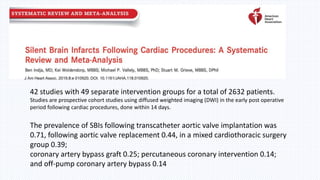
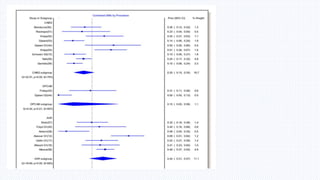
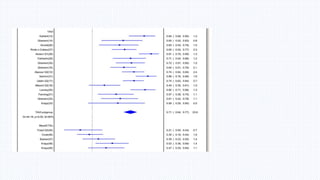
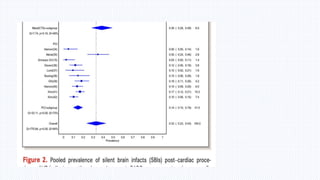
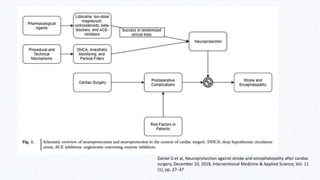
This document summarizes neurological dysfunction that can occur after cardiac surgery. It notes that postoperative cognitive dysfunction and silent brain infarcts are common, occurring in 30-80% and 50% of patients respectively. The document reviews findings from several studies. One study found silent brain infarct rates of 0.71% after TAVR and 0.25% after CABG. Another study found early postoperative slowing on cognitive tests that normalized by 3 months post-op. The document recommends neuroprotective strategies like lidocaine and hypothermia to reduce neurological complications after cardiac surgery.


![Neurological Dysfunction
• Exist in broad spectrum from major stroke/TIA to subclinical brain
injury such as postoperative cognitive dysfunction (POCD) and silent
brain infarct (SBI).
• SBI associated with significant morbidities; such as increase to
subsequent stroke to more than x5.
• Associated sequelae include cognitive dysfunction, increased risk of
dementia, psychiatric disturbances and reduced quality of life.
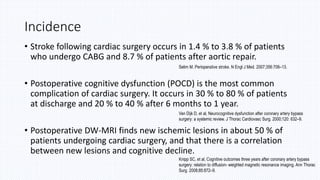
Indja, B., Woldendorp, K., Vallely, M.P. and Grieve, S.M. (2019). Silent
Brain Infarcts Following Cardiac Procedures: A Systematic Review and
Meta-Analysis. Journal of the American Heart Association, [online] 8(9),
p.e010920.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/neurologicaldysfunctionpostcardiacsurgery-200303135347/85/Neurological-dysfunction-post-cardiac-surgery-5-320.jpg)





![References
1. Cormack, F., Shipolini, A., Awad, W.I., Richardson, C., McCormack, D.J., Colleoni, L.,
Underwood, M., Baldeweg, T. and Hogan, A.M. (2012). A meta-analysis of cognitive
outcome following coronary artery bypass graft surgery. Neuroscience and
Biobehavioral Reviews, [online] 36(9), pp.2118–2129.
2. Indja, B., Woldendorp, K., Vallely, M.P. and Grieve, S.M. (2019). Silent Brain Infarcts
Following Cardiac Procedures: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Journal of the
American Heart Association, [online] 8(9), p.e010920.
3. Goto, T. and Maekawa, K. (2013). Cerebral dysfunction after coronary artery bypass
surgery. Journal of Anesthesia, 28(2), pp.242–248.
4. Jovin, D.G., Katlaps, K.G., Ellis, B.K. and Dharmaraj, B. (2019). Neuroprotection against
stroke and encephalopathy after cardiac surgery. Interventional Medicine and Applied
Science, 11(1), pp.27–37.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/neurologicaldysfunctionpostcardiacsurgery-200303135347/85/Neurological-dysfunction-post-cardiac-surgery-16-320.jpg)