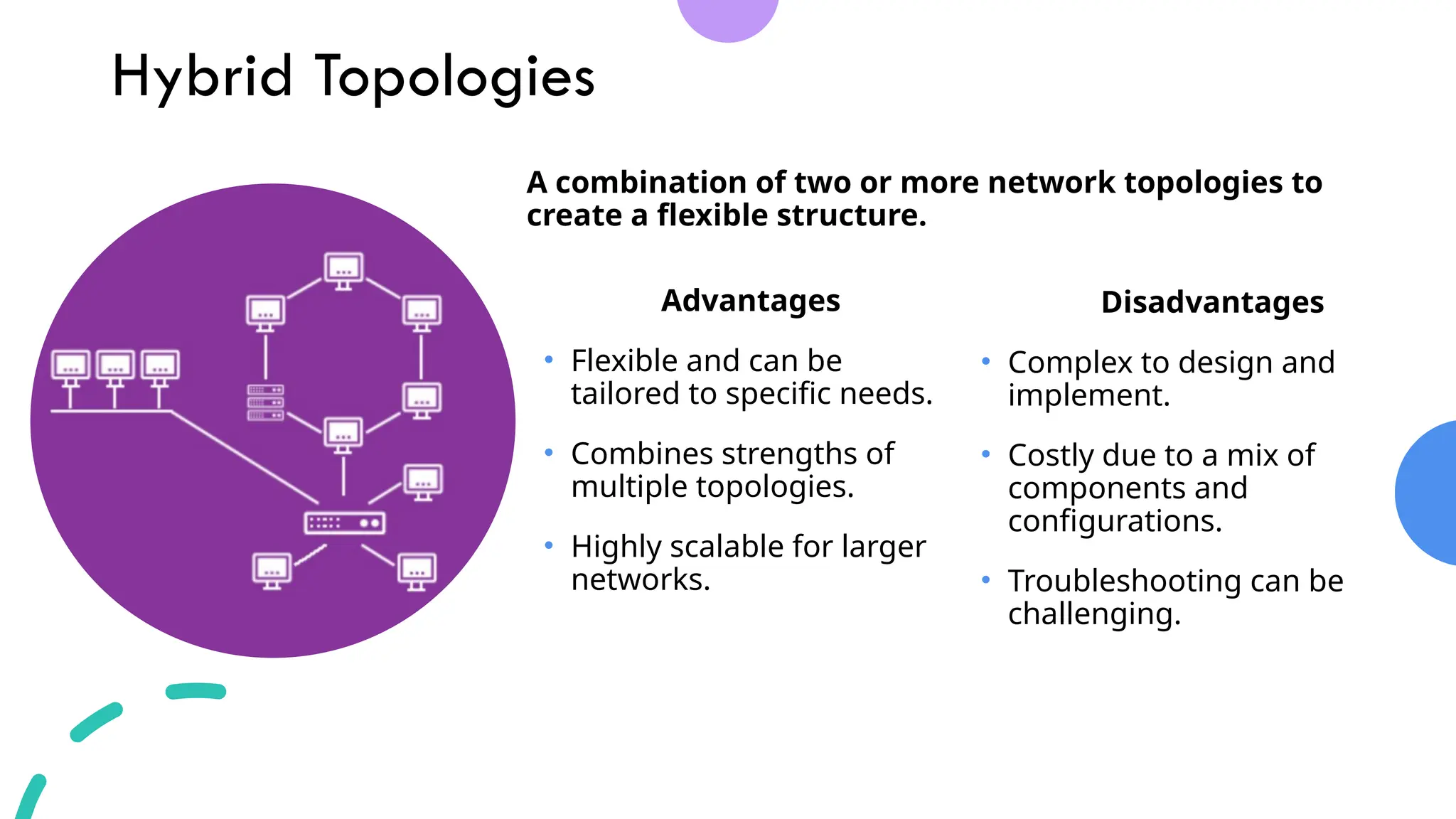
The document discusses network topology, defining it as the arrangement of devices, connections, and data circuits in a network. It outlines various types of topologies including bus, star, ring, mesh, tree, and hybrid, detailing their advantages and disadvantages. The conclusion emphasizes the importance of choosing the appropriate topology based on factors like scalability, cost, fault tolerance, and performance for effective network design.