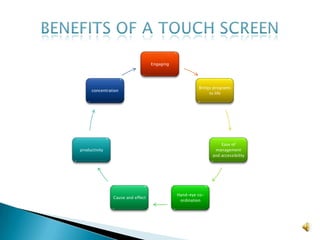
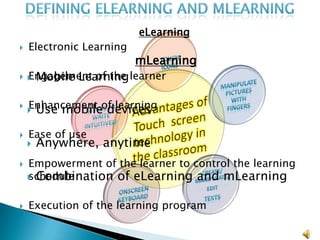
This document discusses touch screen technology and its uses in education. It describes different types of touch screen devices like interactive whiteboards, tablets, and smart tables. The benefits of touch screens in the classroom are outlined, such as enabling individual and collaborative work, and appealing to students. Pedagogical approaches like active learning are discussed. Legal and copyright issues are also mentioned. Finally, links to other subjects like English, math, and science are provided.