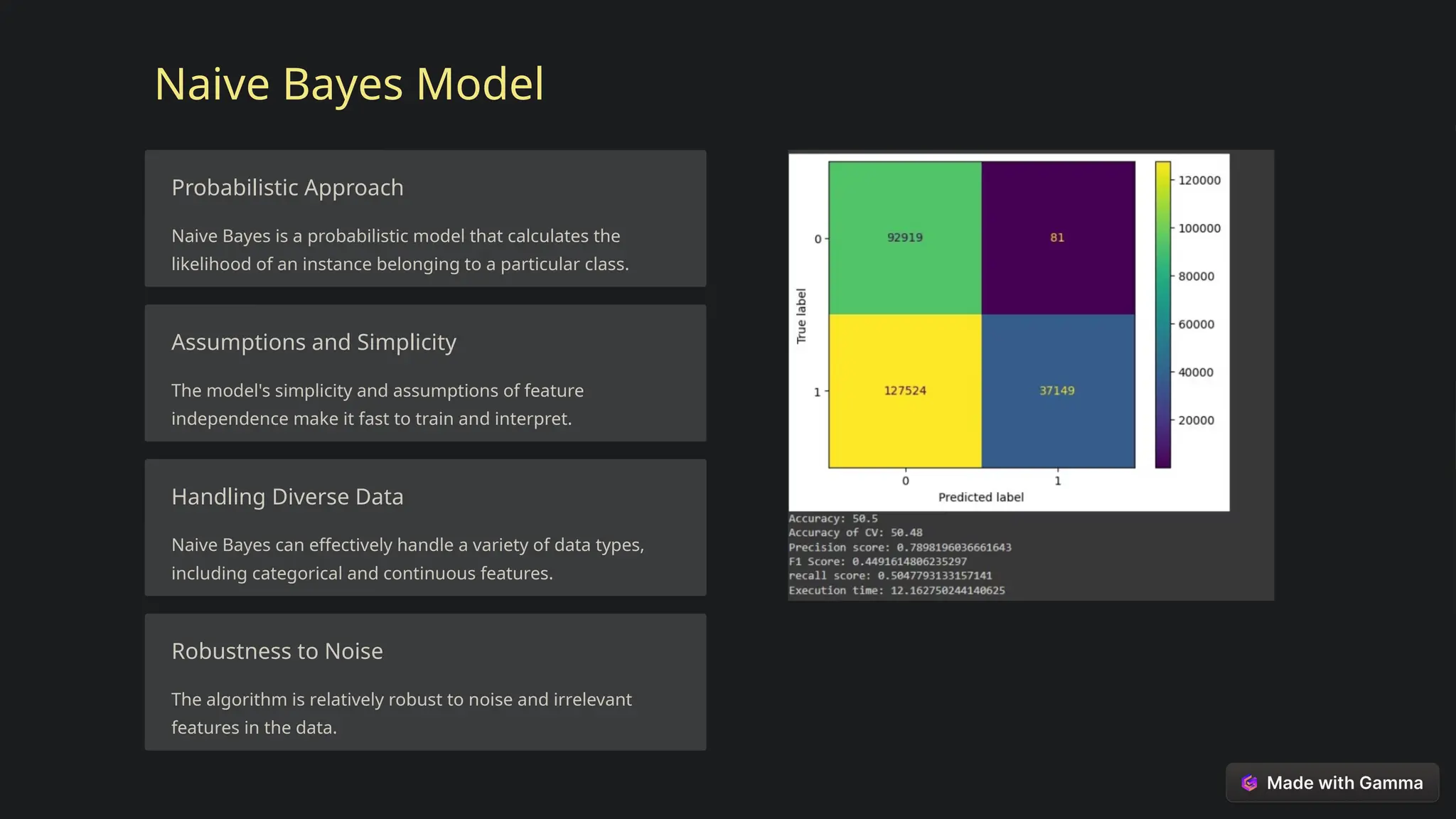
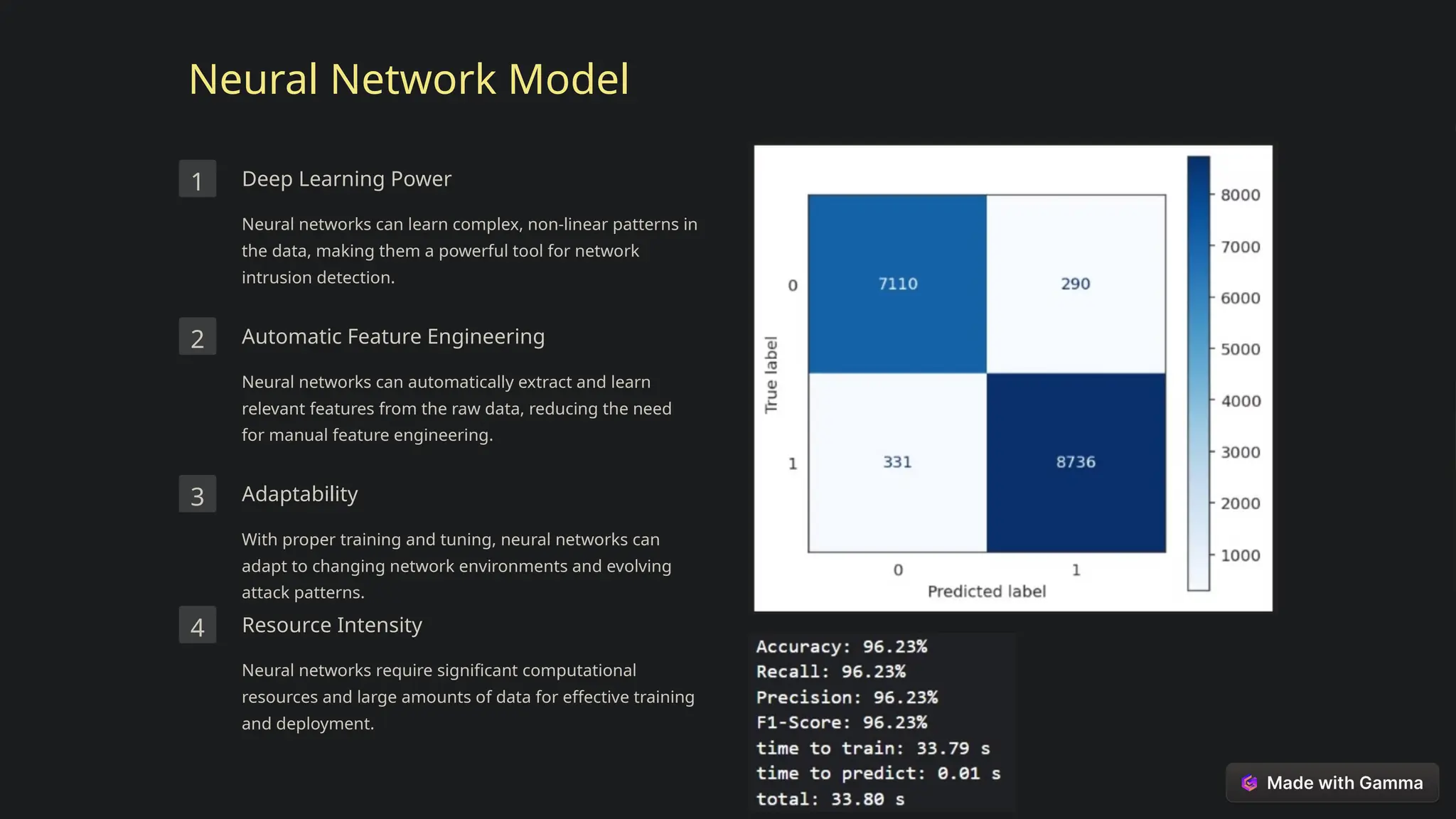
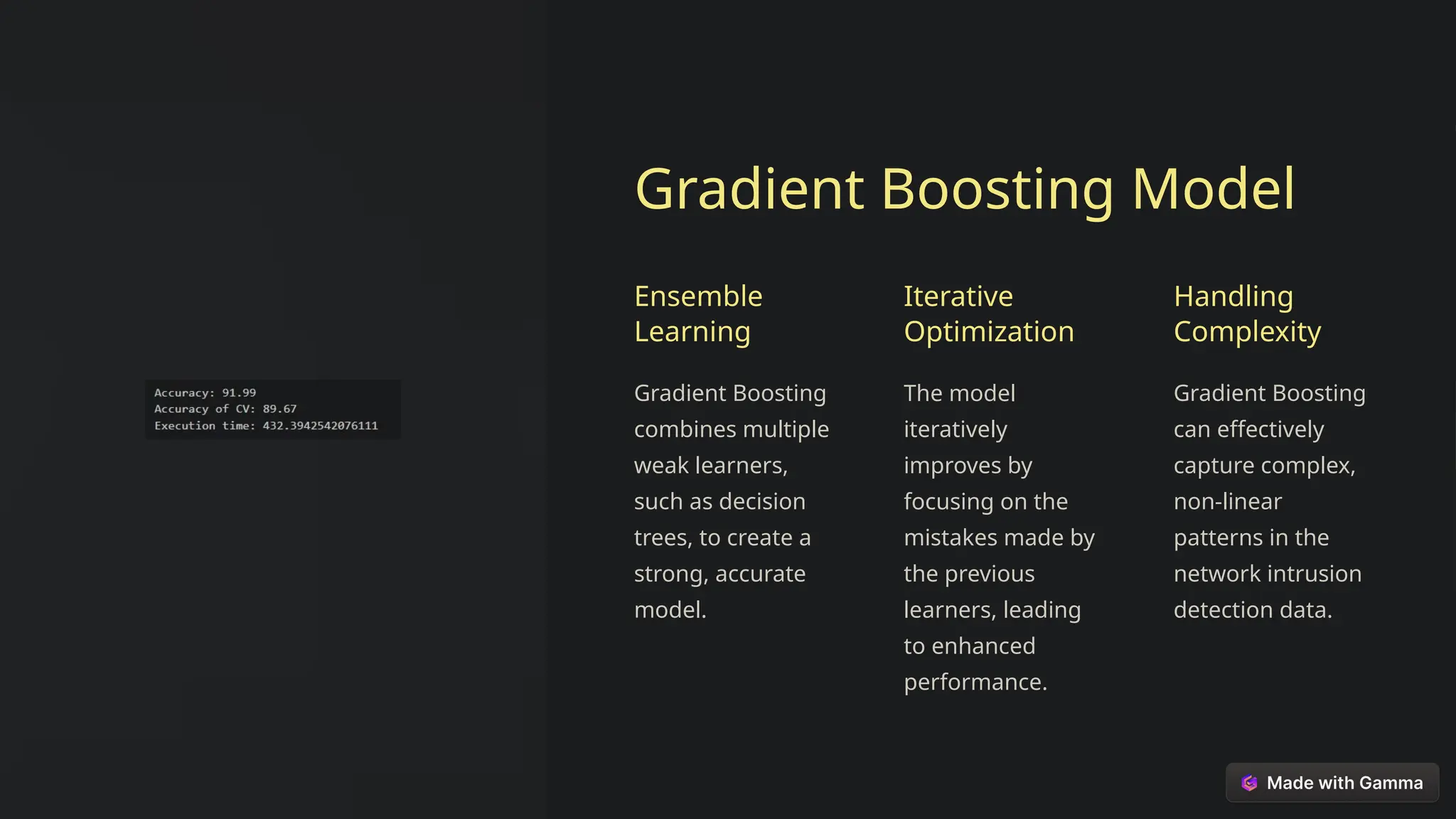
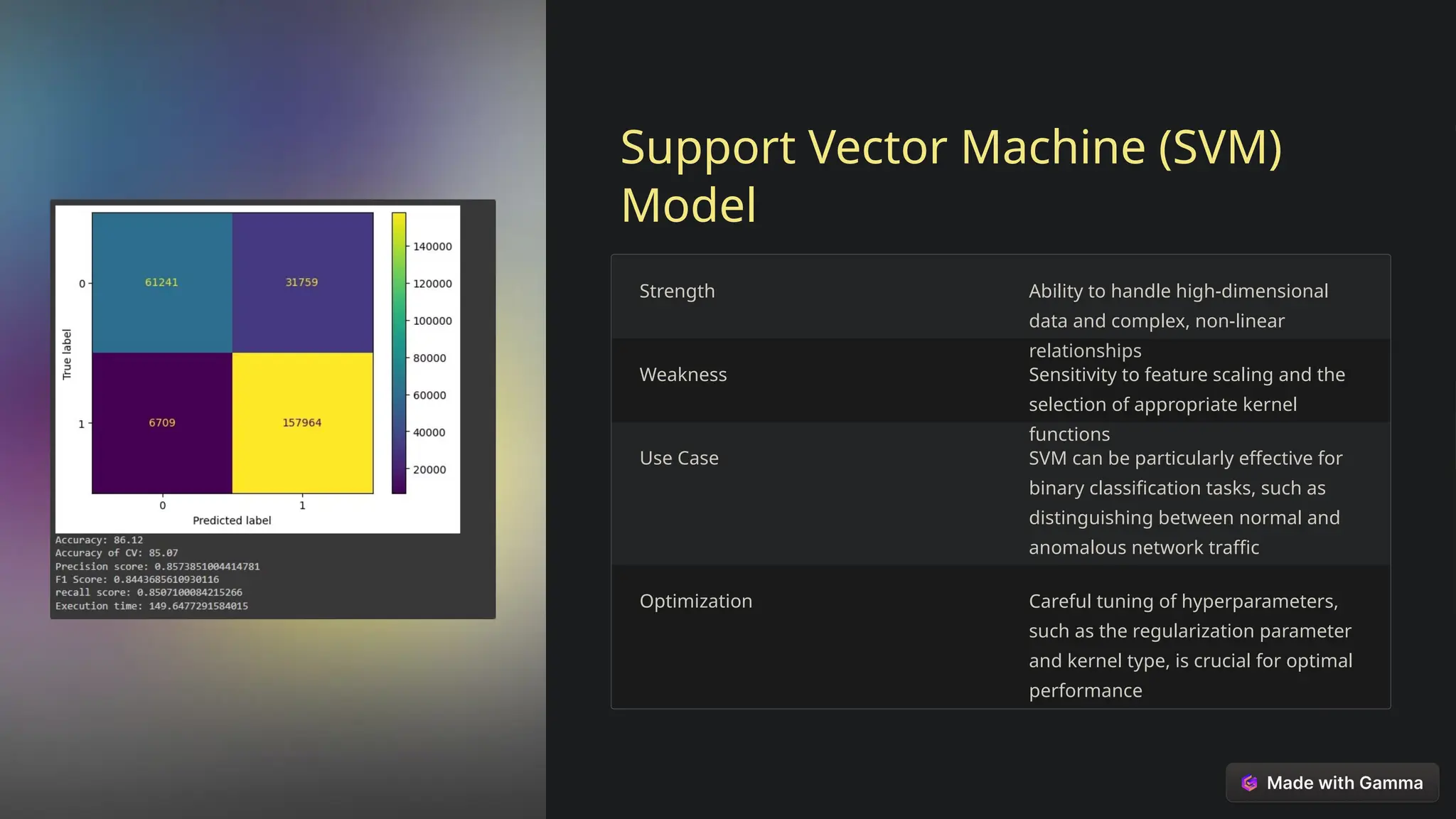
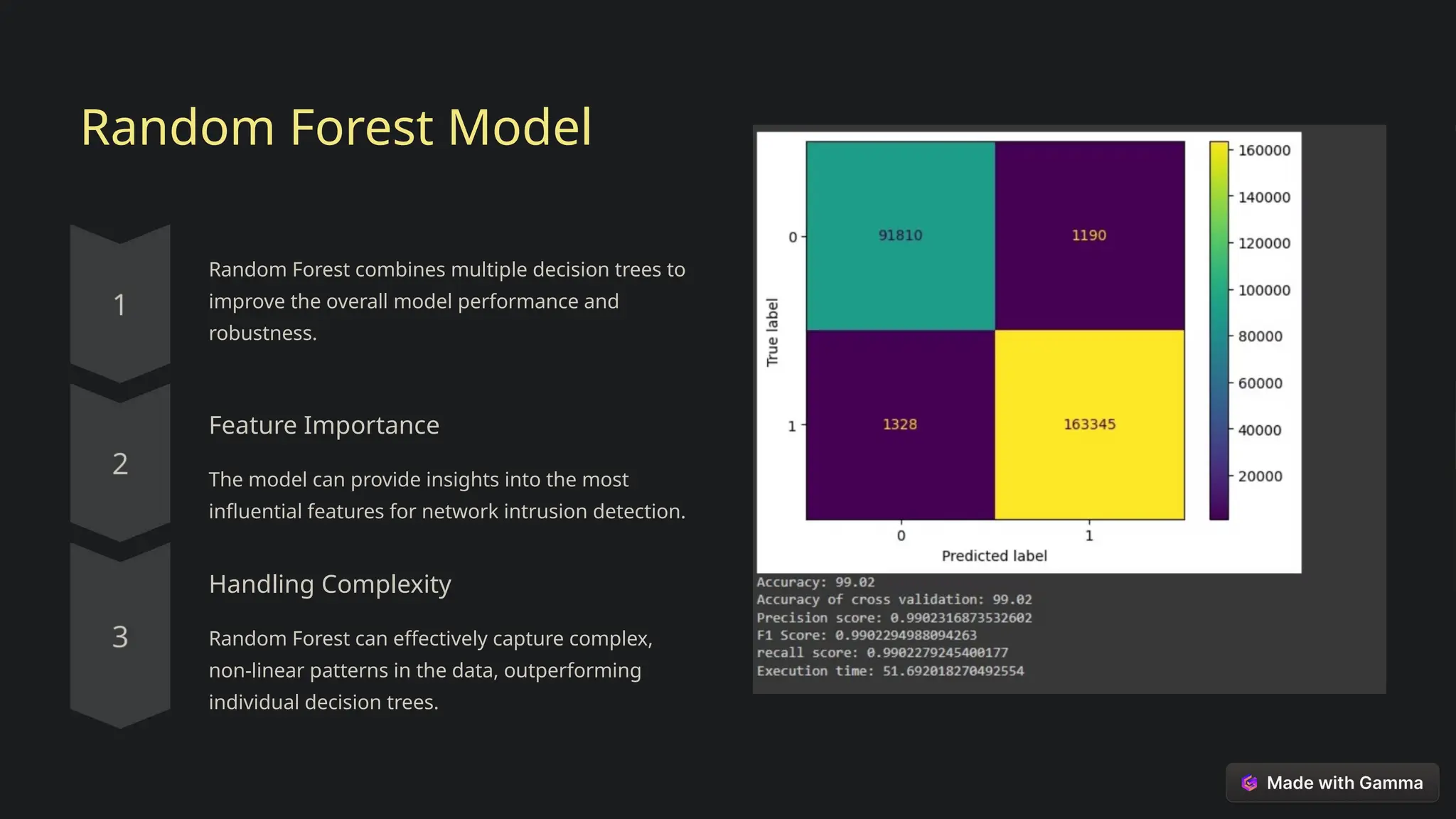
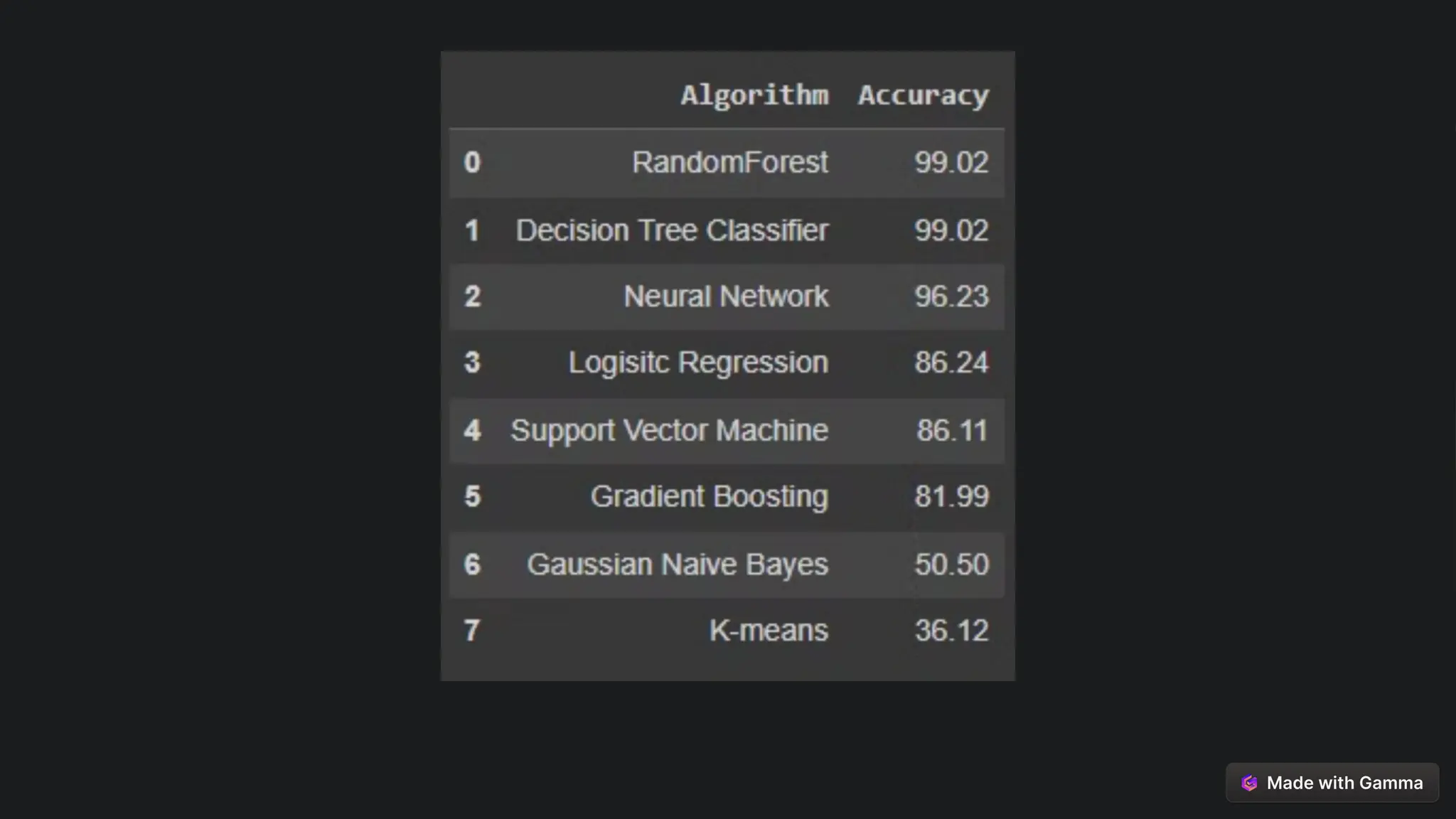
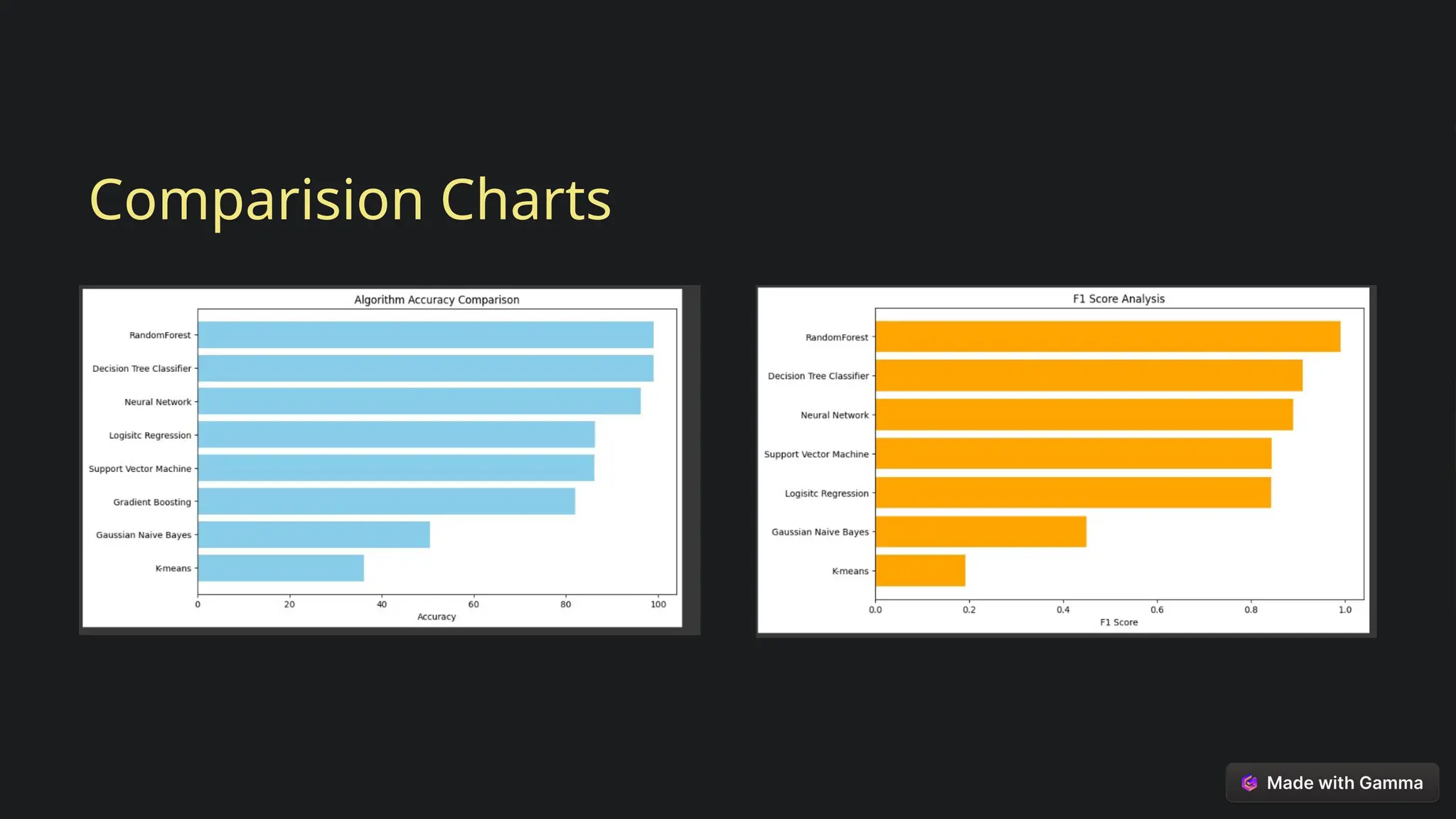
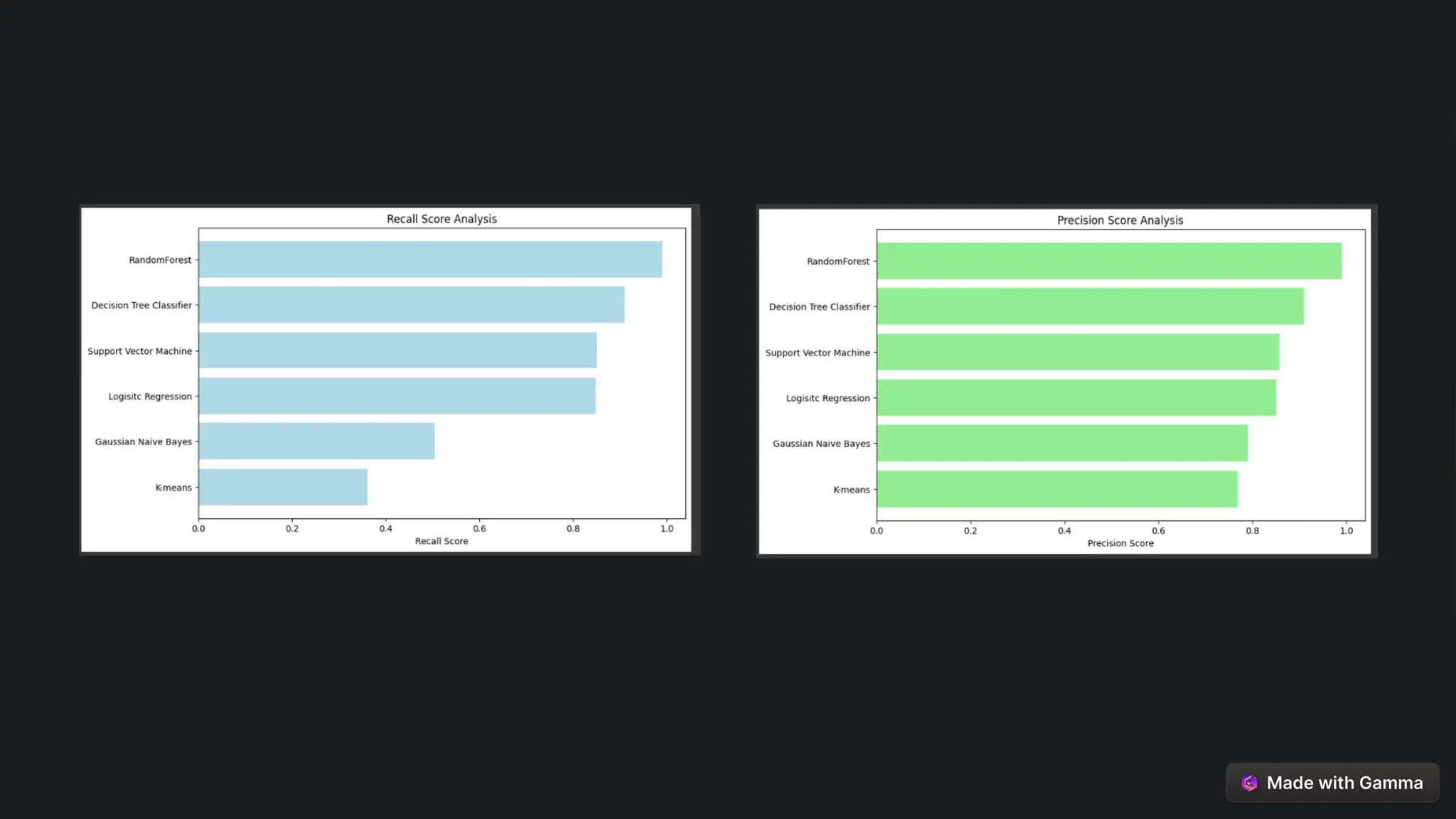
This document explores the critical role of machine learning in enhancing network intrusion detection systems (NIDS) to address the evolving landscape of cyber threats. It highlights the limitations of traditional detection methods and advocates for adaptive AI-powered solutions to improve cybersecurity effectiveness. Furthermore, it outlines key objectives, methodologies, and future research directions aimed at optimizing NIDS for real-time deployment and enhancing their ability to identify sophisticated network attacks.