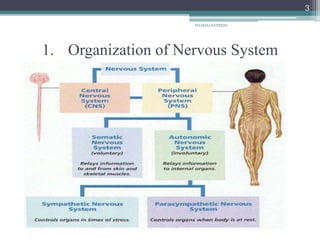
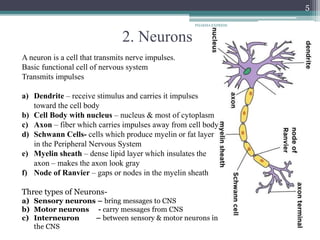
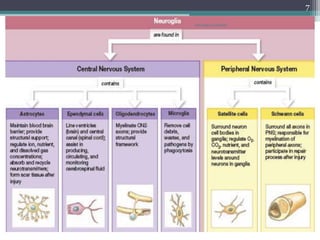
The document provides an overview of the nervous system, including its organization and main components. It discusses the functions of the nervous system in gathering sensory information and coordinating motor responses to maintain homeostasis. The central and peripheral nervous systems are introduced. Key aspects of neurons like dendrites, axons, and types are summarized. The roles of neuroglia in supporting neurons is outlined. Classification and properties of nerve fibers are presented. The generation and propagation of action potentials and nerve impulses are described briefly. An overview of receptors, synapses, and major neurotransmitters is also provided.