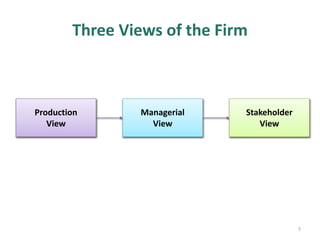
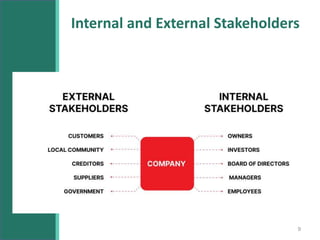
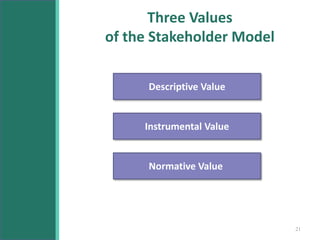
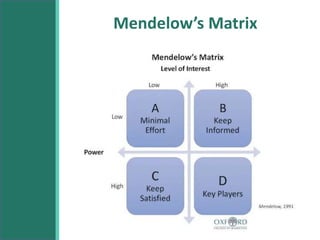
This document discusses stakeholders in business organizations. It defines stakeholders as any individual or group that can affect or is affected by an organization's actions. Stakeholders are then categorized as internal (e.g. employees, managers) or external (e.g. customers, suppliers, community). The document outlines what each key stakeholder group looks for from the organization. It emphasizes the importance of long-term stakeholder relationships and using stakeholder feedback to help a business succeed. The document also introduces Mendelow's Matrix for analyzing stakeholders based on their power and interest, and notes that addressing conflicting stakeholder goals is important for an organization's performance.