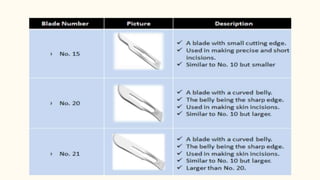
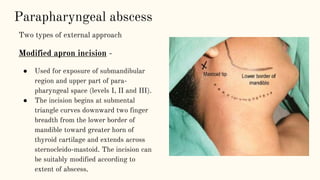
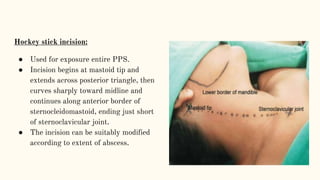
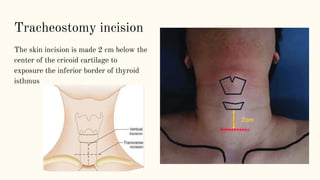
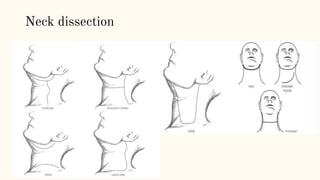
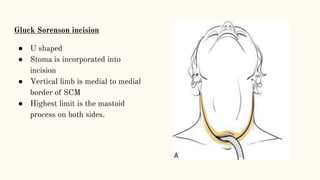
This document discusses various incisions used for neck surgeries. It describes incisions for procedures like submandibular gland excision, parapharyngeal abscess drainage, thyroid surgery, tracheostomy, neck dissection, and total laryngectomy. Key factors in choosing an incision include exposure needs, tumor location, and avoiding previous sites. Common incisions mentioned are the transverse neck incision, modified apron incision, hockey stick incision, Kocher's thyroid incision, modified Schobinger incision, and Gluck Sorenson incision. Goals are adequate exposure, vascularization, inclusion of prior sites, and acceptable cosmesis.