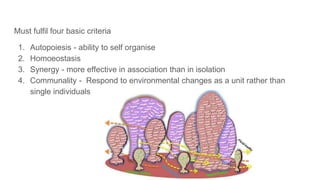
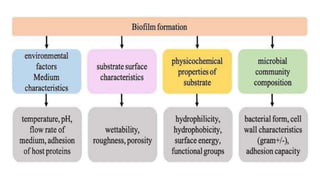
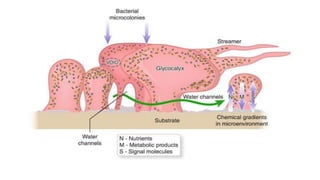
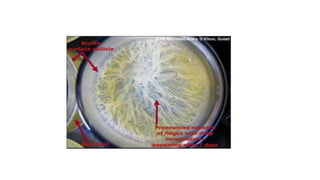
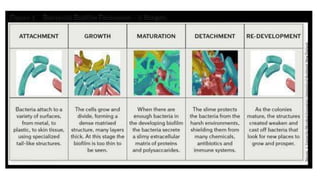
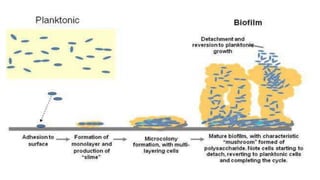
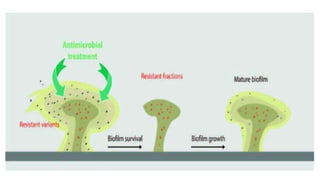
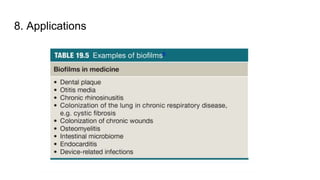
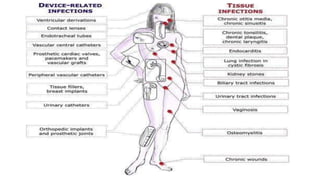
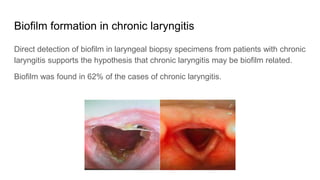
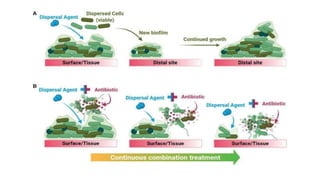
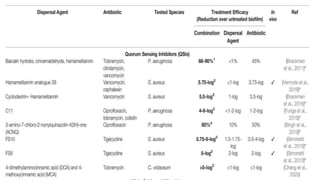
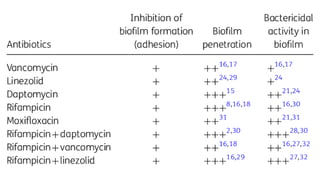
Biofilm is a complex community of microorganisms that attach to surfaces and produce an extracellular matrix. It forms in stages including initial attachment, adhesion, colonization and maturation. Biofilm provides microbes protection from environmental threats and antimicrobial agents. It is characterized by surface attachment, an extracellular matrix, structural heterogeneity and genetic diversity. Biofilm plays a role in various chronic infections like chronic rhinosinusitis, otitis media, mastoiditis and laryngitis. New therapies targeting biofilms include agents that neutralize, disperse or disrupt quorum sensing in biofilms.