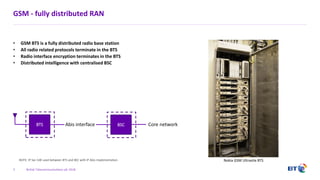
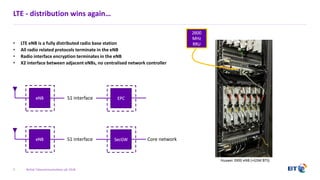
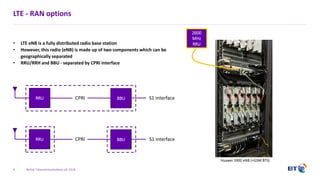
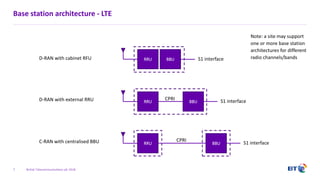
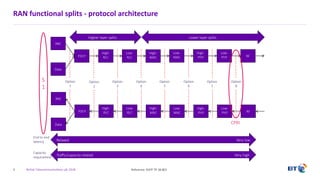
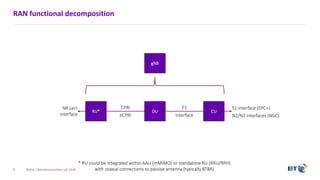
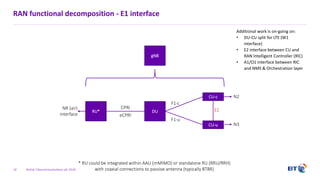
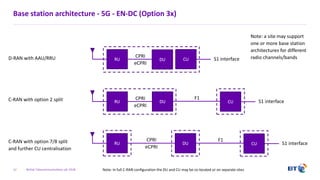
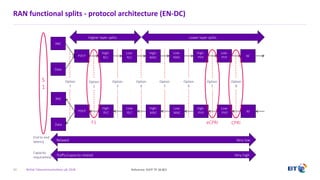
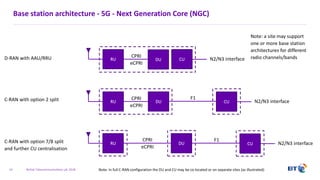
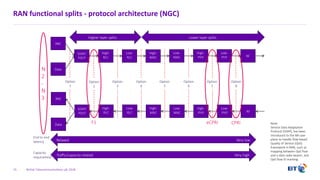
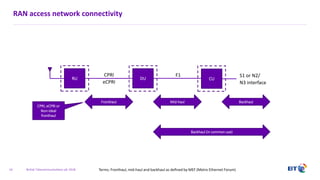
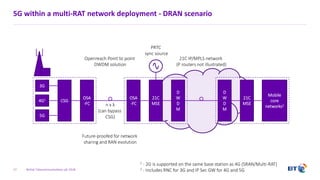
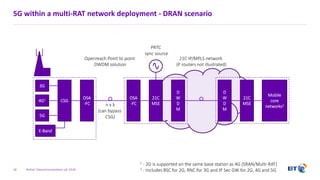
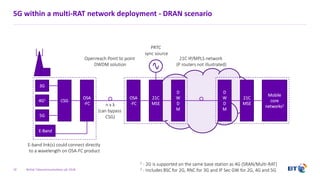
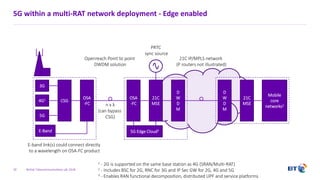
The document outlines the evolution of 5G radio access network (RAN) architecture, highlighting the transition from GSM, UMTS, and LTE to the more advanced functionalities of 5G. It discusses RAN functional decomposition and accessibility for various architectural options, conveying the necessity for disaggregation to meet increasing demands. BT is actively developing the required infrastructure to lead in 5G and converged networks, while addressing challenges associated with traditional centralized architectures through initiatives like eCPRI.