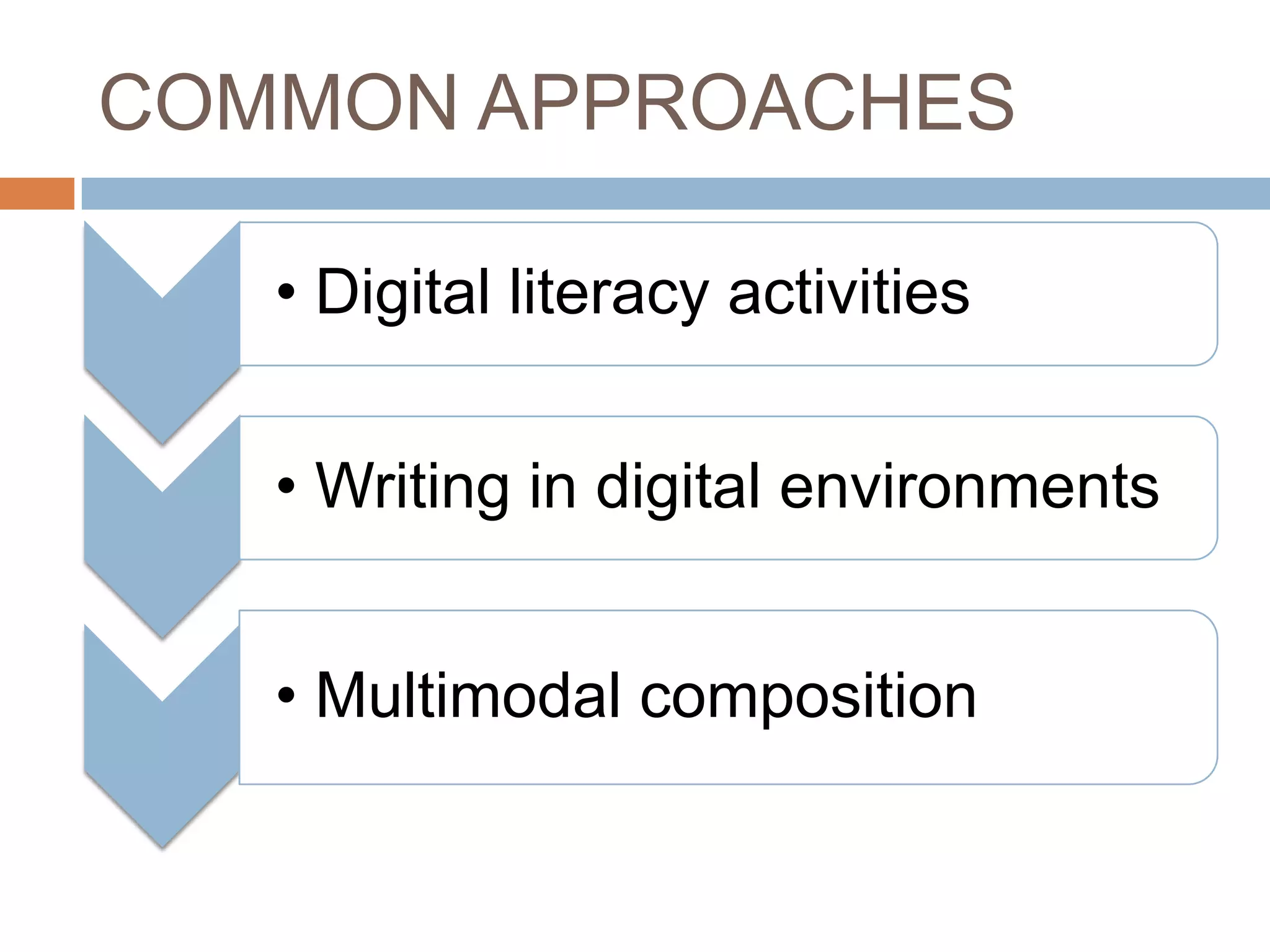
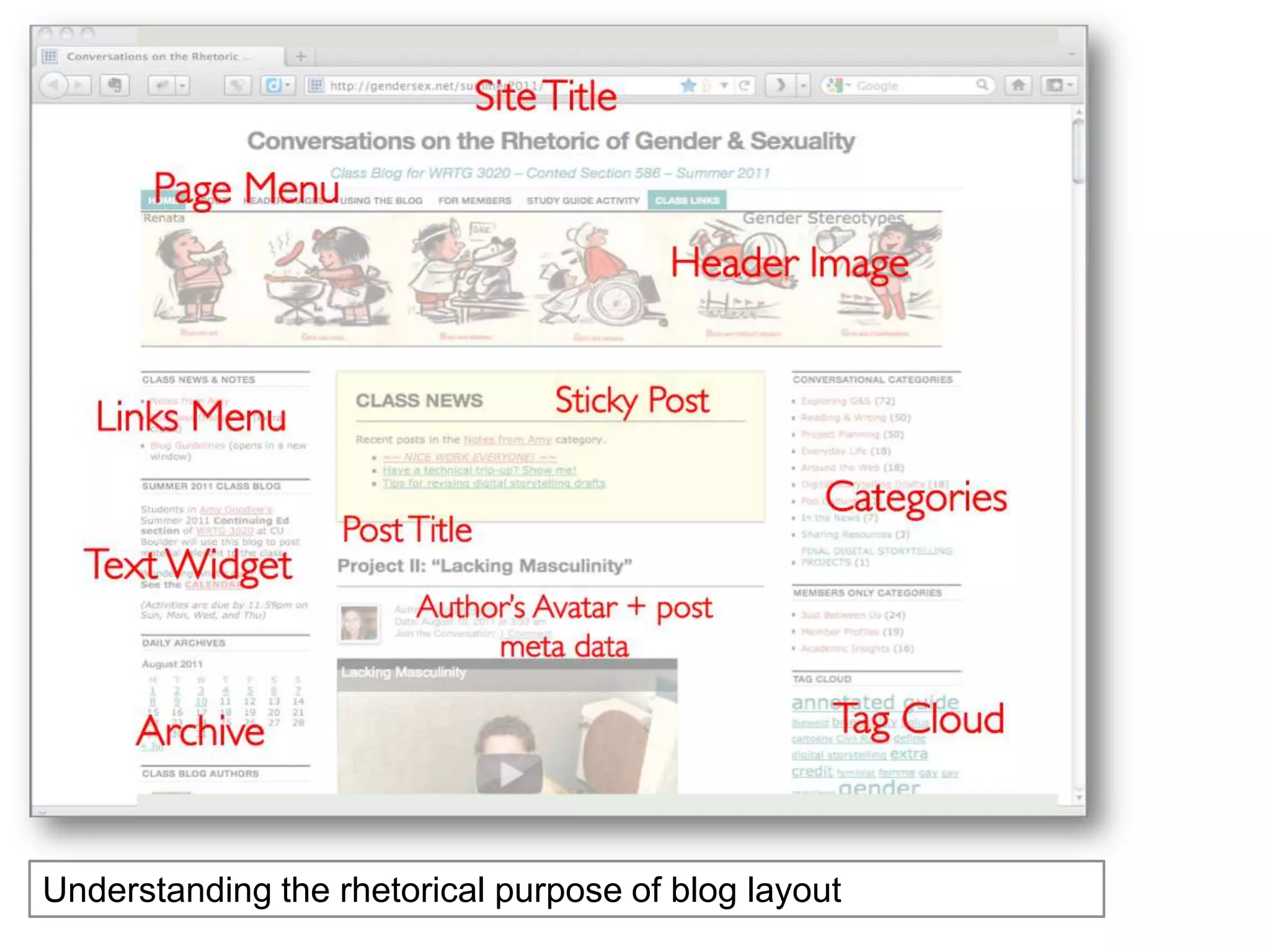
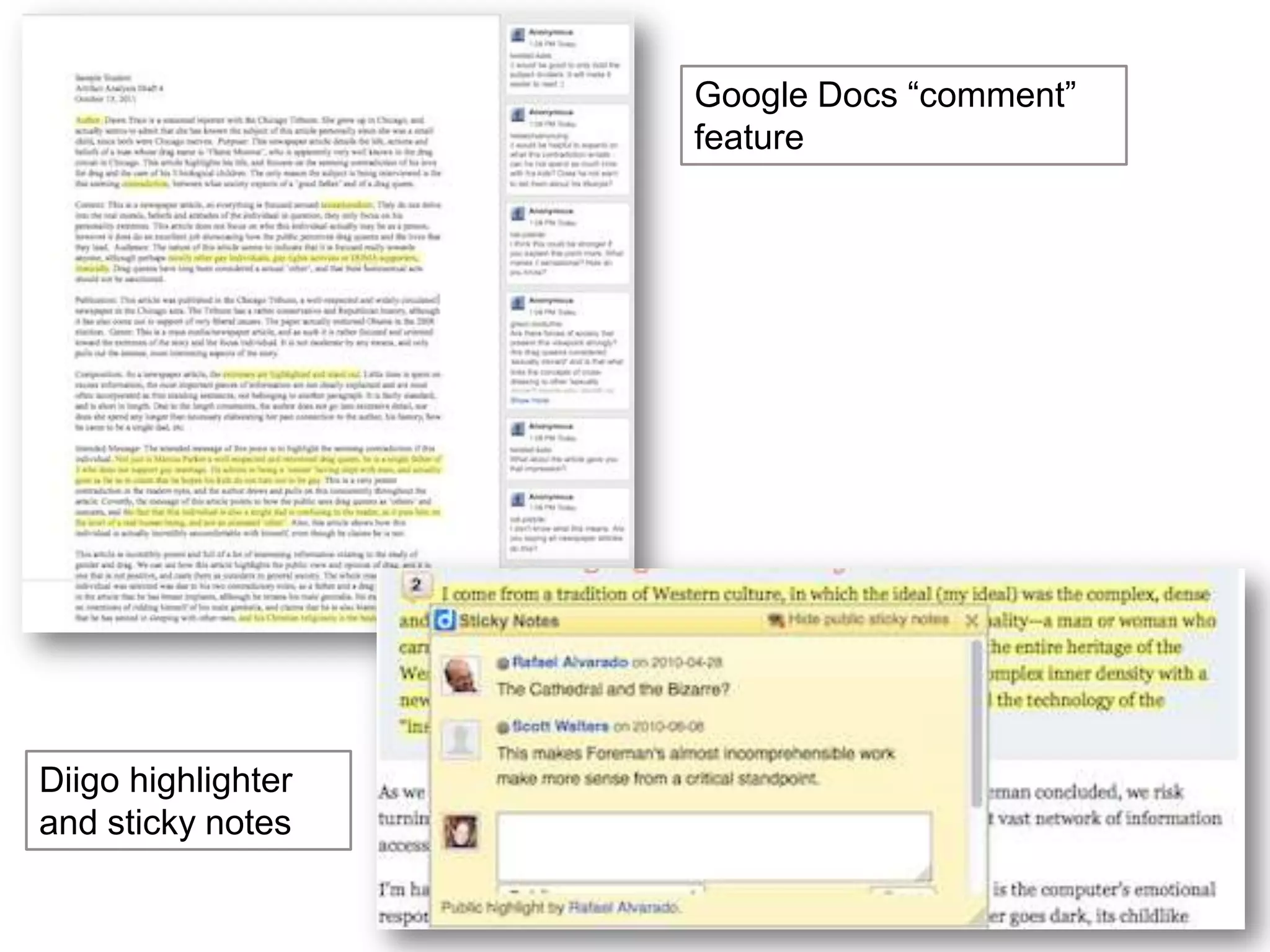
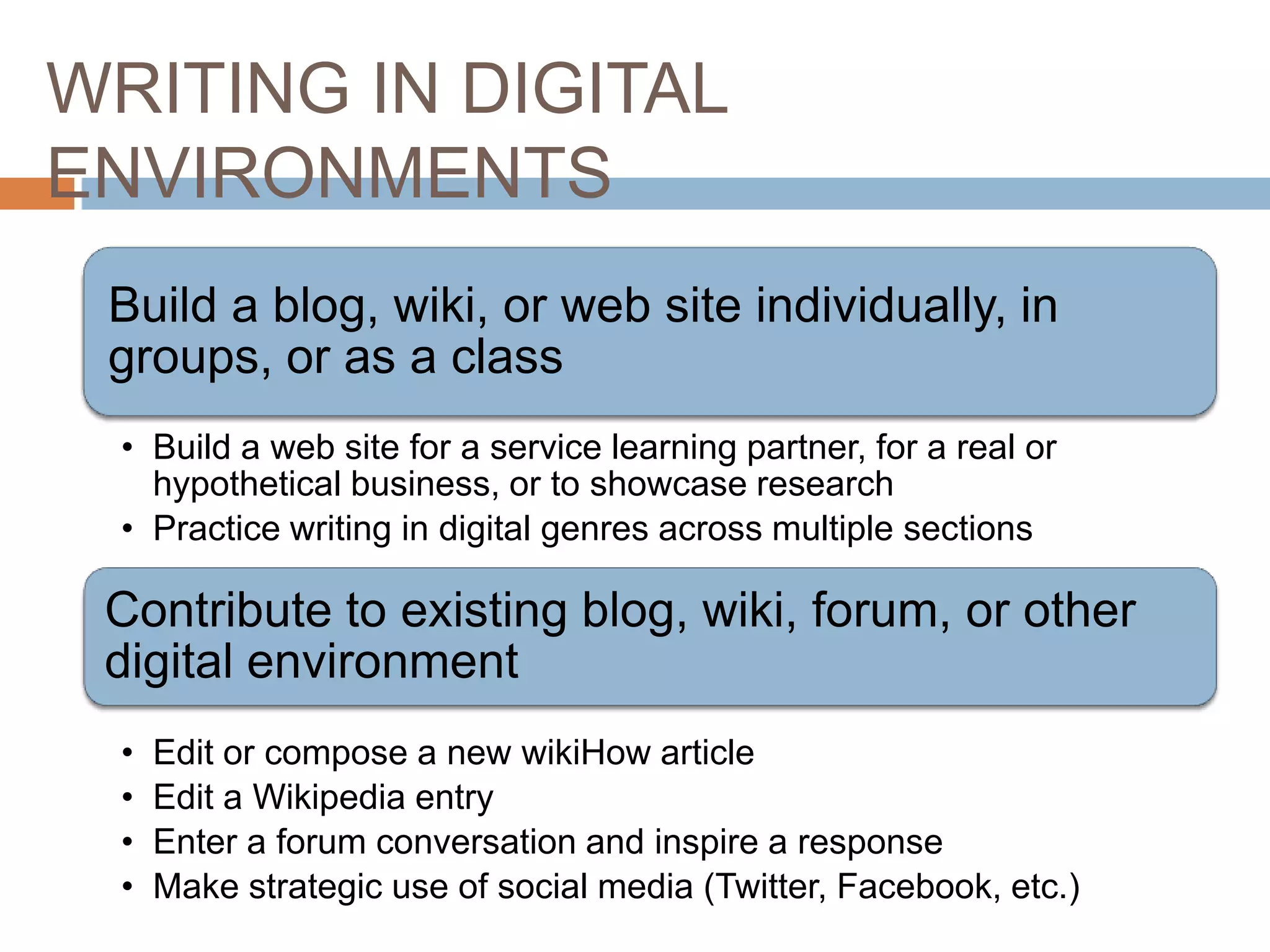
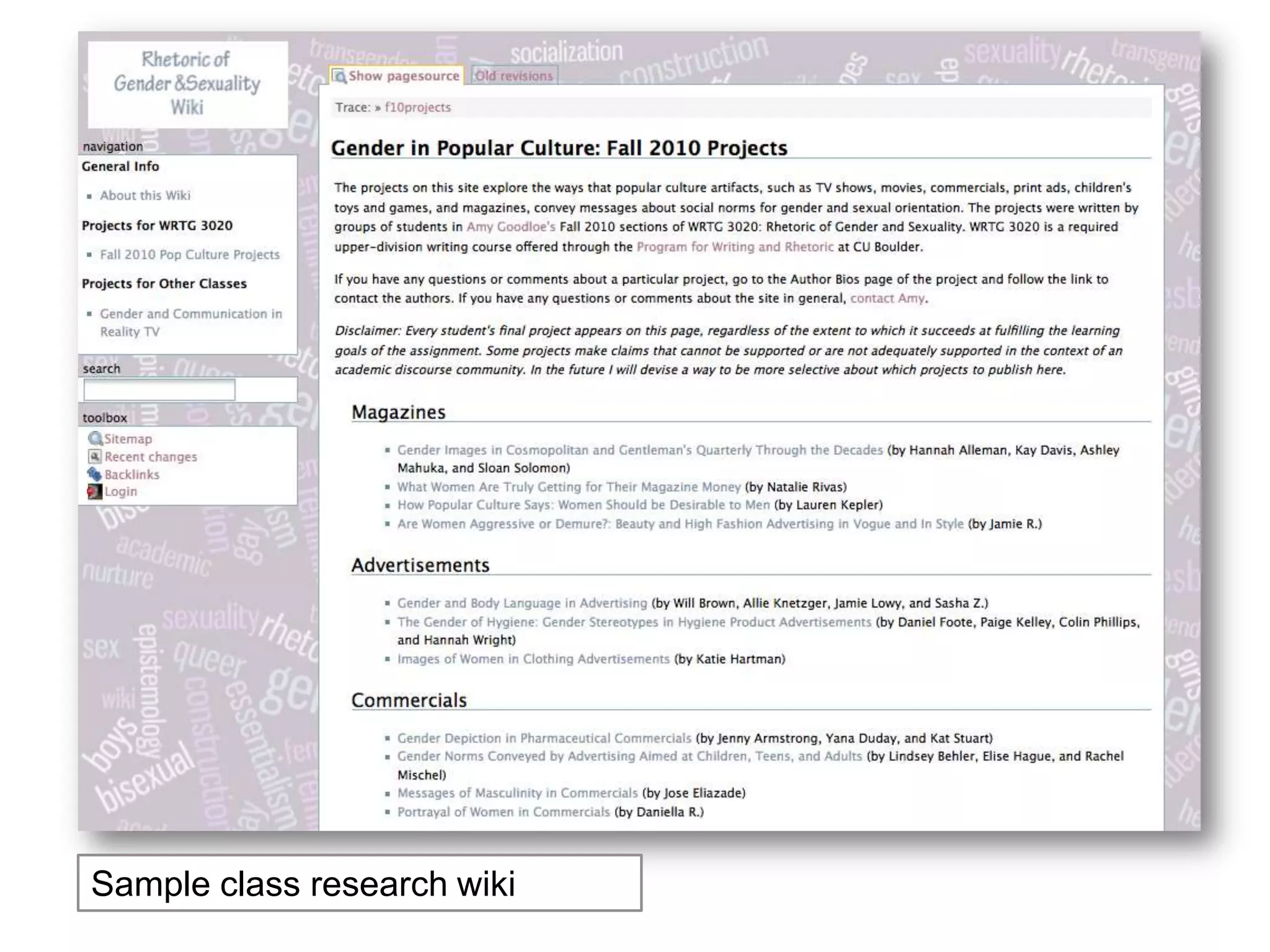
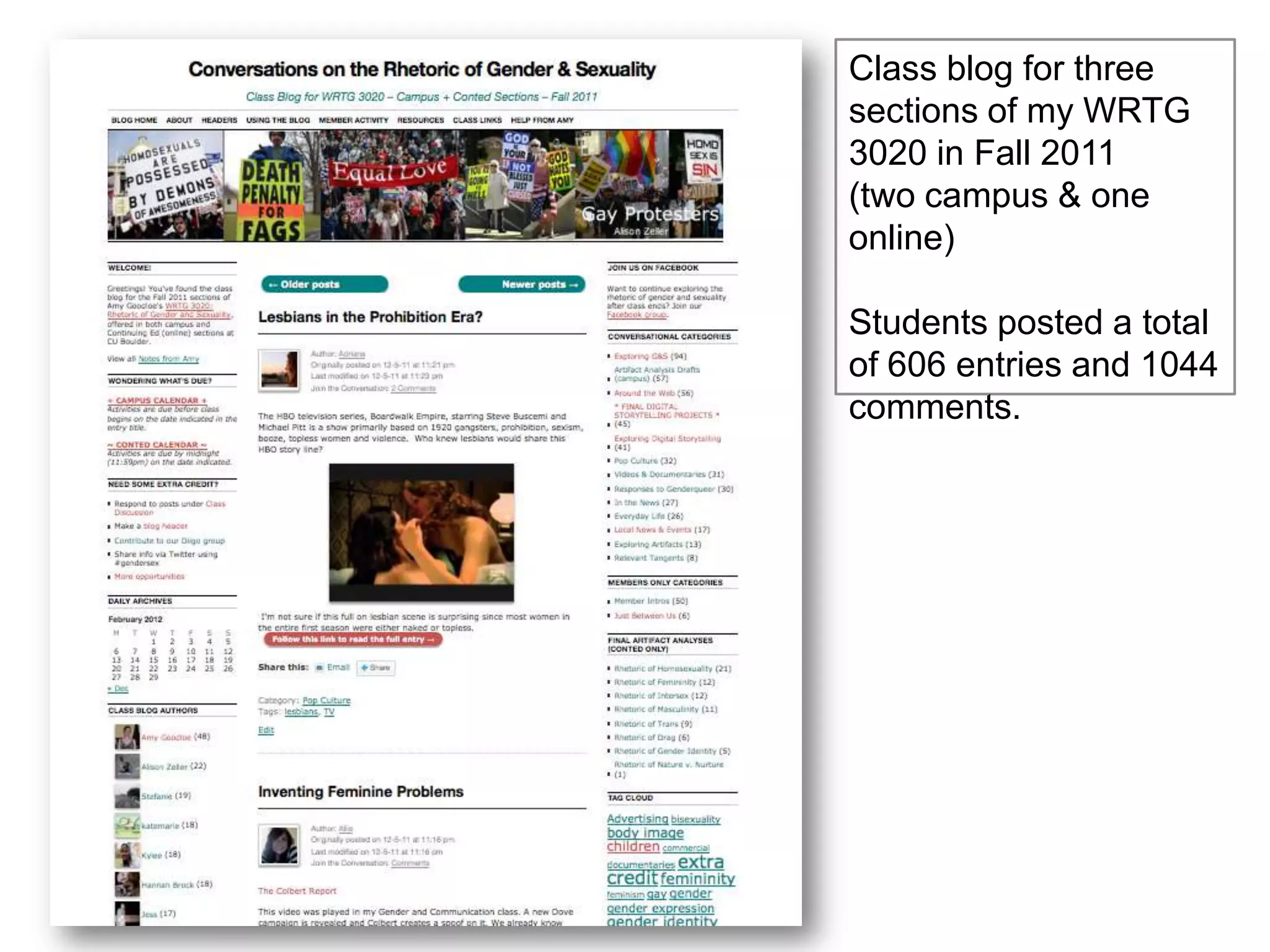
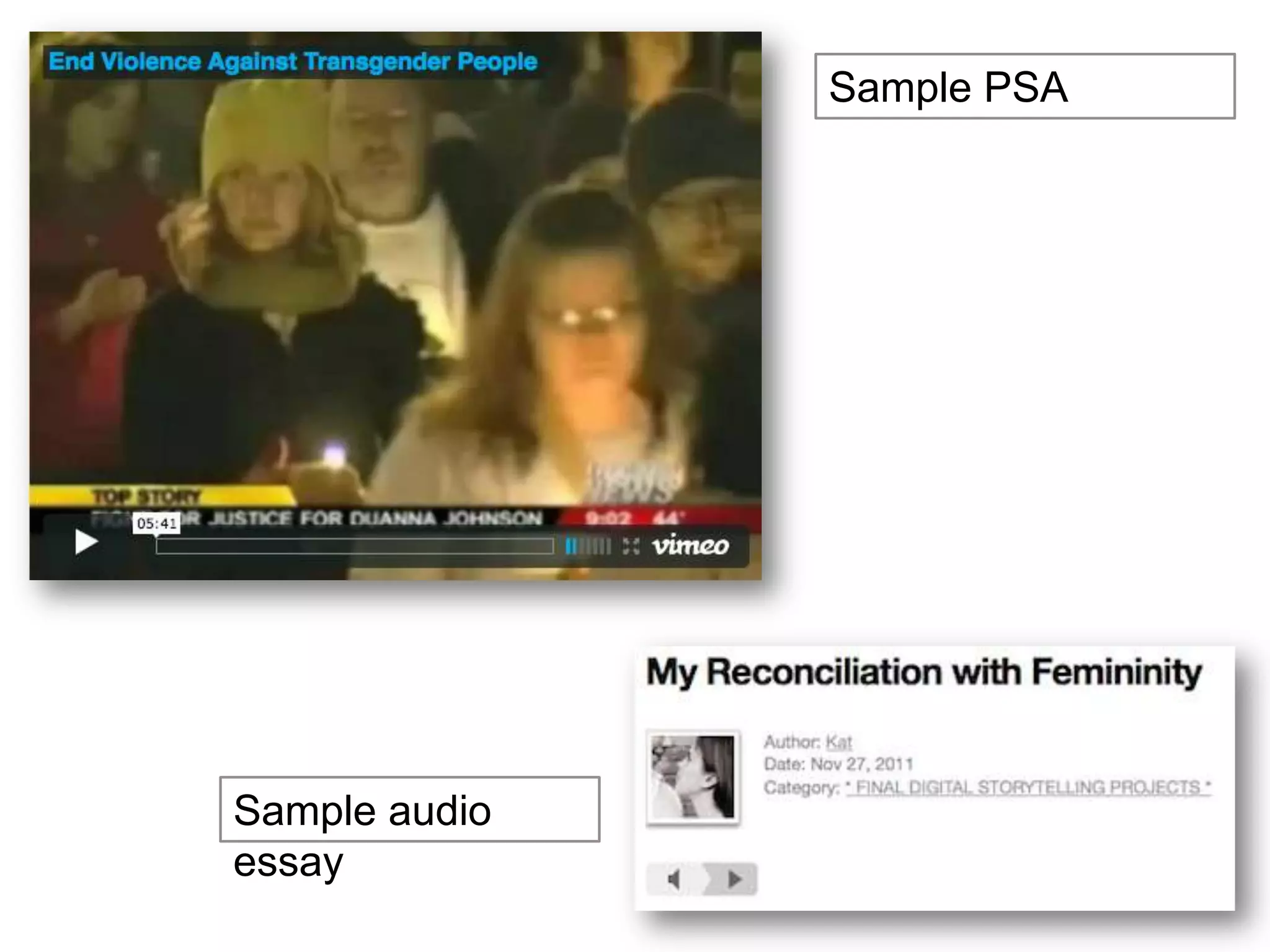
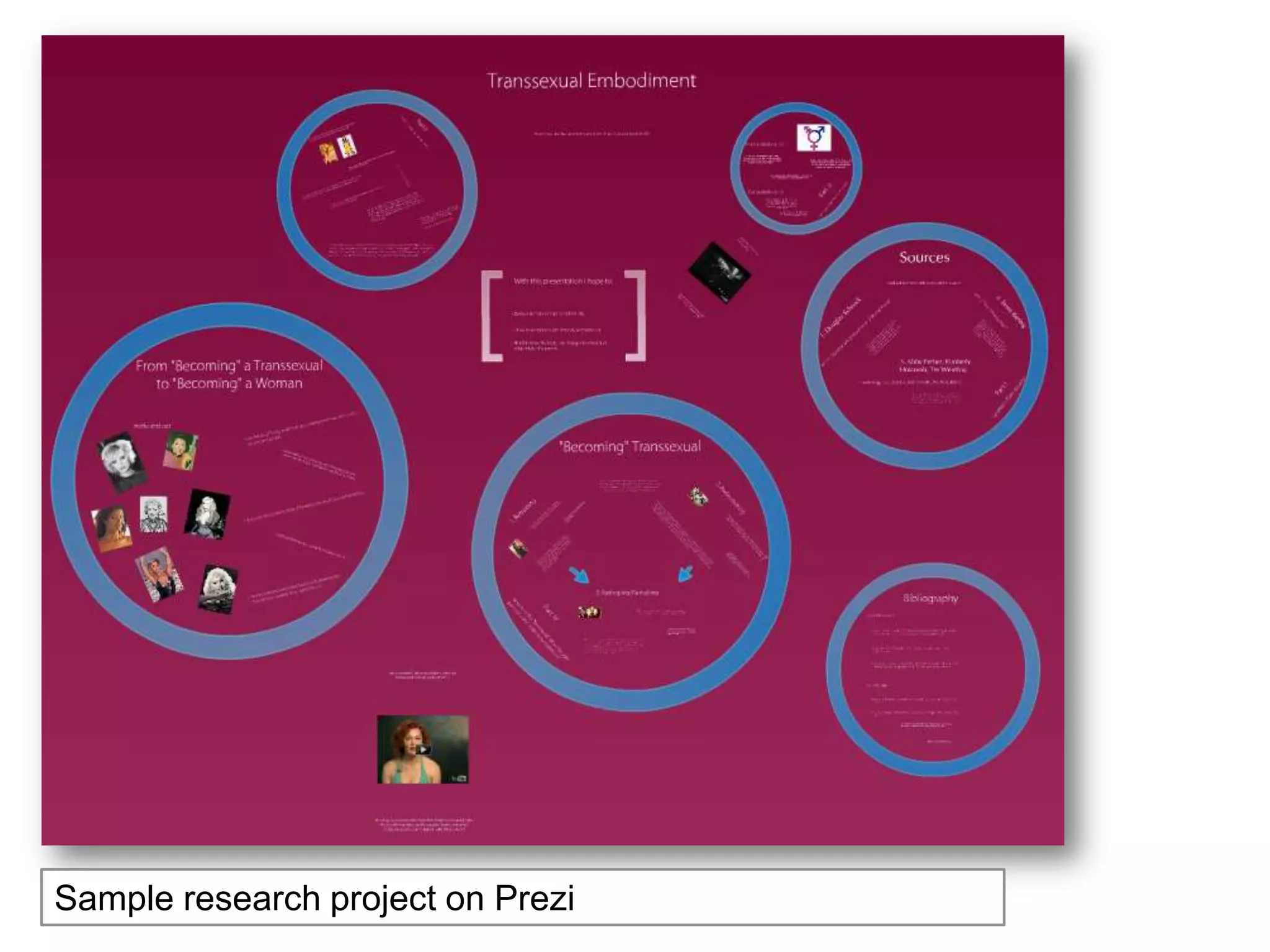
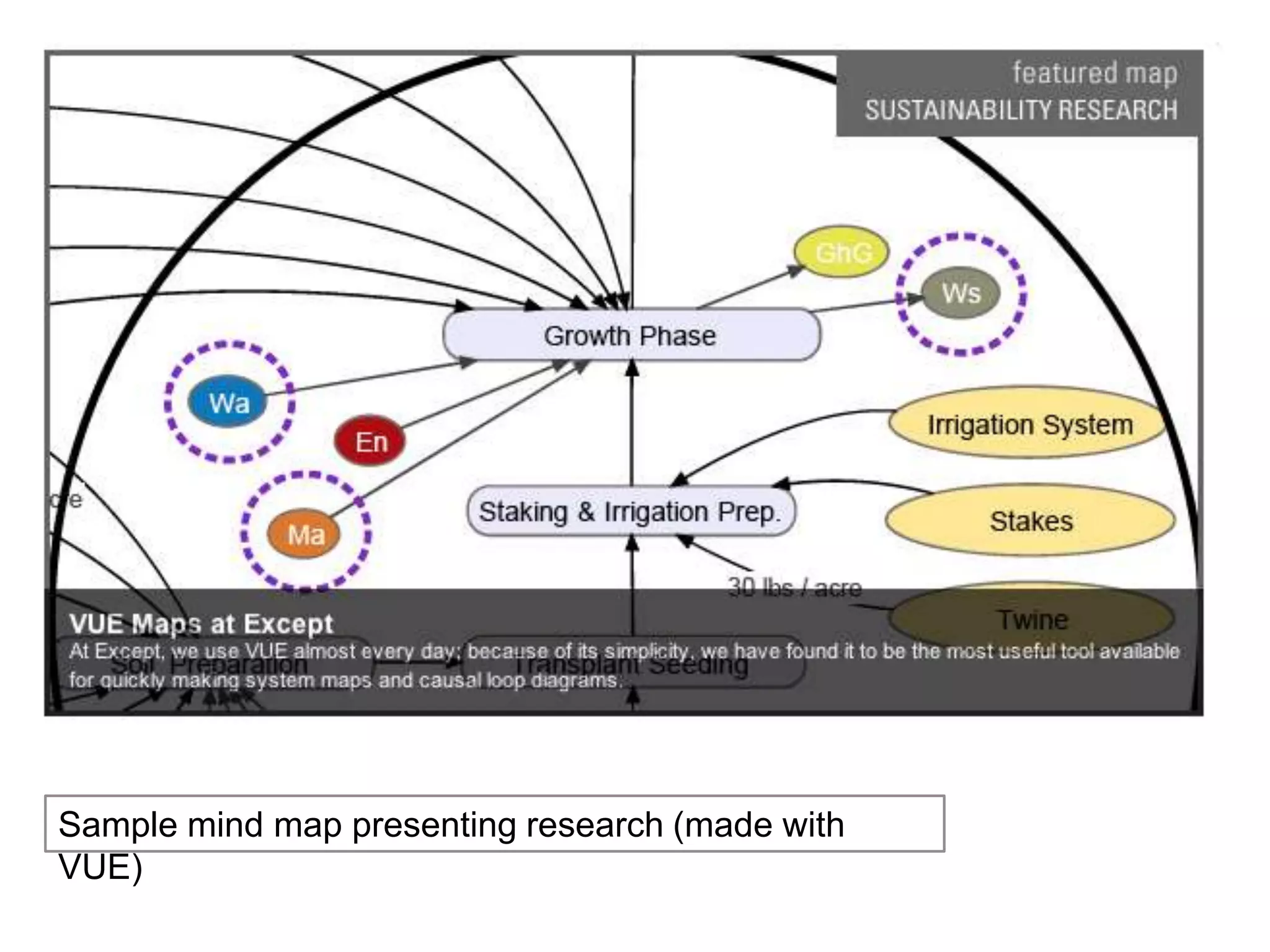
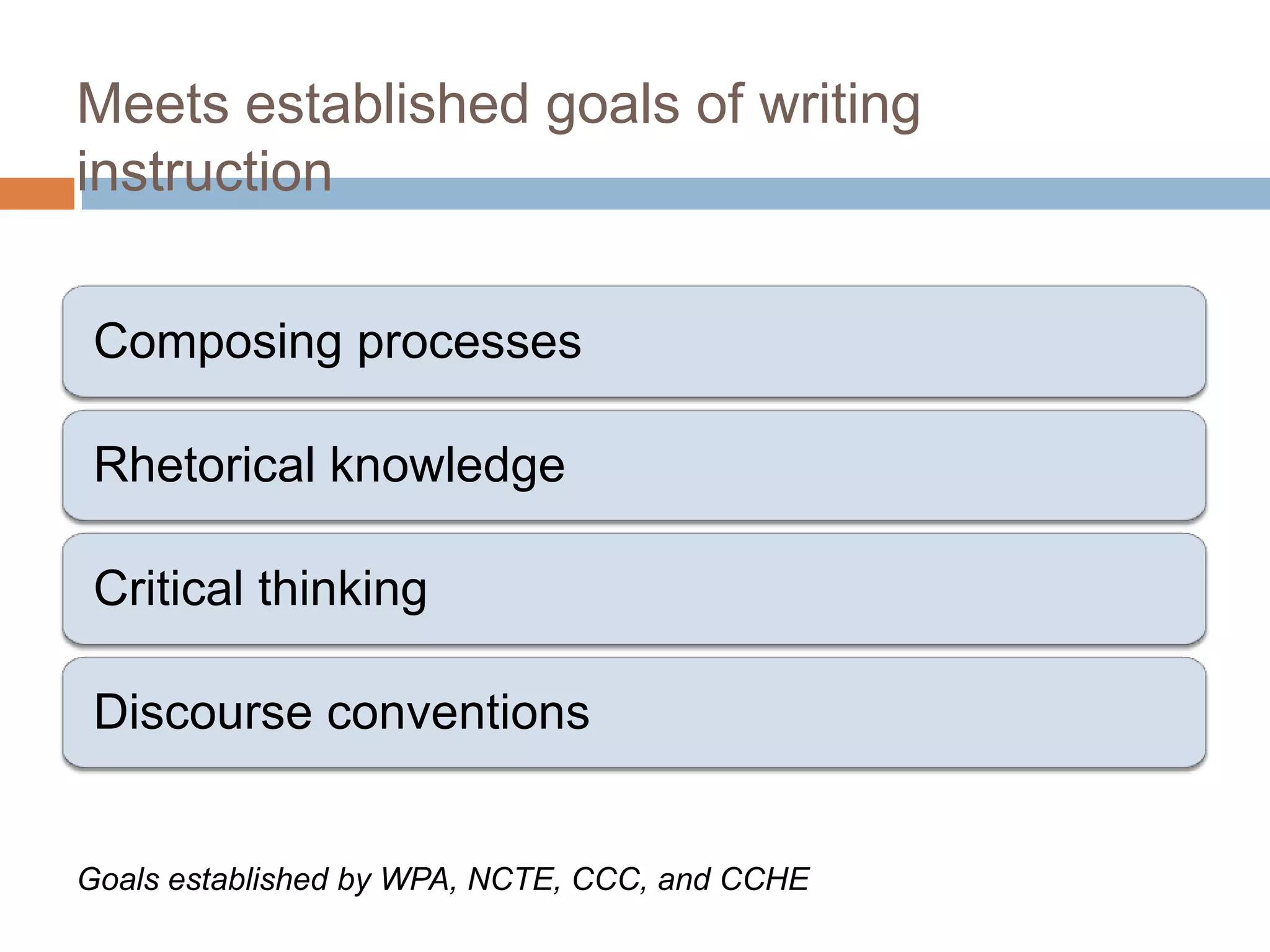
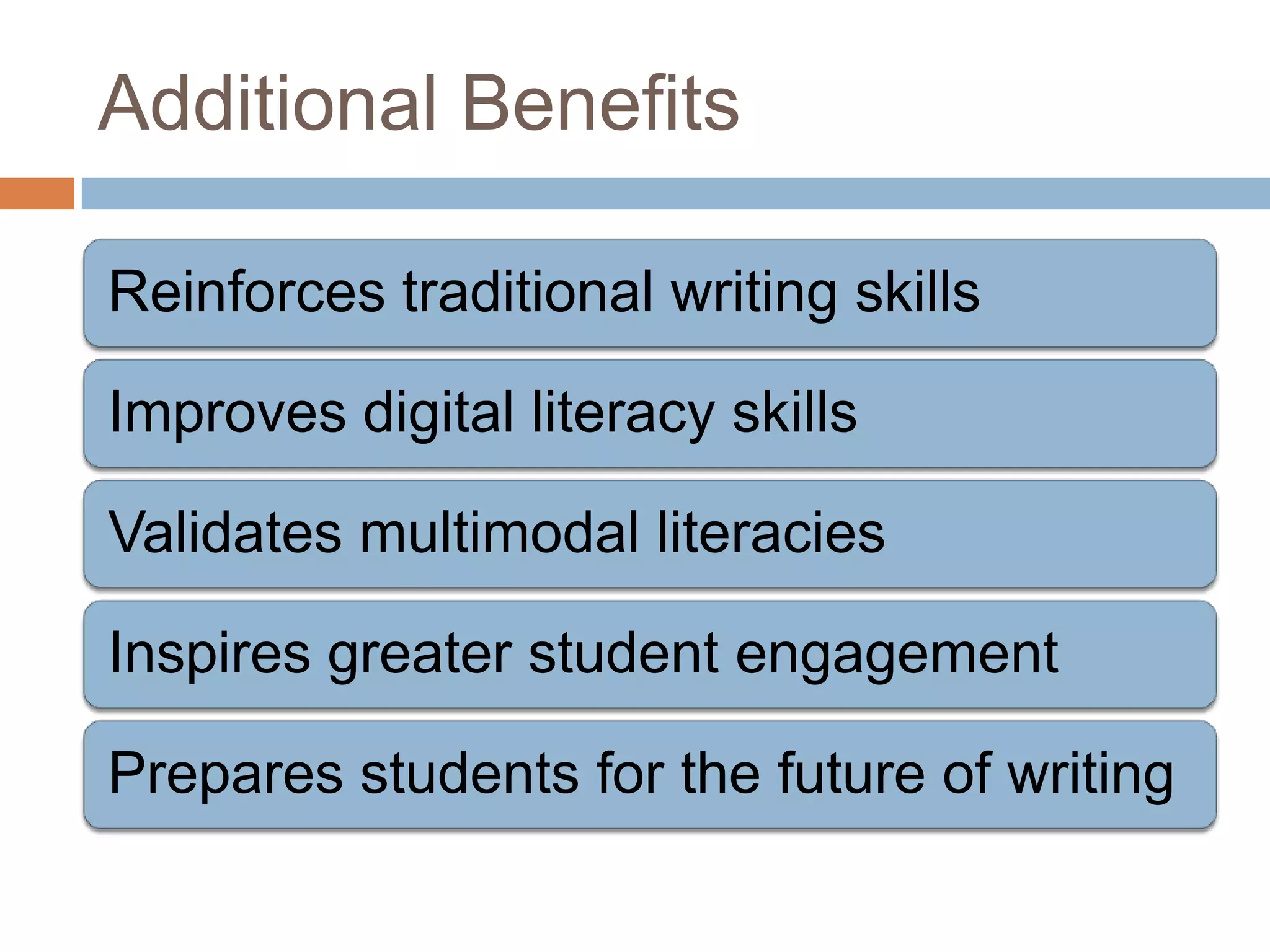
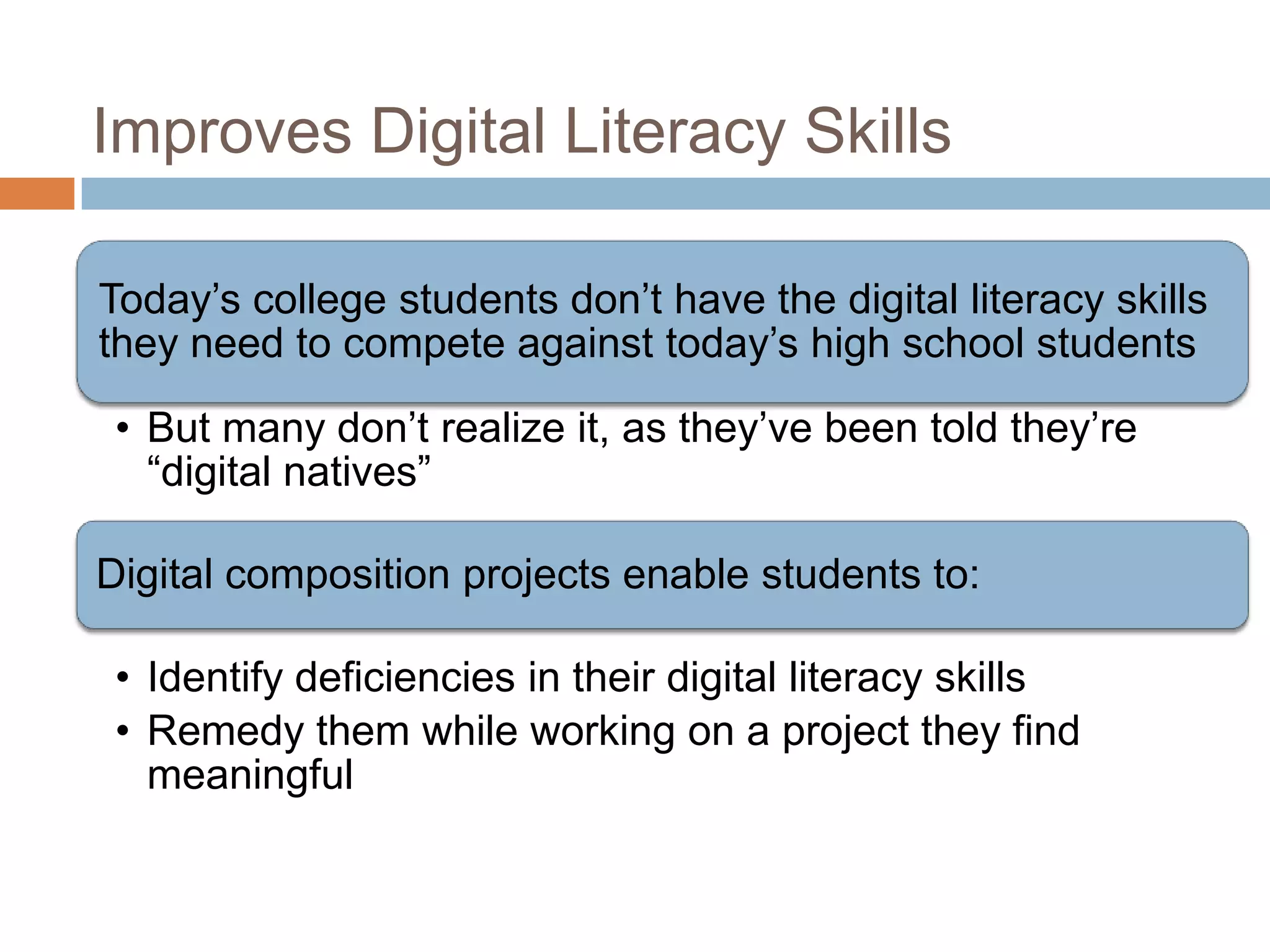
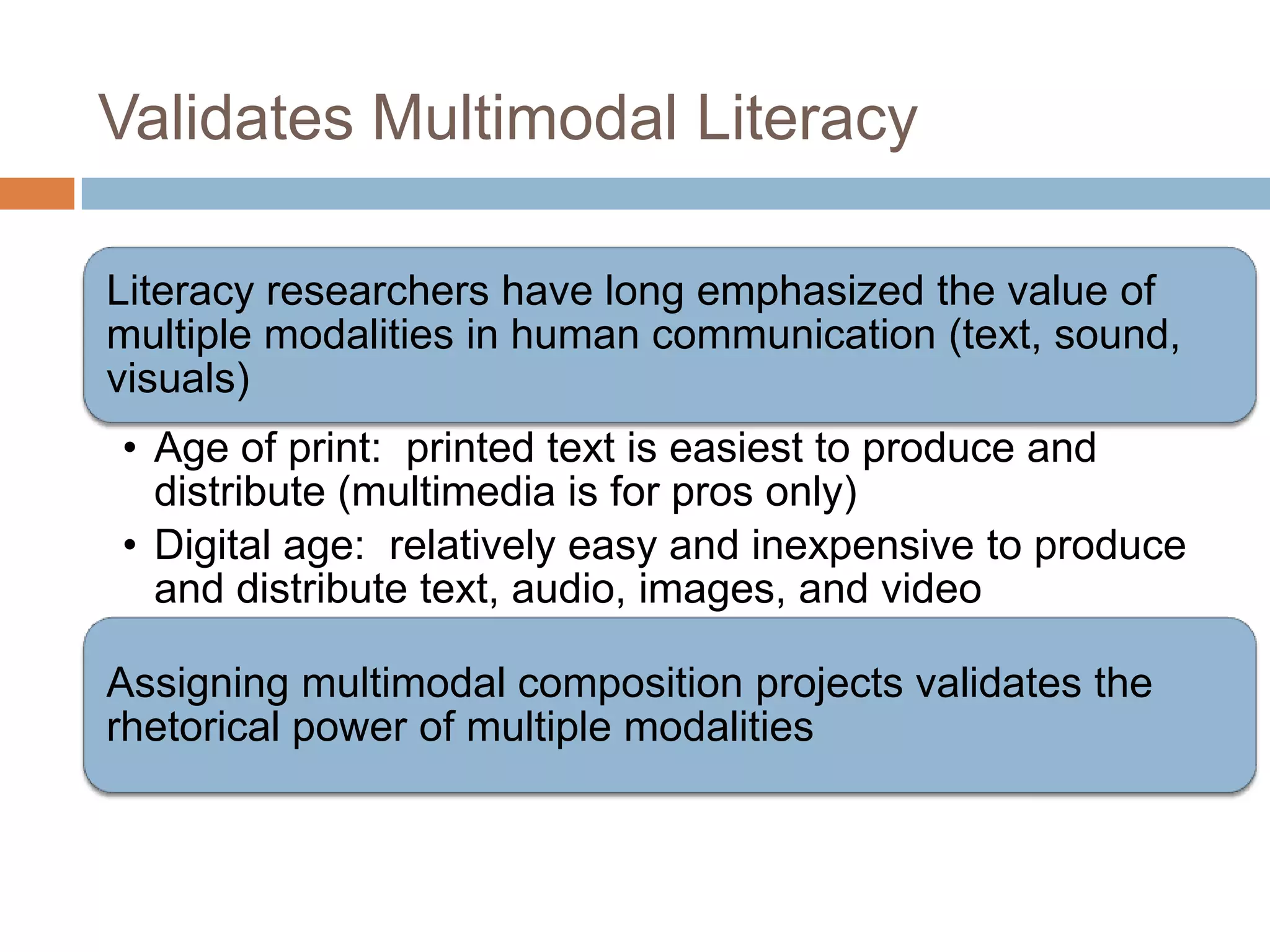
The document is an introduction to the PWR Digital Composition Sampler, presenting various approaches to digital composition, including digital literacy activities and multimodal composition. It discusses the benefits for students, emphasizing the development of critical thinking, rhetorical knowledge, and digital literacy skills through projects that engage with real audiences and modern platforms. The presentation also highlights how digital composition prepares students for the evolving landscape of writing and communication.