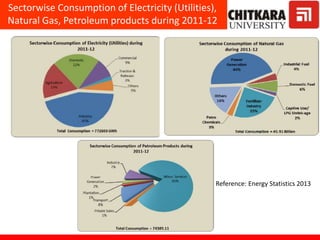
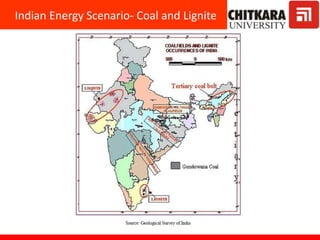
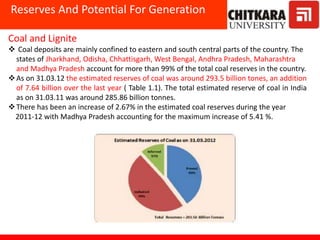
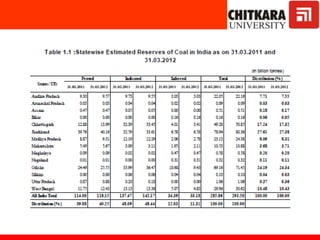
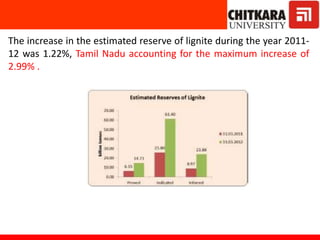
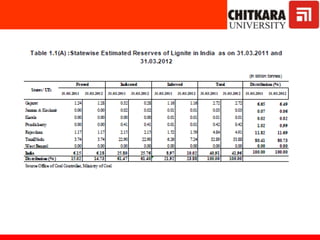
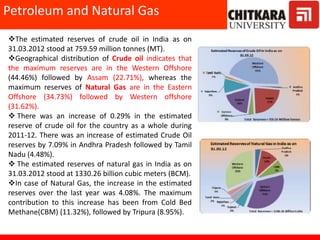
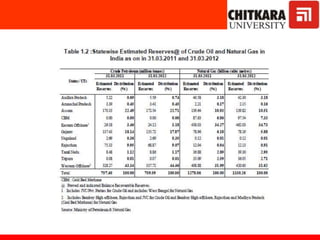
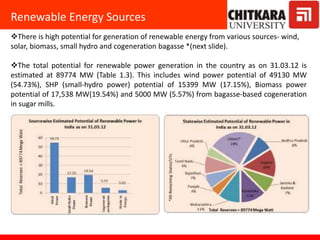
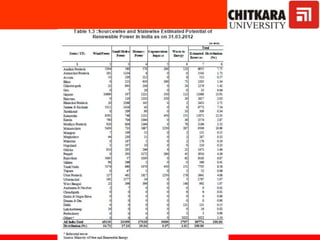
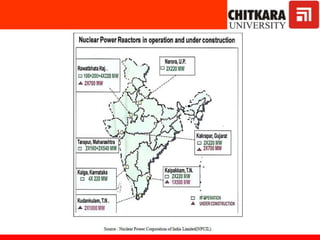
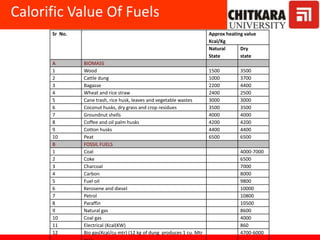
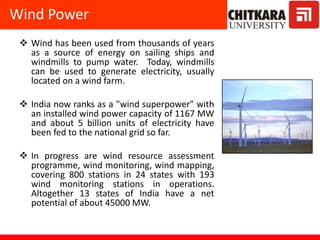
This document provides an introduction to non-conventional energy sources. It defines various types of energy sources such as primary and secondary, commercial and non-commercial, and renewable and non-renewable. India's energy scenario is discussed, noting its rapid economic growth places high demand on energy resources. Coal, petroleum and natural gas make up a large portion of India's energy production and consumption currently, though renewable sources such as solar, wind and biomass have significant untapped potential.