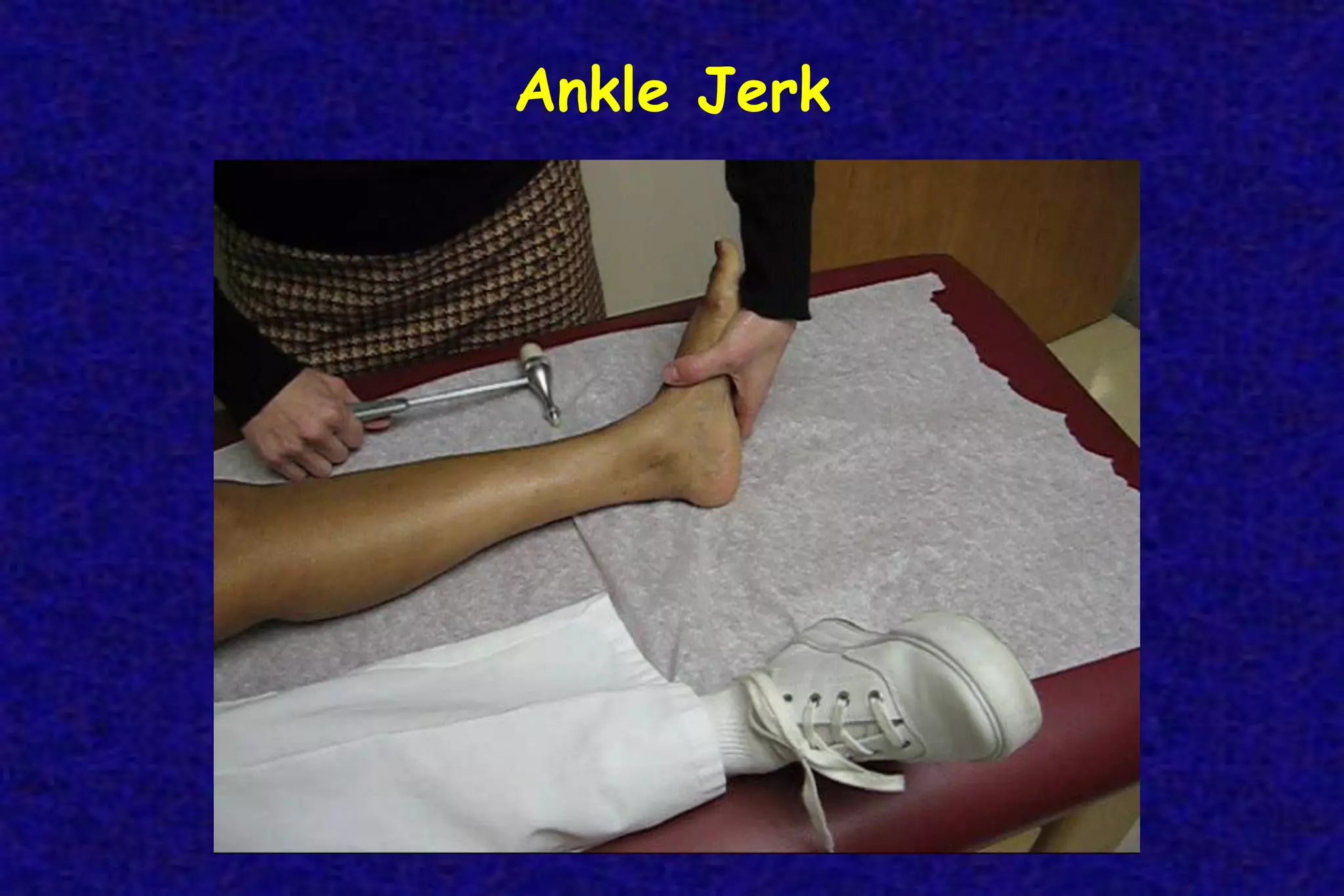
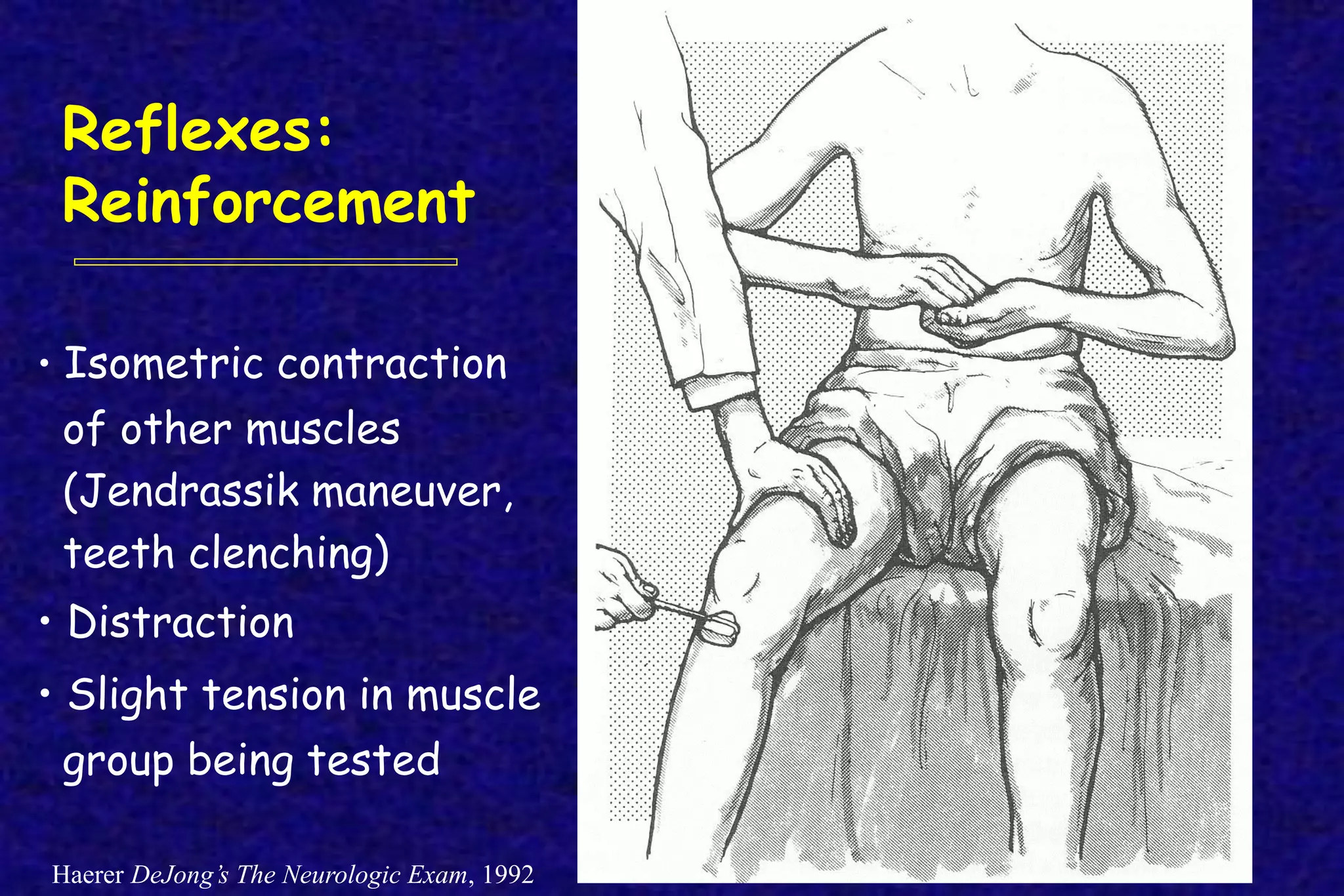
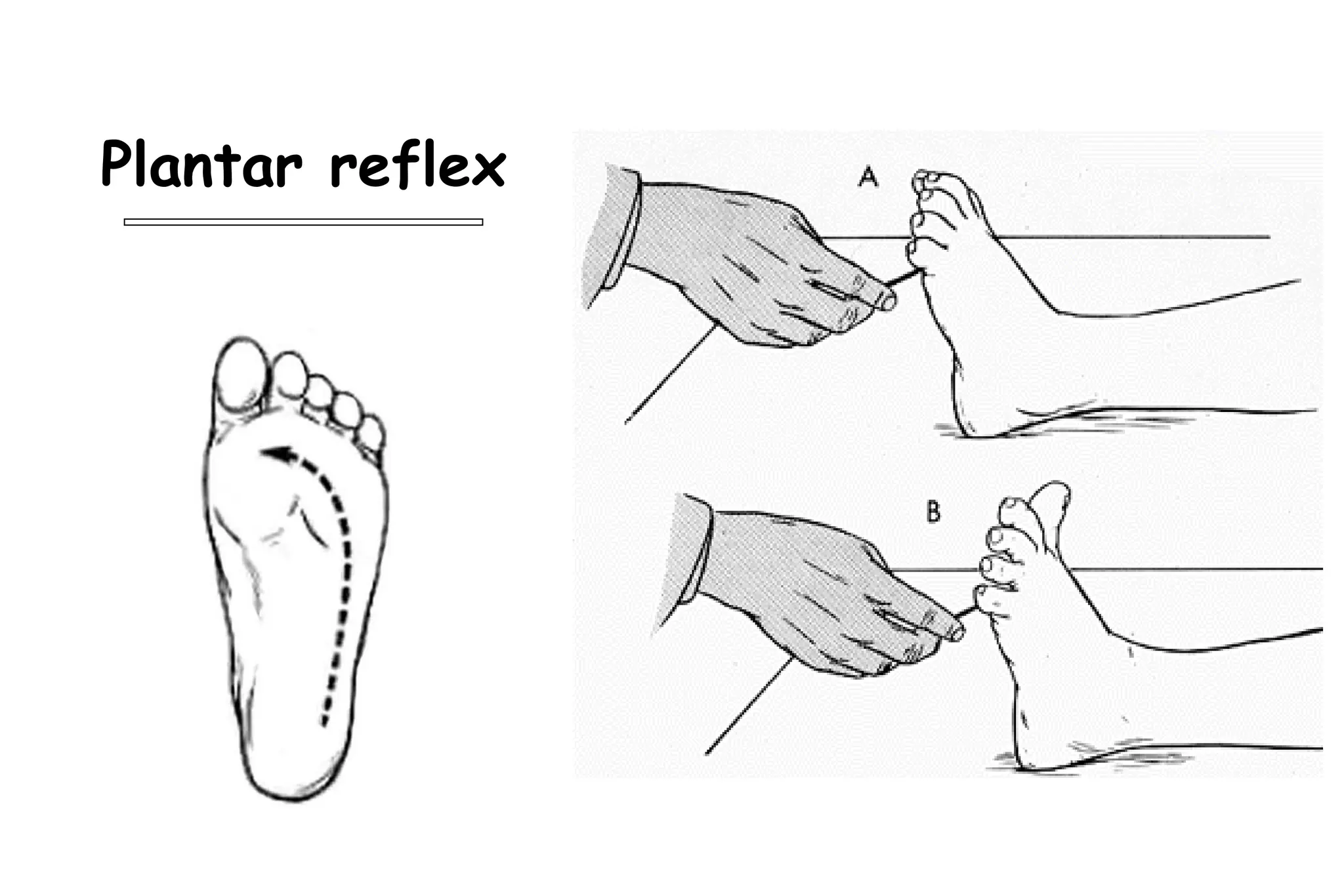
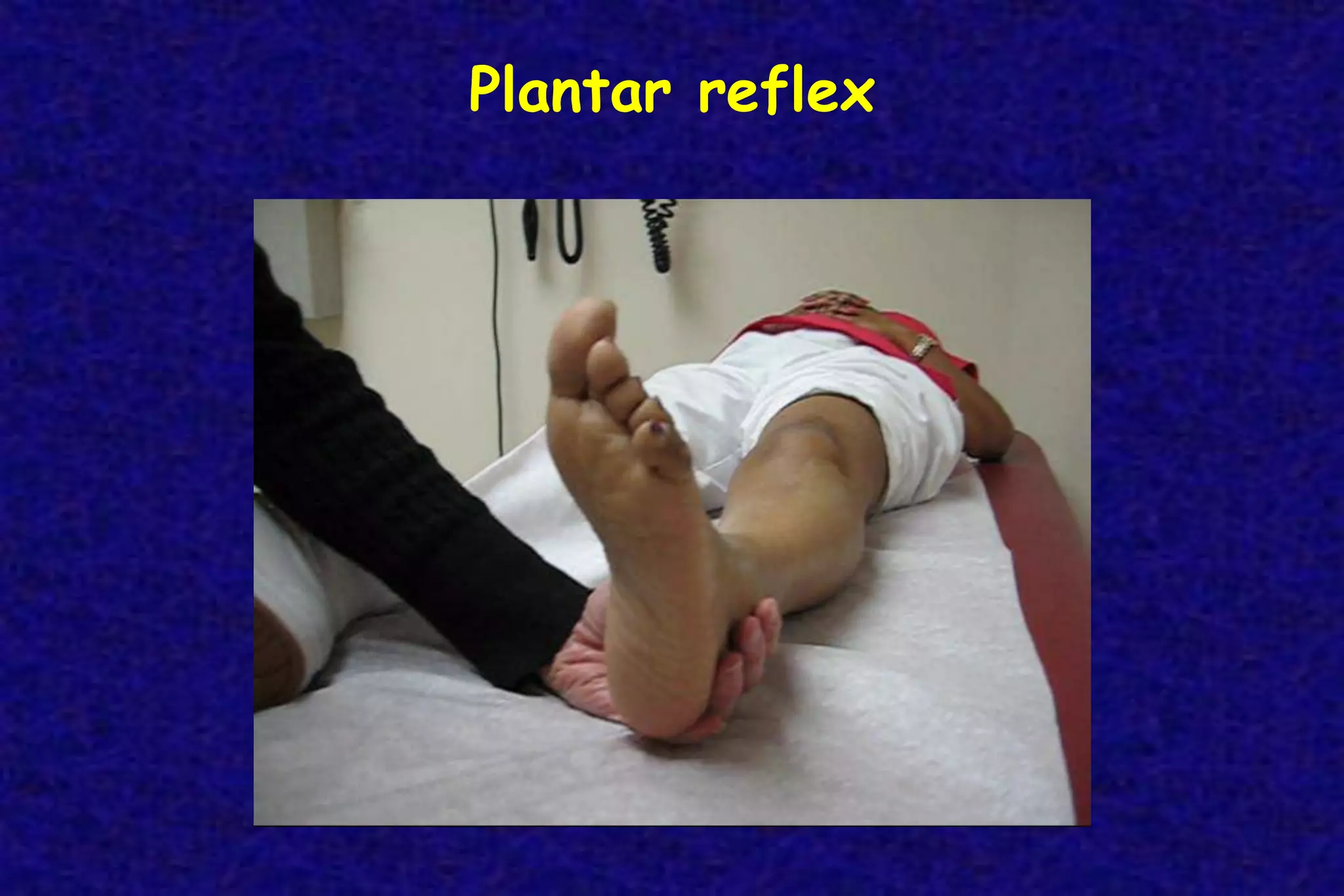
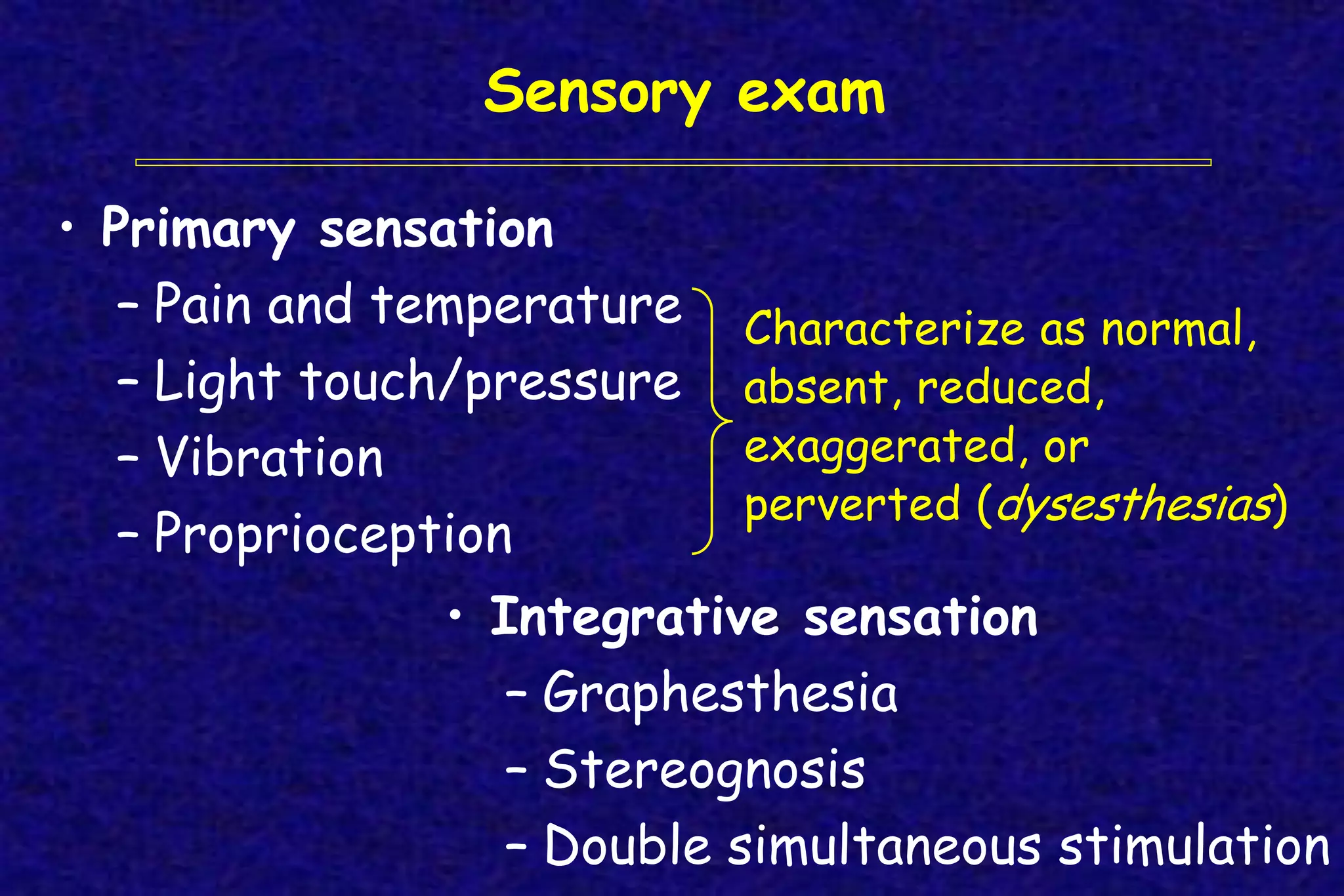
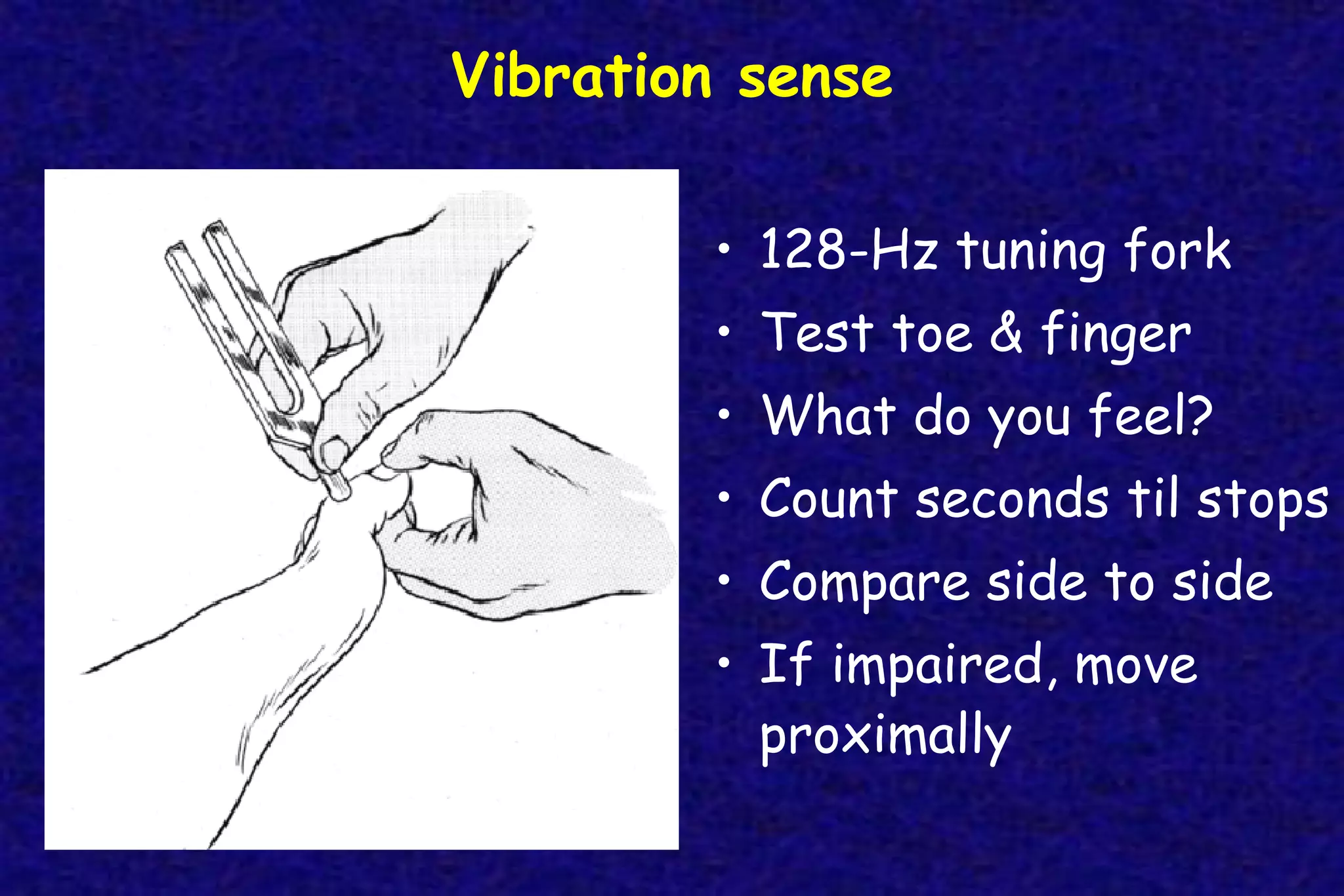
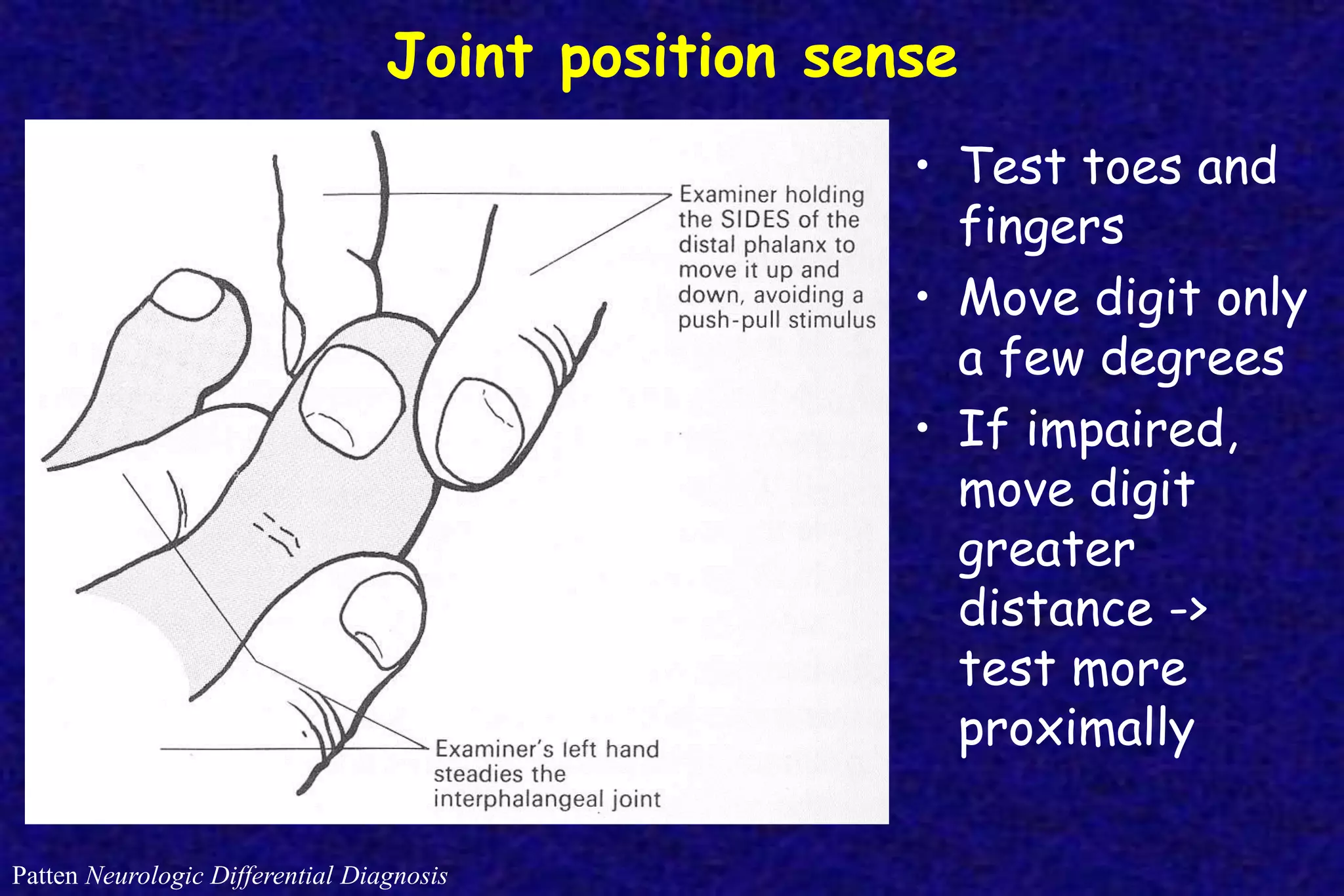
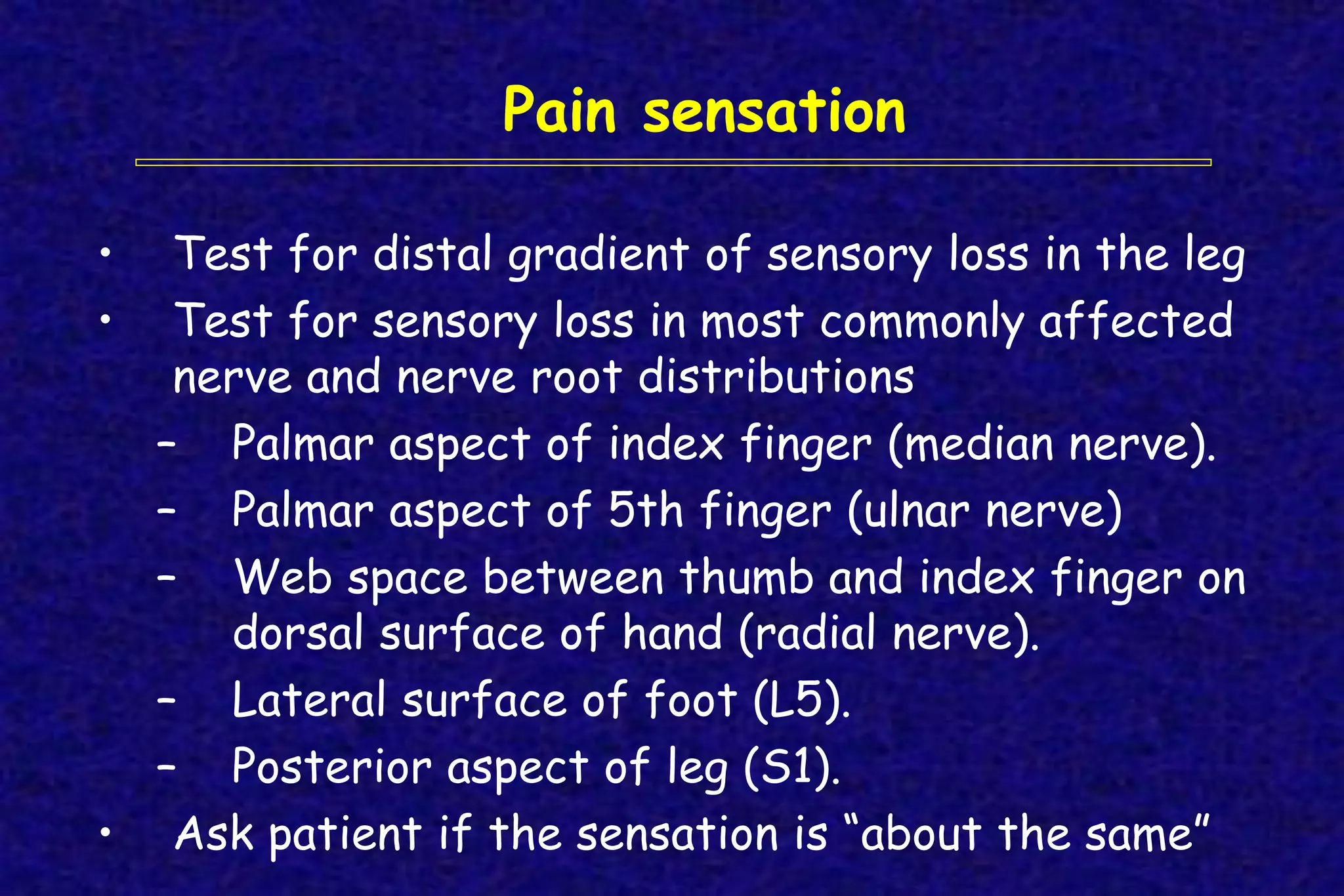
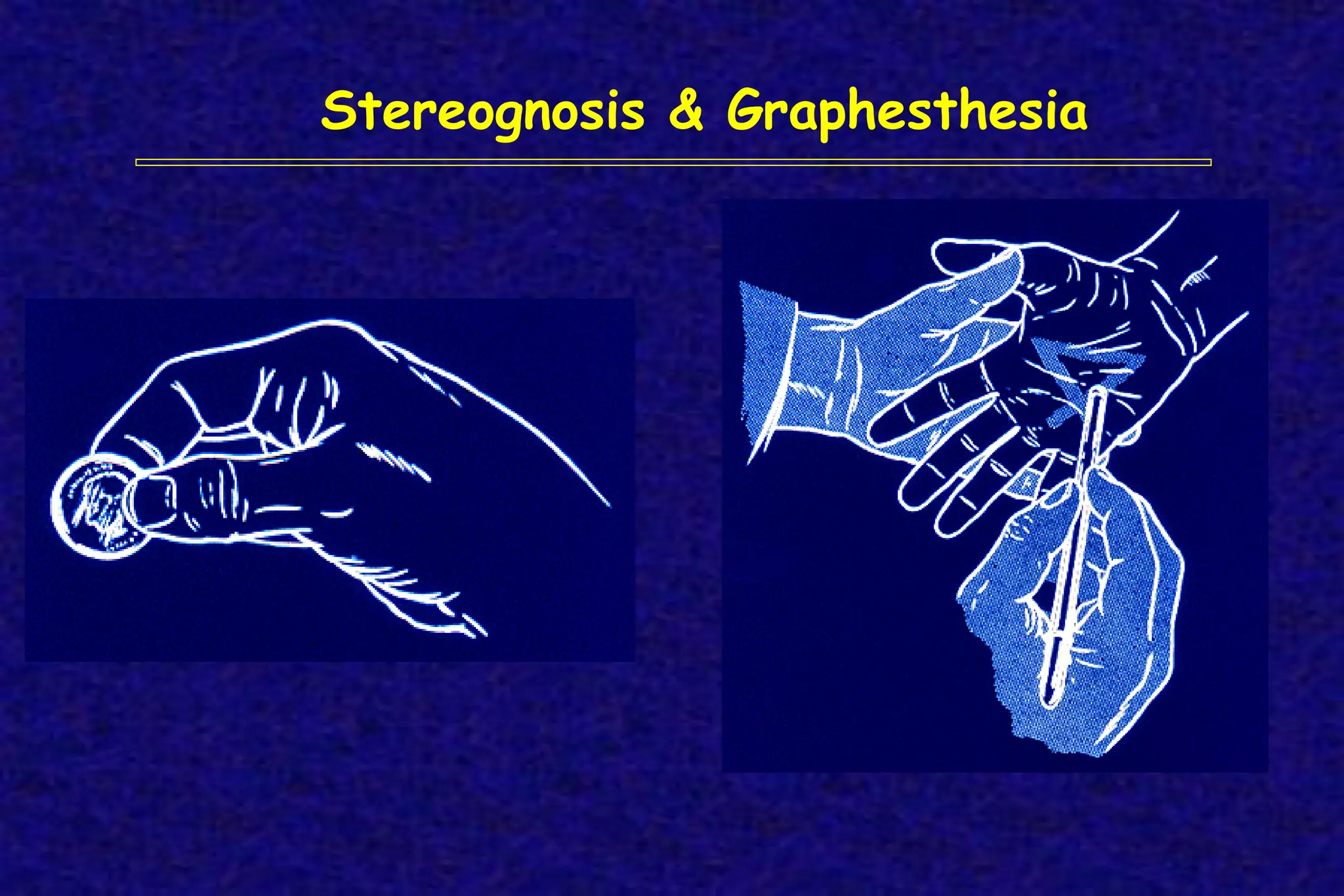
This document outlines the components of a neurological examination. It discusses the 7 categories examined which include mental status, cranial nerves, motor system, reflexes, sensory system, coordination, and gait. For each category, it provides details on the specific tests, techniques, and what is evaluated. It examines each of the 12 cranial nerves in depth, outlining the relevant anatomy and clinical tests for functions like vision, eye movements, hearing, sensation. It also reviews how to evaluate the motor system, reflexes, coordination, gait, and meningeal signs. The neurological exam is a systematic approach to evaluating the central and peripheral nervous systems.