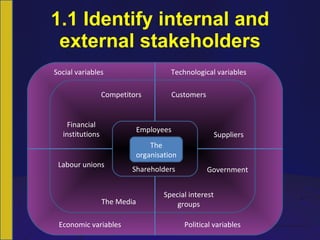
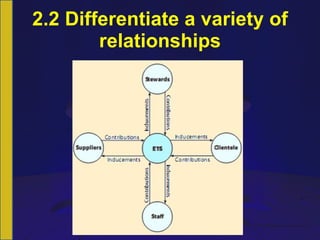
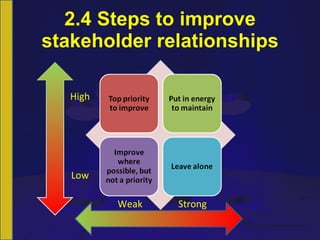
The document discusses internal and external stakeholders of an organization. It defines stakeholders as any person or group with an interest in the business achieving its objectives. Internal stakeholders are inside the business, while external stakeholders are outside. It provides examples of common internal and external stakeholders. The document also discusses identifying and prioritizing stakeholder requirements, as well as differentiating relationships between stakeholders and the organization. It outlines steps to improve stakeholder relationships, including identifying key stakeholders, contributions/inducements, prioritizing them, measuring contributions/inducements, evaluating relationships, and ranking stakeholders by influence and expected outcomes.