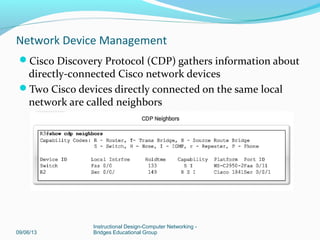
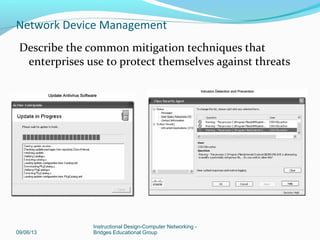
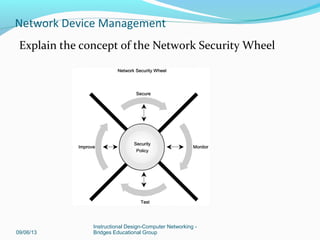
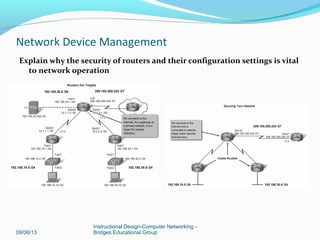
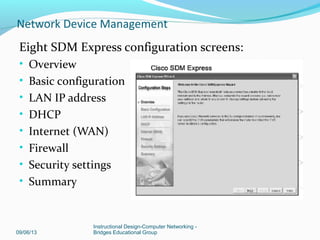
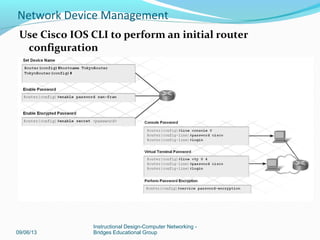
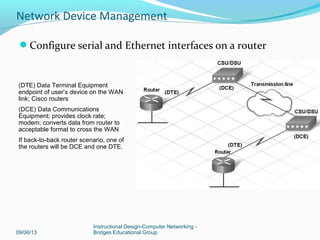
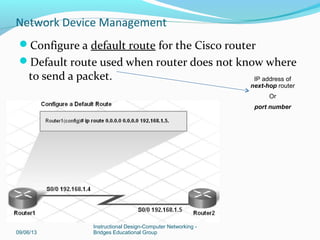
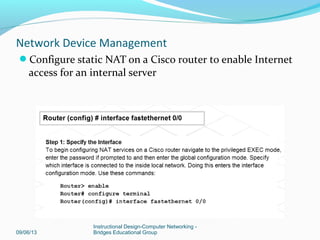
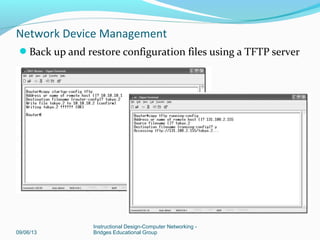
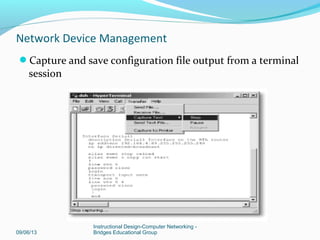
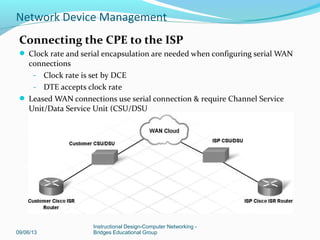
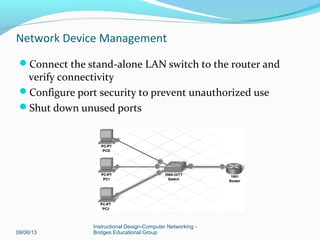
This document discusses network device management and configuration. It covers initial configuration of Cisco routers and switches, including connecting interfaces, setting IP addresses and default routes. It also discusses securing devices by configuring passwords, ACLs and port security. Common security threats to enterprises like malware and DDoS attacks are discussed along with mitigation techniques such as firewalls, IDS/IPS and security policies. The importance of securing routers and applying features like ACLs is emphasized.







![Initial ISR Router Configuration
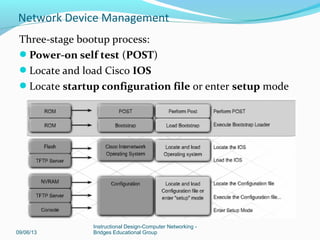
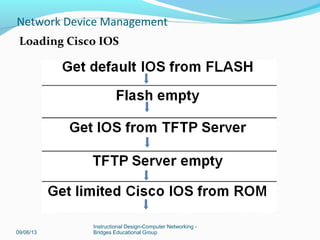
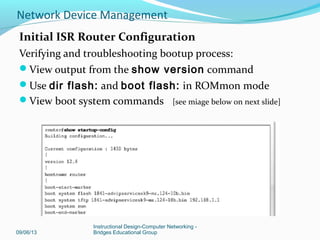
Verifying and troubleshooting bootup process:
View output from the show version command
Use dir flash: and boot flash: in ROMmon mode
View boot system commands [see miage below on next slide]
09/06/13
Instructional Design-Computer Networking -
Bridges Educational Group
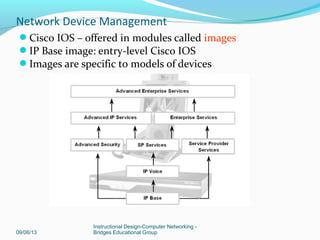
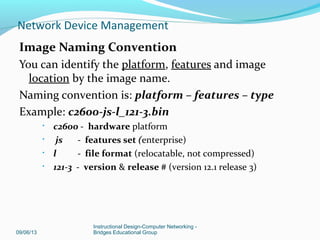
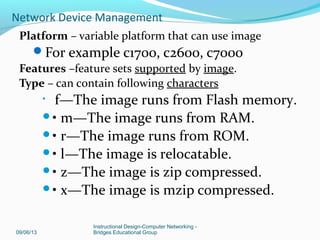
Network Device Management](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/networkdevicemanagement-130906085126-/85/Network-device-management-15-320.jpg)














![Switch port security
Port security limits the # of MAC addresses allowed per port.
Set port to access mode using switchport mode access
command
3 ways to configure port security:
Static – MAC addresses are manually assigned using
switchport port-security mac-address [mac-address]
interface config command.
S1# configure terminal
S1(config-if)#interface fastethernet 0/20
S1(config-if)#switchport mode access
S1(config-if)#switchport port-security mac-address
1000.2000.3000
S1(config-if)#end
09/06/13
Instructional Design-Computer Networking -
Bridges Educational Group
Network Device Management](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/networkdevicemanagement-130906085126-/85/Network-device-management-40-320.jpg)