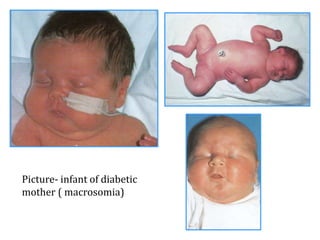
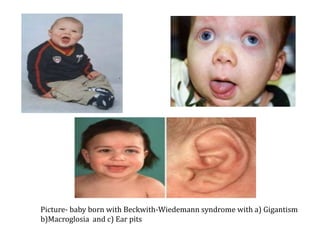
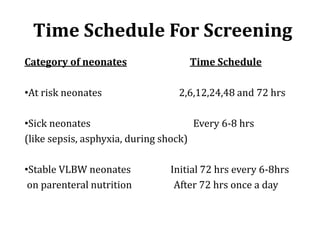
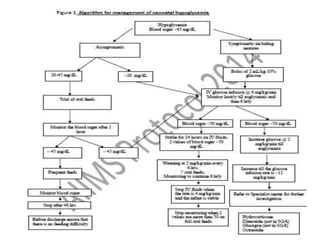
This document discusses neonatal hypoglycemia. It begins by defining neonatal hypoglycemia and describing the typical blood glucose levels in newborns compared to older children and adults. It then discusses the main causes of hypoglycemia including decreased production/stores, increased utilization, and hyperinsulinemic hypoglycemia. The clinical manifestations, diagnosis, management, and outcomes of neonatal hypoglycemia are described. Recurrent or resistant hypoglycemia may require additional treatment such as hydrocortisone, diazoxide, or octreotide to help control blood glucose levels. Infants with symptomatic hypoglycemia should be followed long term to monitor for potential neurological or developmental issues.