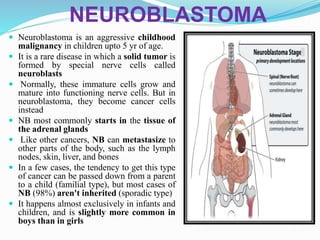
The document investigates the effects of sulfasalazine on human neuroblastoma, focusing on sepiapterin reductase (SPR) as a potential therapeutic target. It details the aggressive nature of neuroblastoma, the role of polyamines in cancer proliferation, and how sulfasalazine may inhibit SPR, resulting in reduced proliferation of neuroblastoma cells. The findings suggest that combining sulfasalazine with DFMO could offer a new therapeutic avenue for treating neuroblastoma due to their synergistic anti-proliferative effects.