The document investigates the use of ethanolic extract from Nerium indicum flowers as a natural acid-base indicator alternative to synthetic indicators like phenolphthalein. The study demonstrates that the extract can effectively determine equivalence points in various titrations, showing close results to traditional indicators with significant color changes. It highlights the environmental and health hazards posed by synthetic indicators, advocating for the use of plant-based solutions as a sustainable alternative.










![Titration:
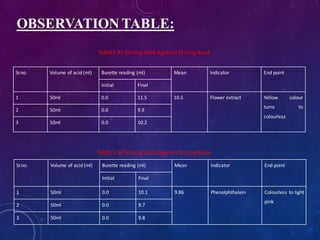
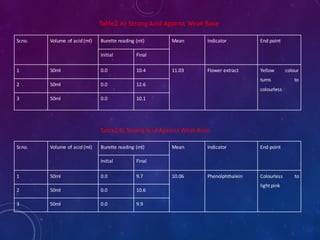
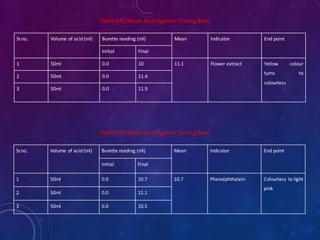
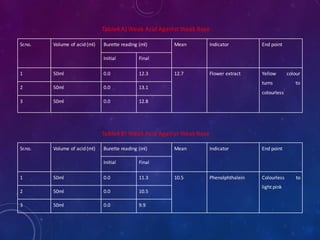
1. Take about 50ml of 1N acid solution in conical flask add 0.1ml of flower extract
as indicator and titrate it agent 1N base solution which is present in burette.
2. All four types of neutralization titration is carry out, strong acid against strong
base[HCl versus NaOH], strong acid against weak base[HCl versus NaHCO3],
weak acid against strong base[CH3COOH versus NaOH], weak acid against weak
base[CH3COOH versus NaHCO3].
3. The trials were repeated 3 times to check the precision.
4. Repeat the titration by using phenolphthalein indicator as standard
5. The results obtained were compared with the results of titrations using the flower
extract indicator.
6. The end points of the titrations using the extract were reached when colour
changed from yellow to light pink](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/naturalindicator-191230113822/85/Natural-Indicator-Preparation-11-320.jpg)