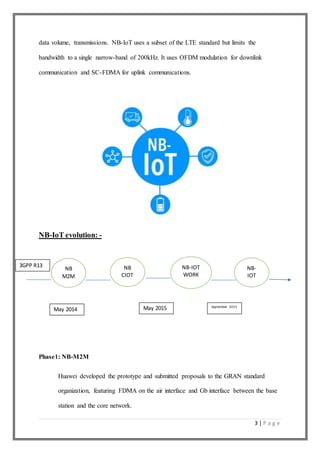
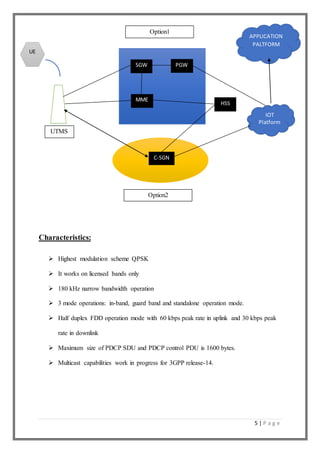
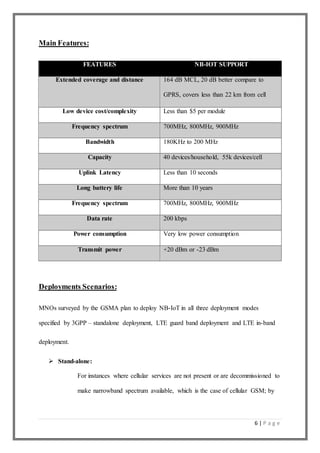
Narrowband Internet of Things (NB-IoT) is a low power wide area network technology developed by 3GPP to enable connectivity for battery powered devices. It uses a narrow bandwidth of 200kHz within existing cellular spectrums to provide long battery life, support for many connected devices, and indoor coverage. NB-IoT can co-exist with 2G, 3G, and 4G networks and is expected to support over 3 billion connected devices by 2020 across various applications in industries like agriculture, healthcare, automotive and more. It operates with low data rates and focuses on enabling low cost, low power devices to wirelessly transmit infrequent small amounts of data over long distances.