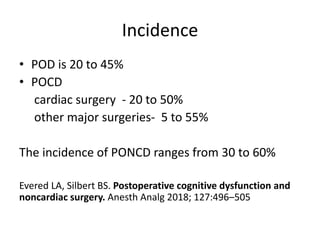
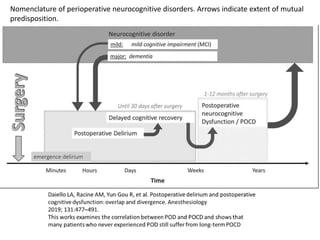
POCD is defined as impairment of cognitive function after surgery. It can occur in the immediate postoperative period as postoperative delirium or emerge later as delayed neurocognitive recovery or PONCD. The reported incidence ranges from 5-60% depending on the surgery and assessment time period. Risk factors include increasing age, pre-existing cognitive impairment, major surgery and cardiac surgery specifically. Prevention strategies involve a multidisciplinary approach with careful preoperative assessment, avoidance of delirogenic medications, monitoring anesthesia depth, early mobilization and multicomponent prevention programs. Treatment of established POCD focuses on managing symptoms though efficacy is limited.