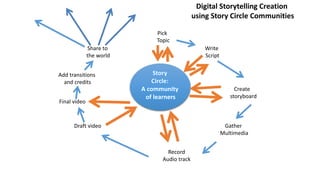
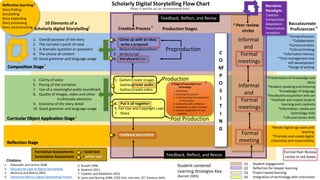
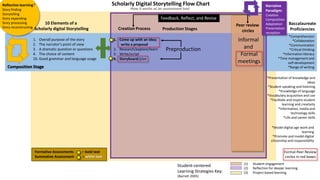
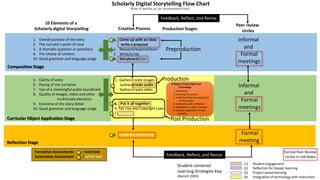
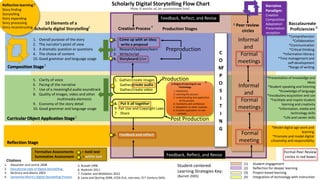
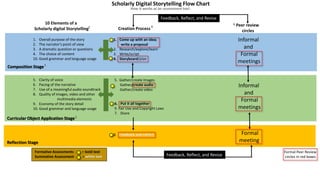
The document outlines the creation and assessment process of scholarly digital storytelling, emphasizing the importance of peer review circles and student-centered learning strategies. It elaborates on ten essential elements for effective digital storytelling, such as clarity of voice, pacing, and quality of multimedia. The document also details the steps involved in the storytelling process from initial idea conception to sharing the final product.