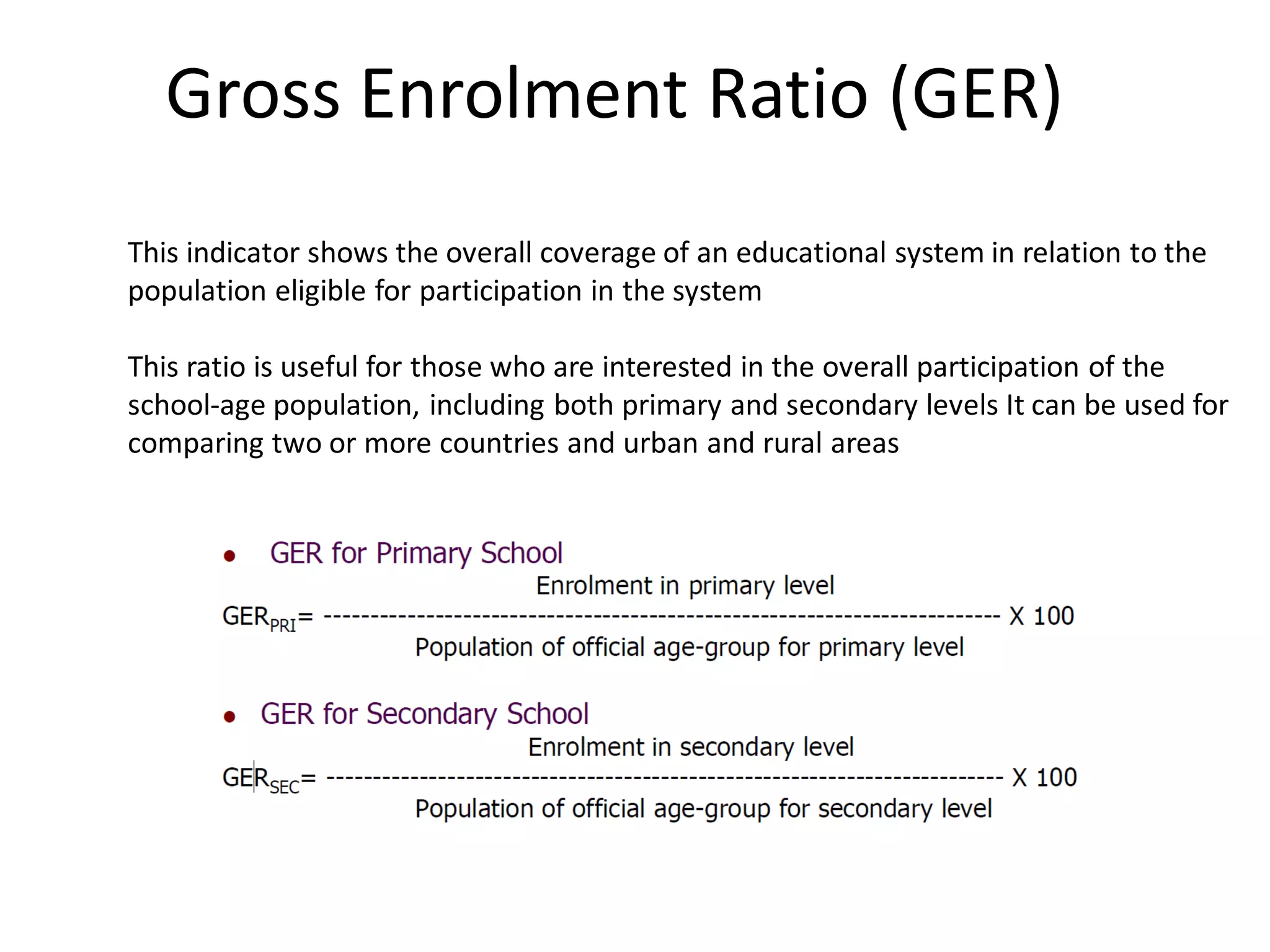
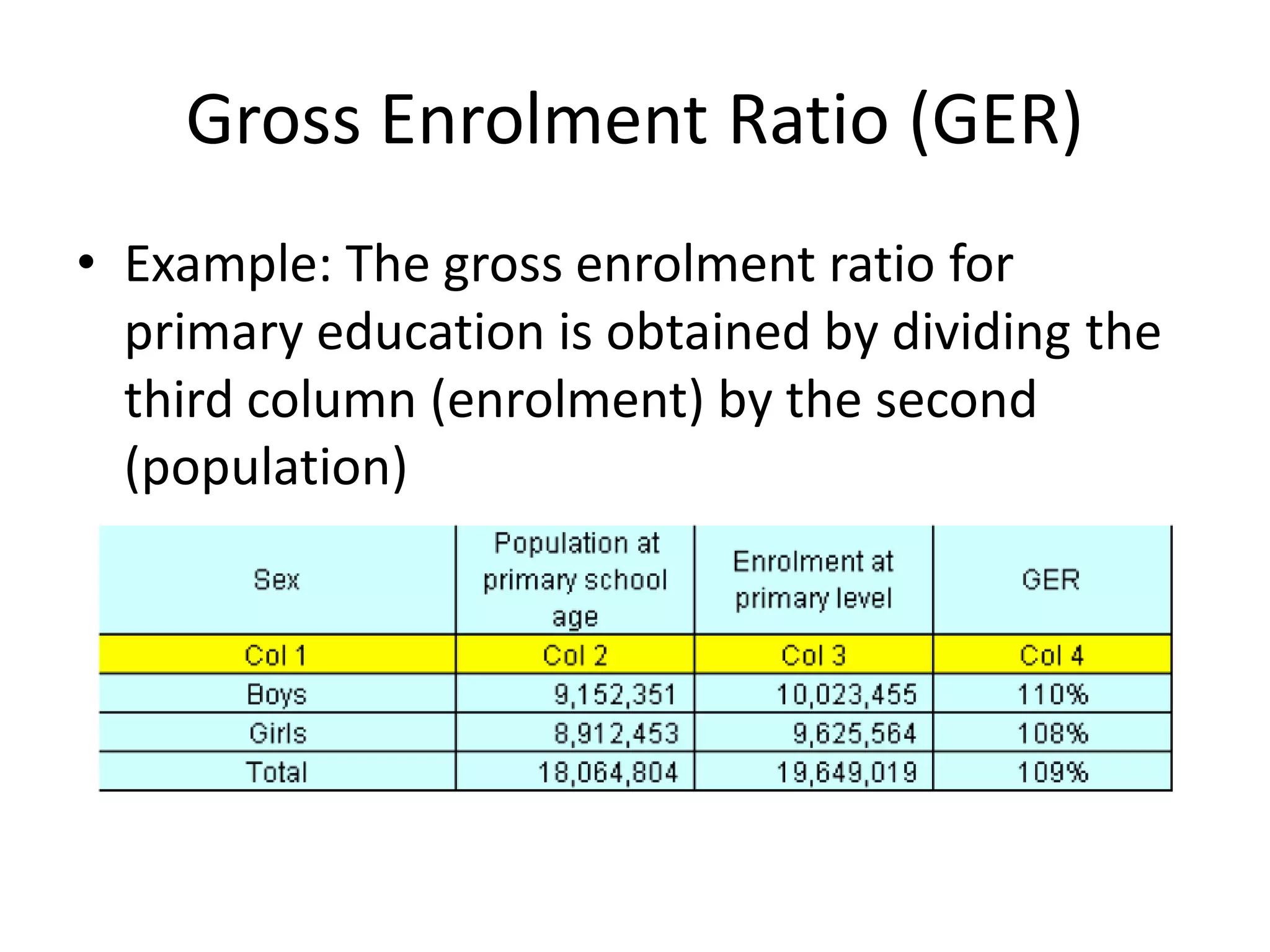
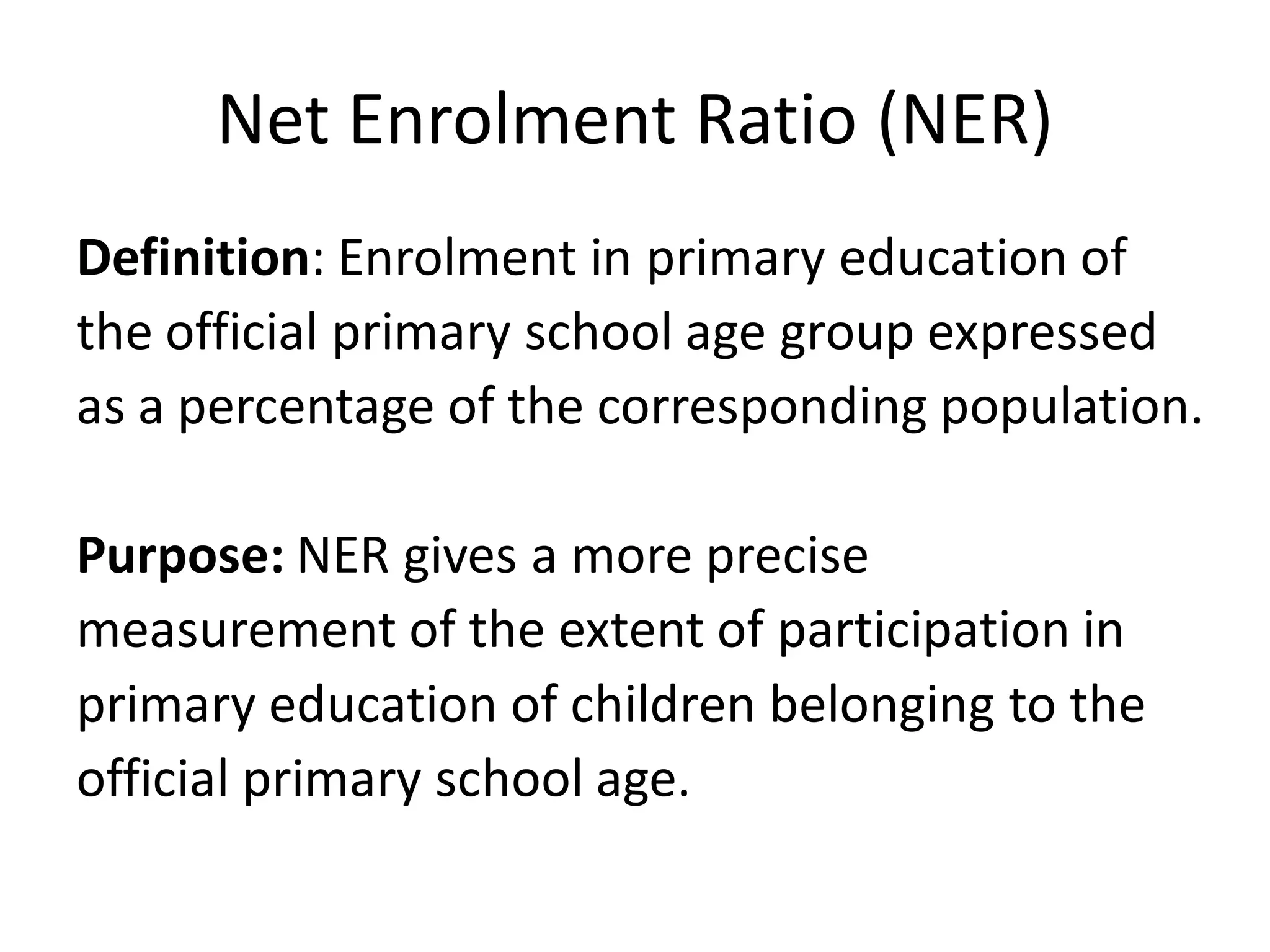
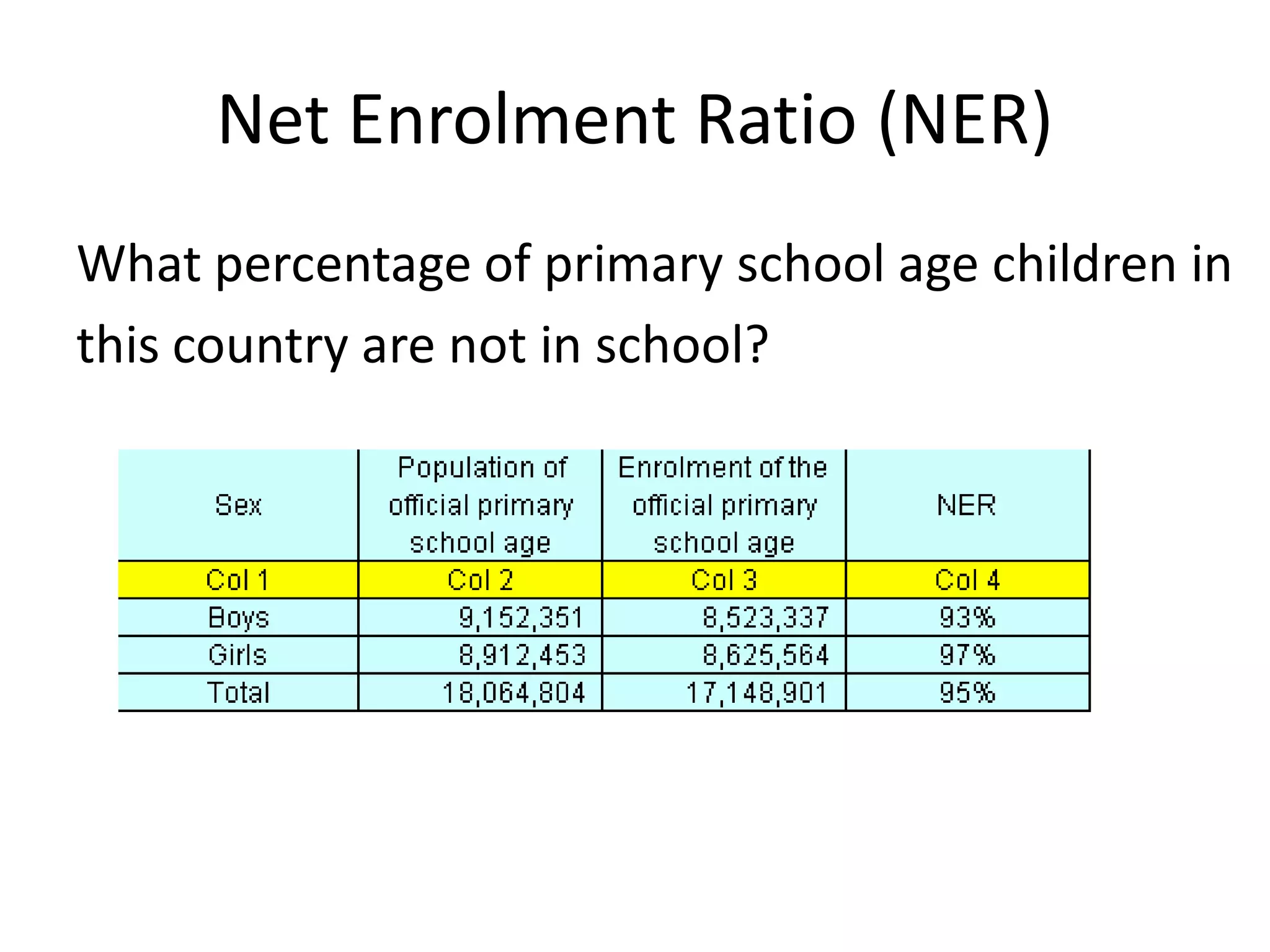
The Gross Enrolment Ratio (GER) is a statistical measure used to show the general level of participation in primary education. It represents total enrolment in primary education, regardless of age, expressed as a percentage of the eligible official primary school-age population. The GER is used when more precise data on enrolment by single years of age is unavailable. It can indicate if a country has sufficient capacity to accommodate all primary school-aged children, but does not show what proportion is actually enrolled. A GER over 100% suggests there are over-aged or under-aged children enrolled.