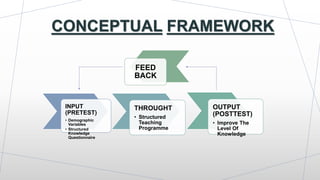
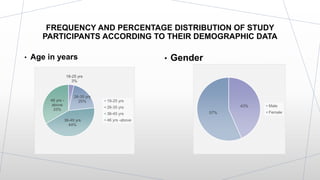
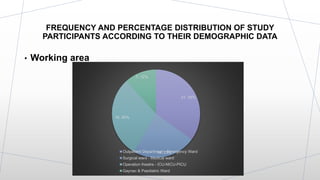
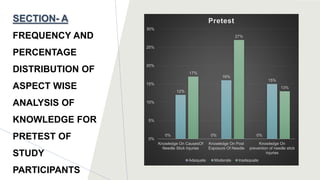
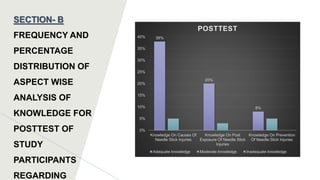
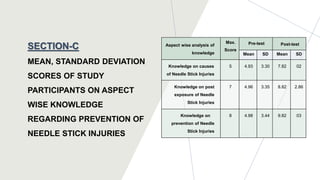
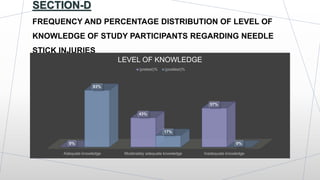
This dissertation presentation summarizes Ms. Krupa Patel's research study on assessing the effectiveness of a structured teaching program on knowledge of needle stick injury among class-IV hospital workers in Sabarkantha District, Gujarat. The study used a pre-test post-test design with 60 participants. Results found a significant improvement in knowledge after the teaching program, with 50 participants having adequate knowledge post-test compared to none pre-test. The structured teaching program was effective in improving knowledge of needle stick injuries.