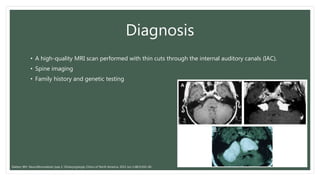
Neurofibromatosis type 2 (NF2) is a rare genetic syndrome characterized by bilateral vestibular schwannomas and other tumors. It has an average age of diagnosis of 25 years. Care requires a multidisciplinary team approach due to the variety of tumors involved. Management may include observation, surgery, radiation, or drug therapies targeting tumor growth pathways.