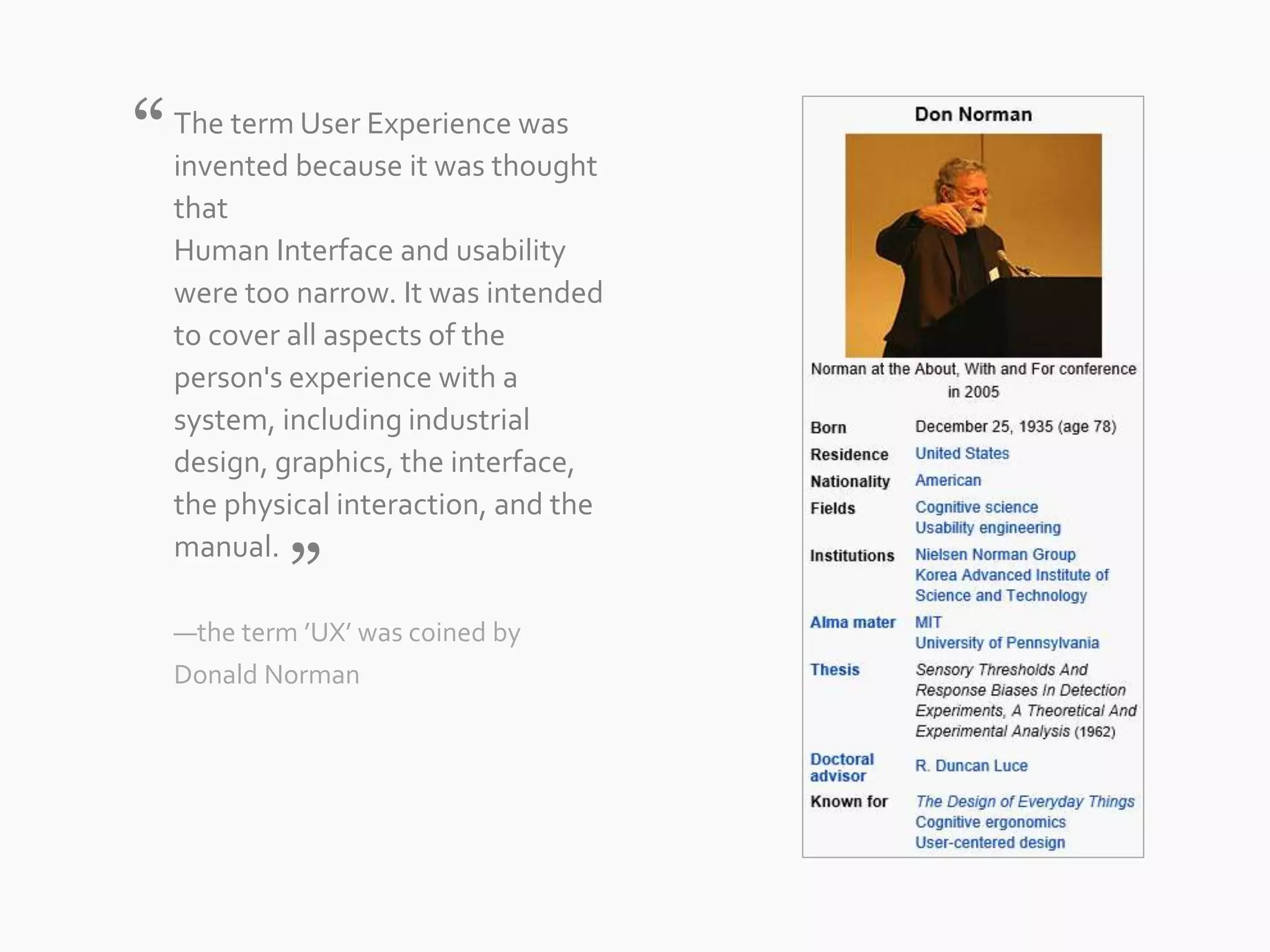
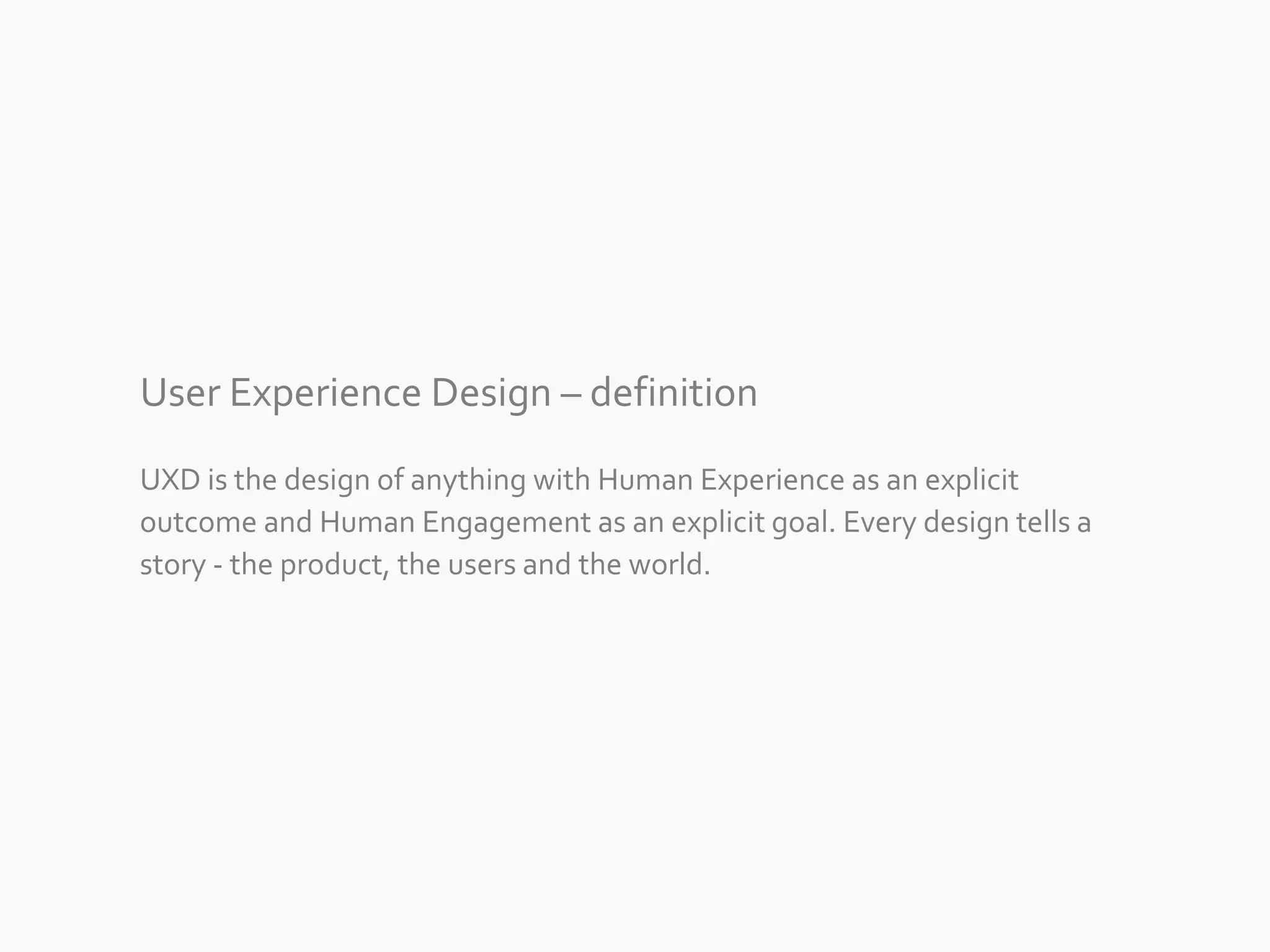
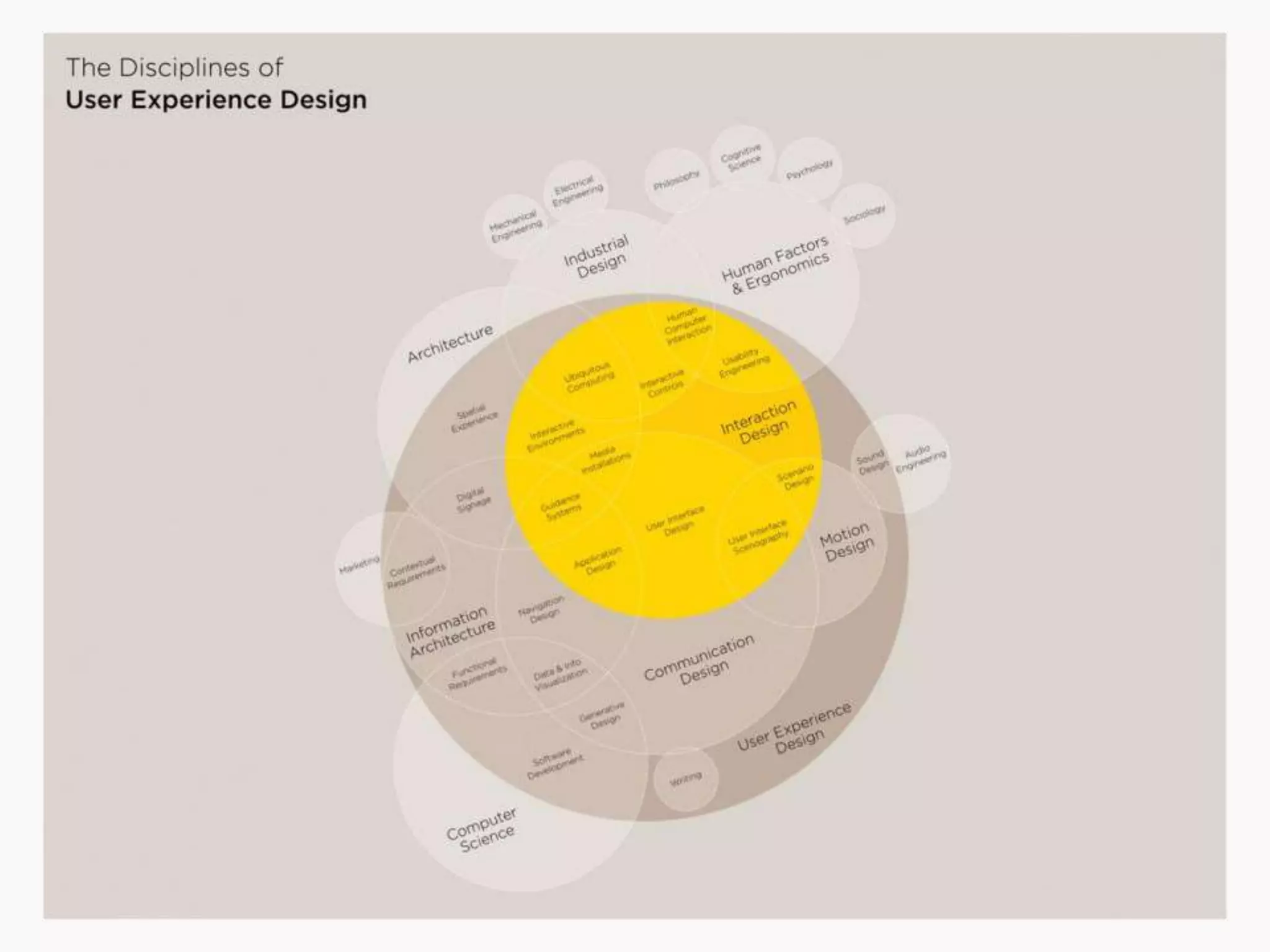
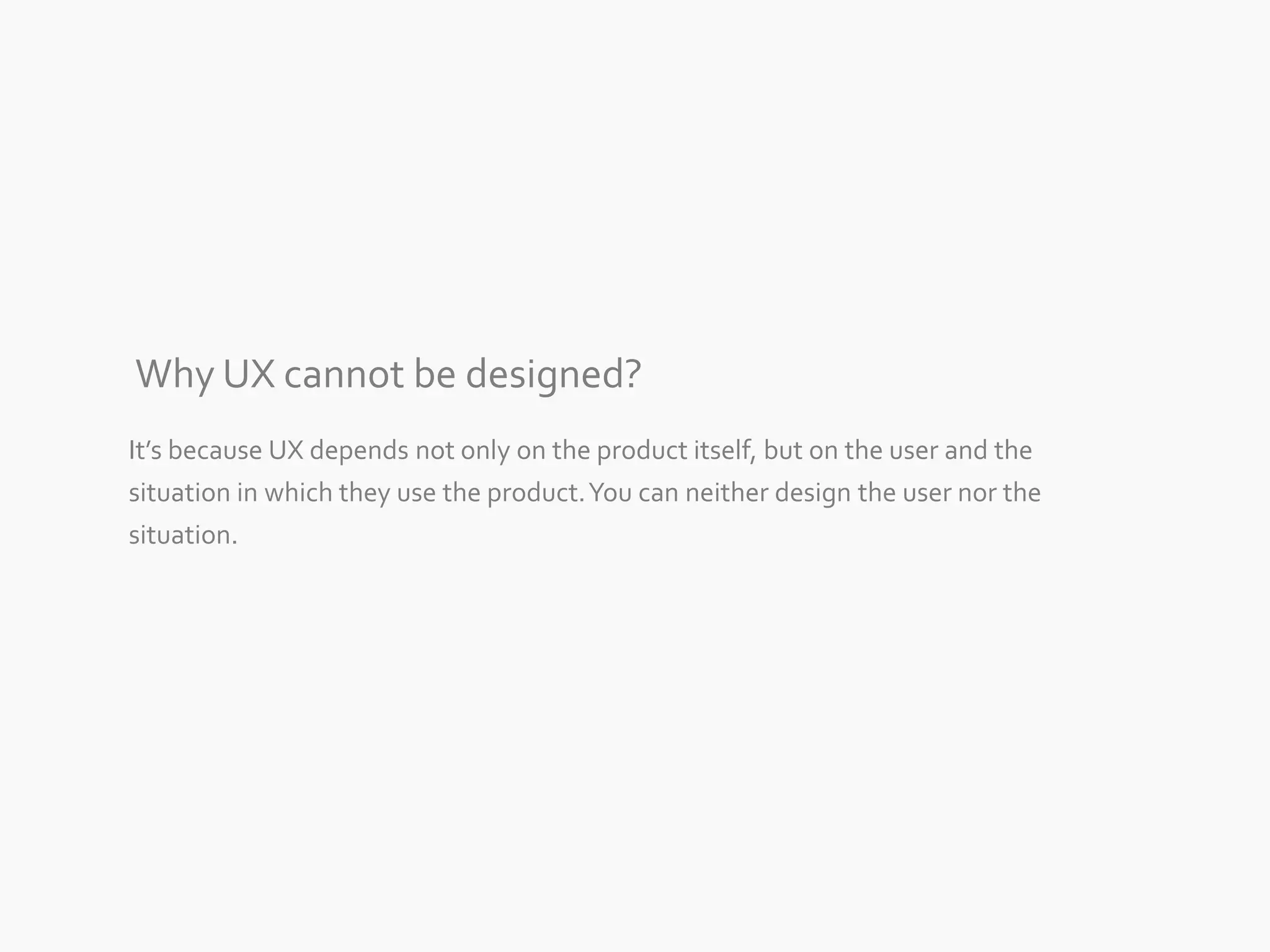
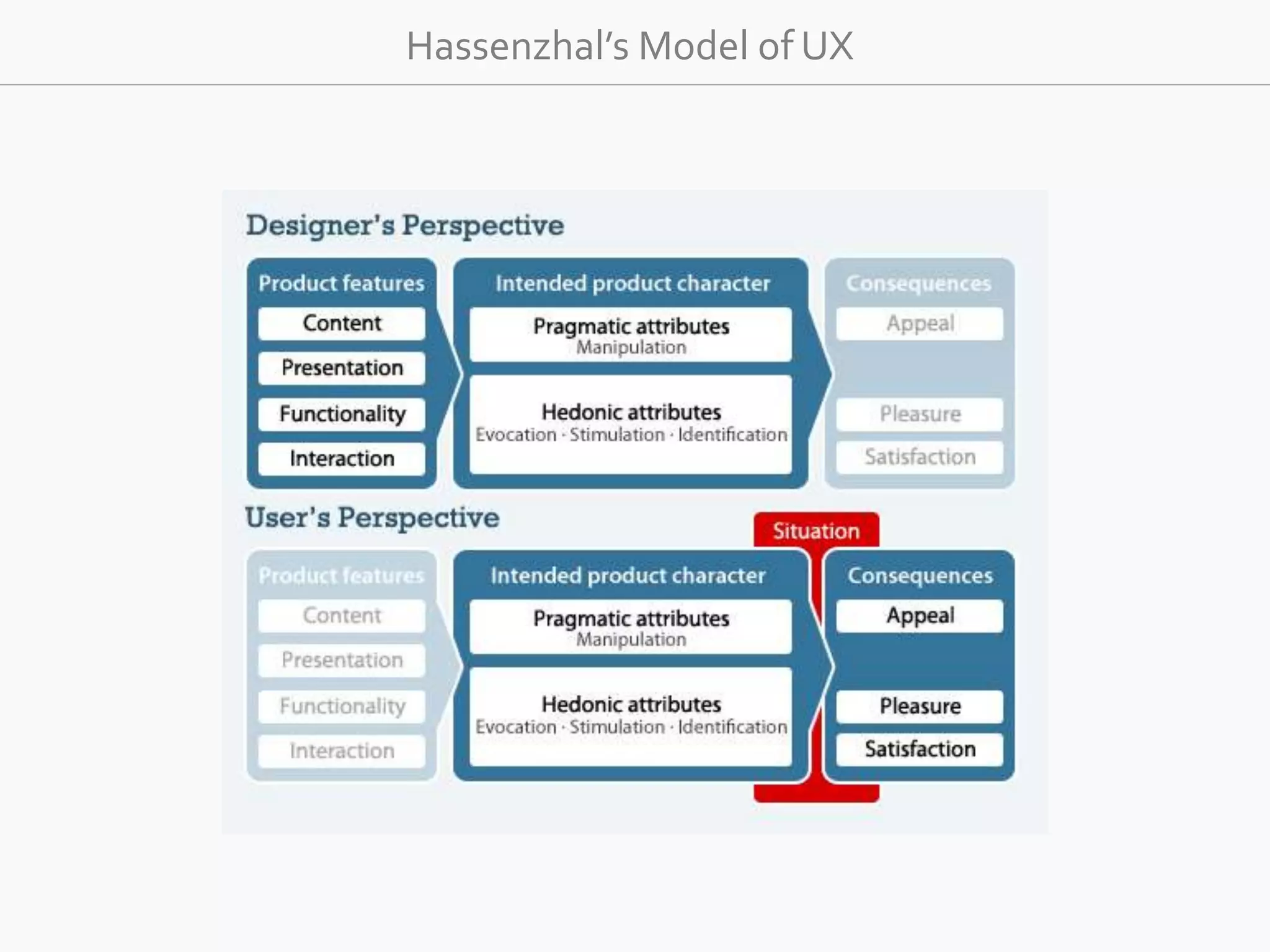
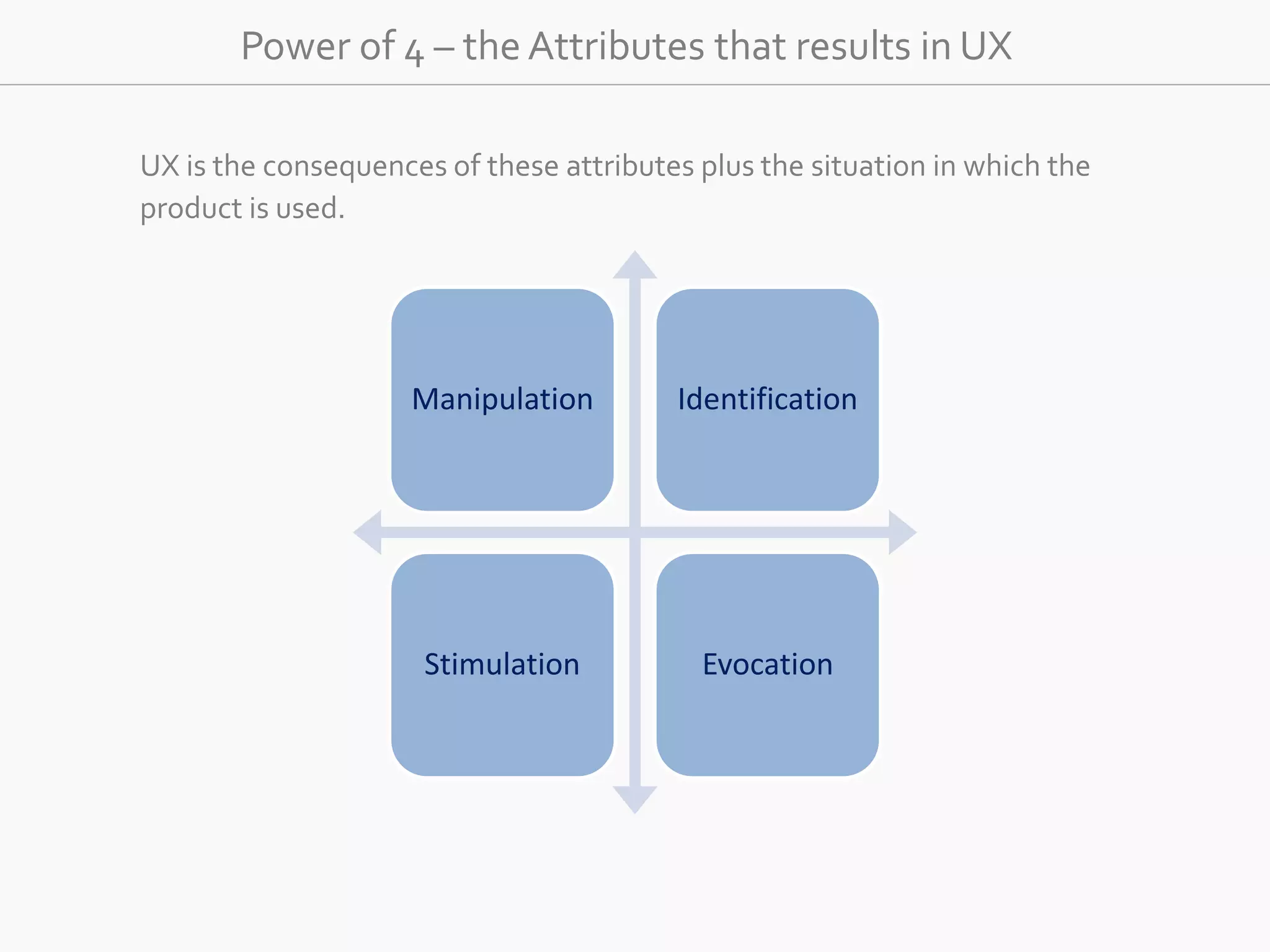
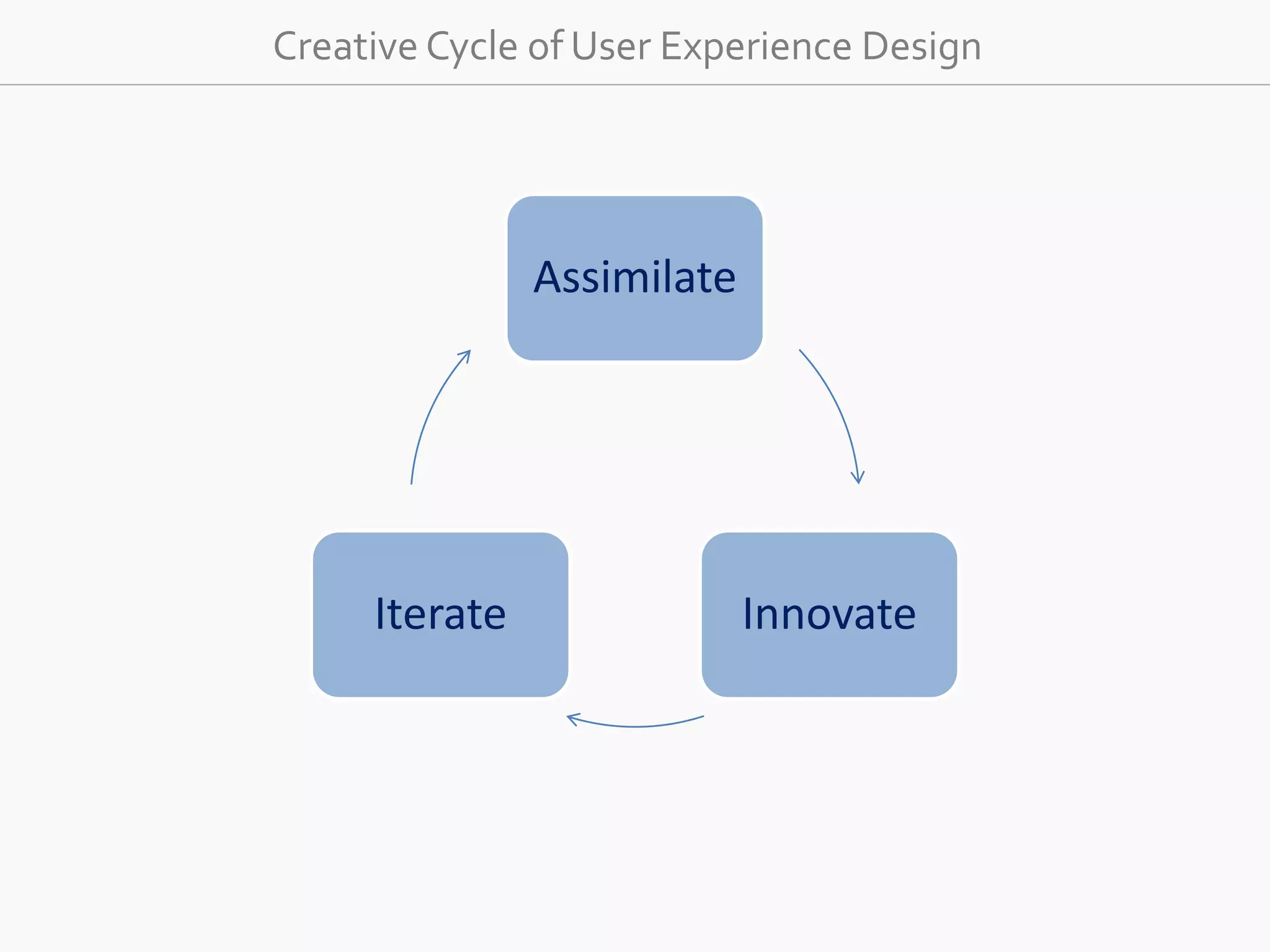
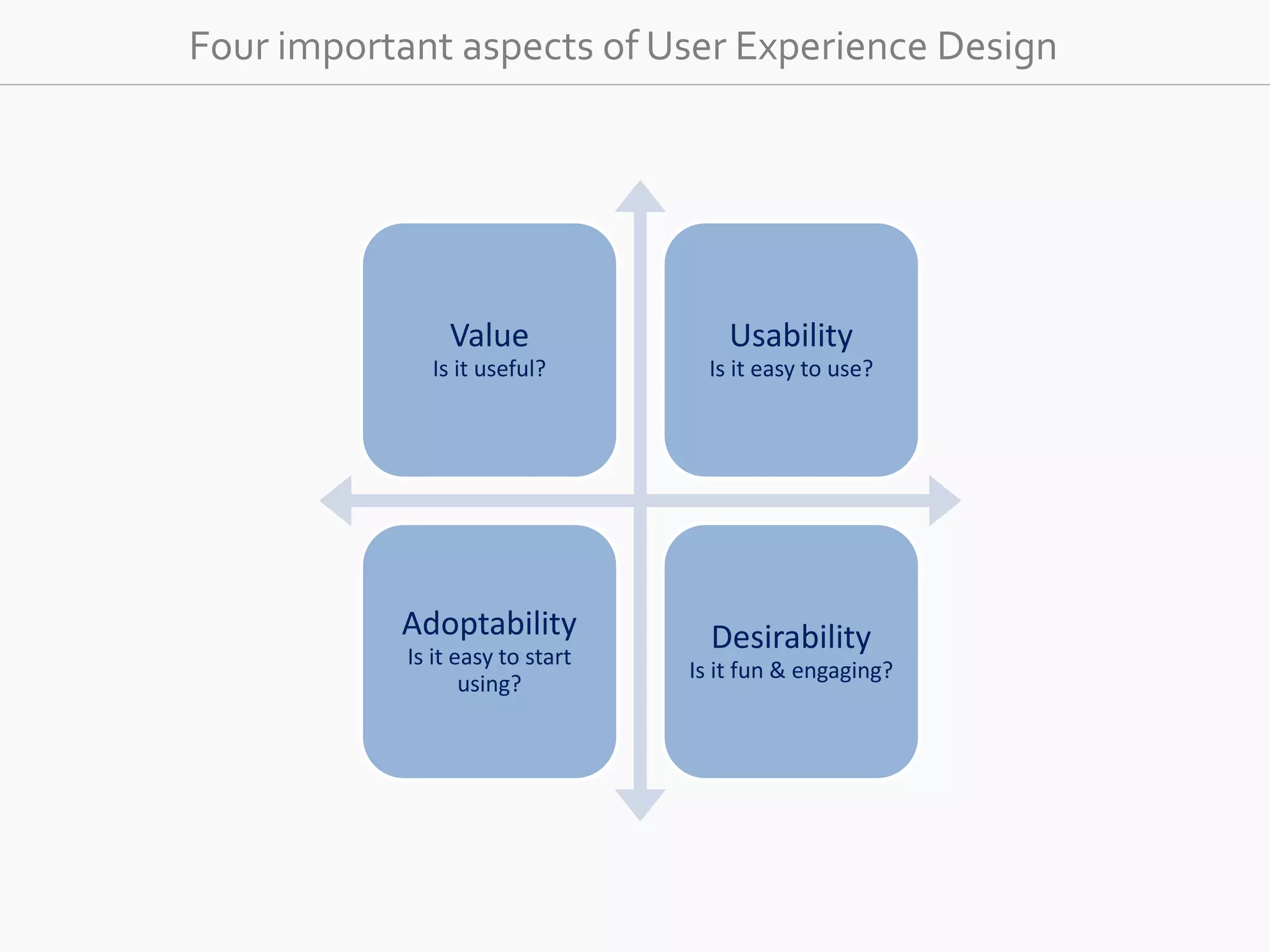
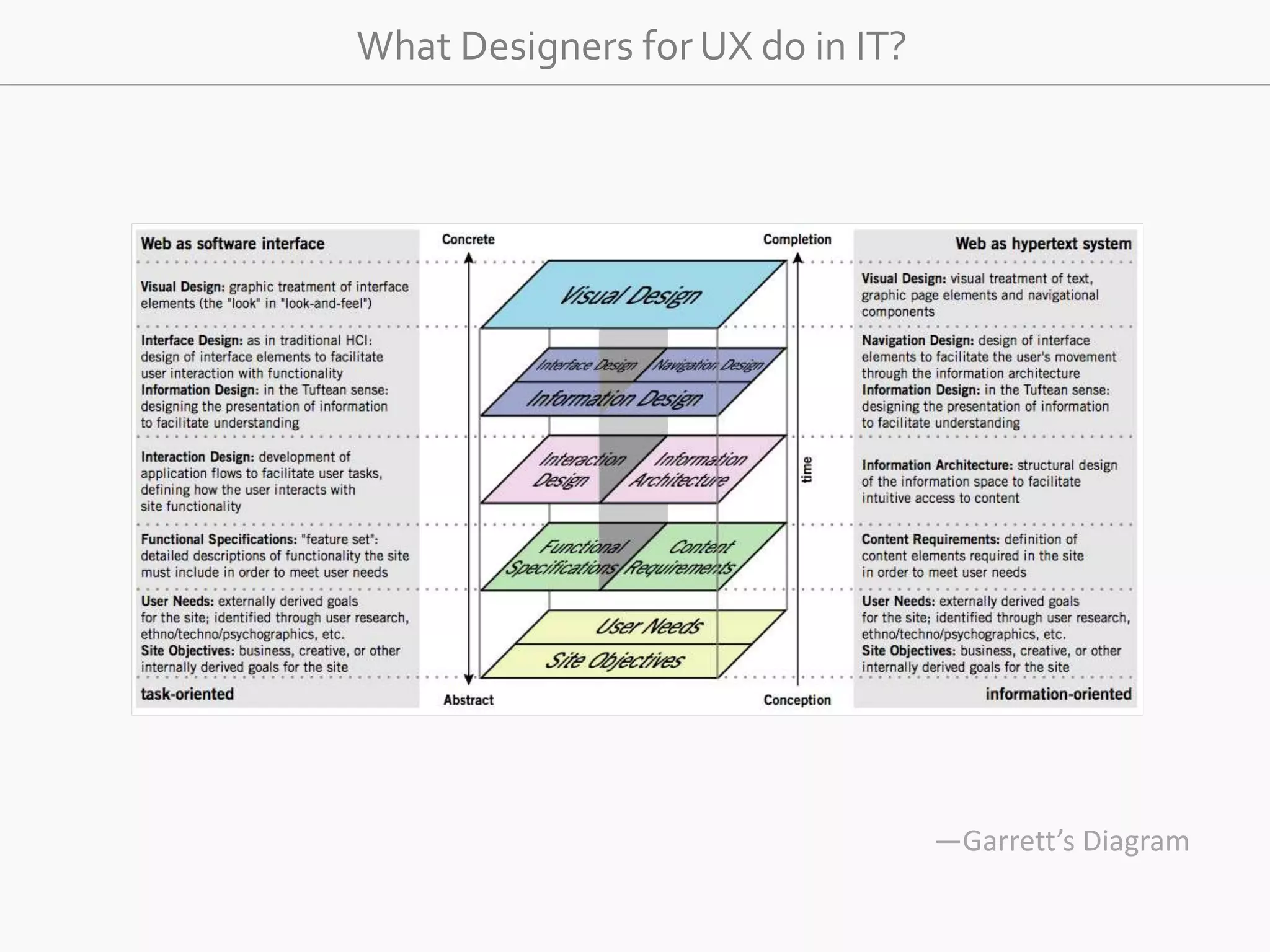
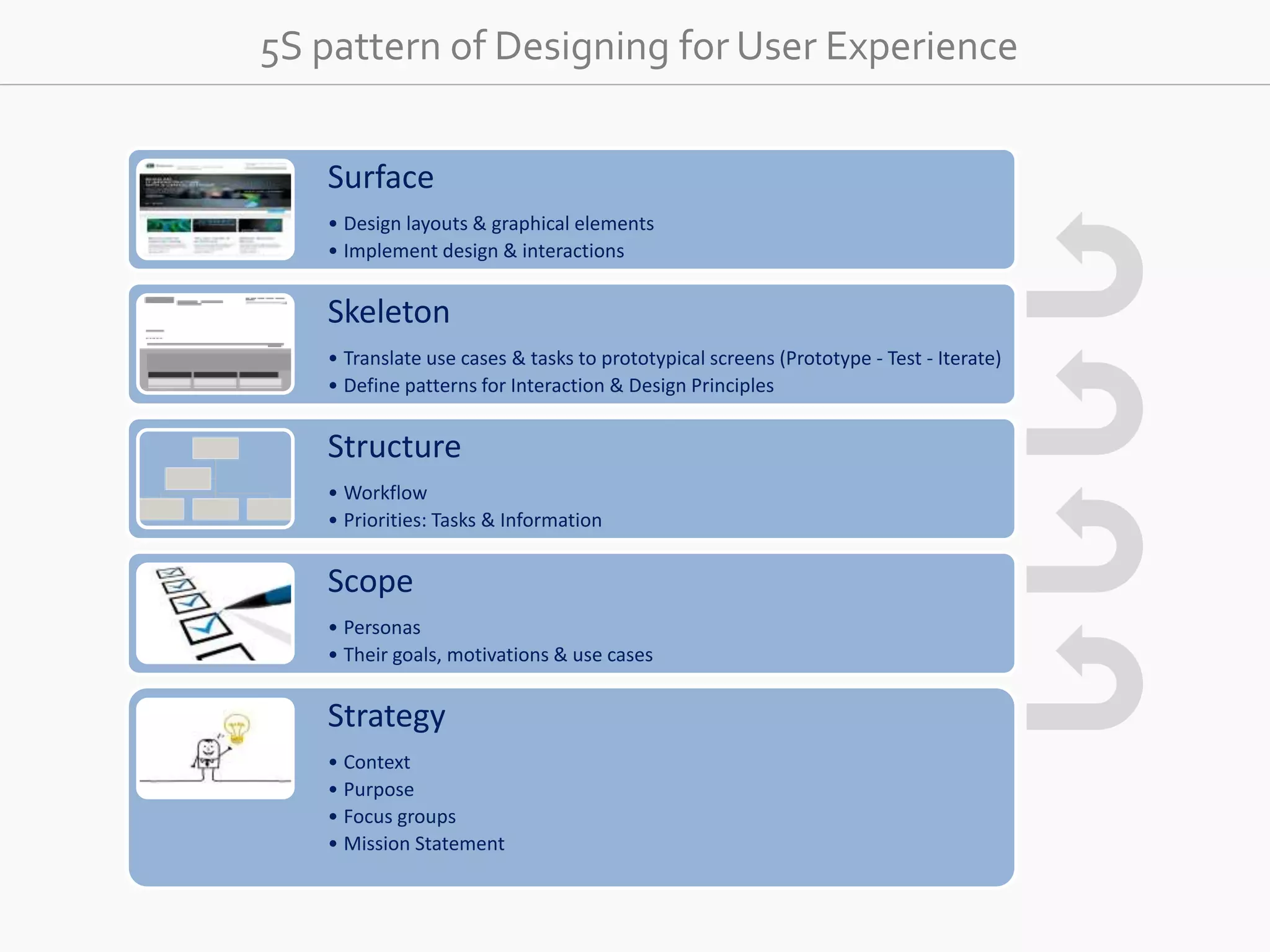
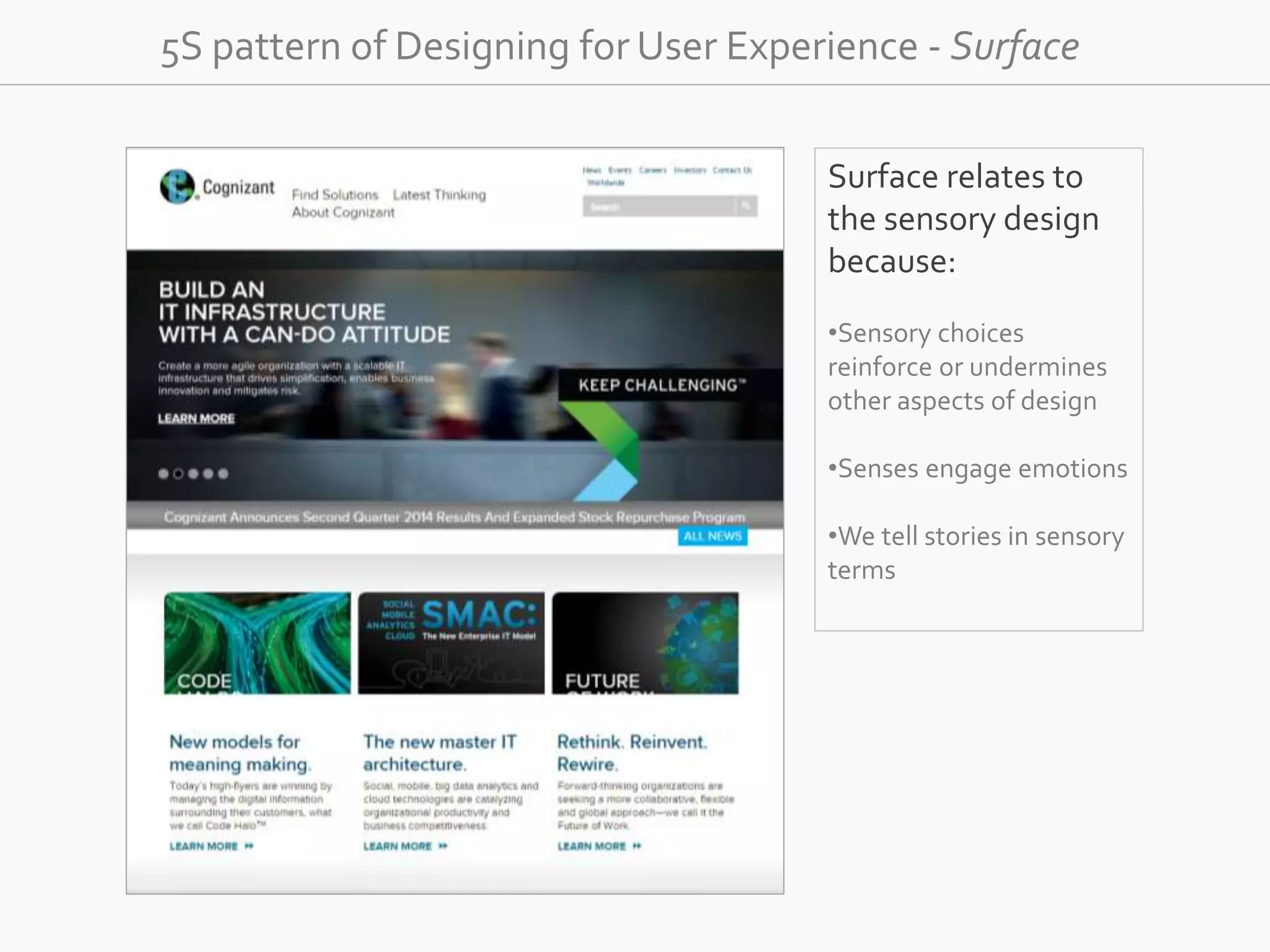
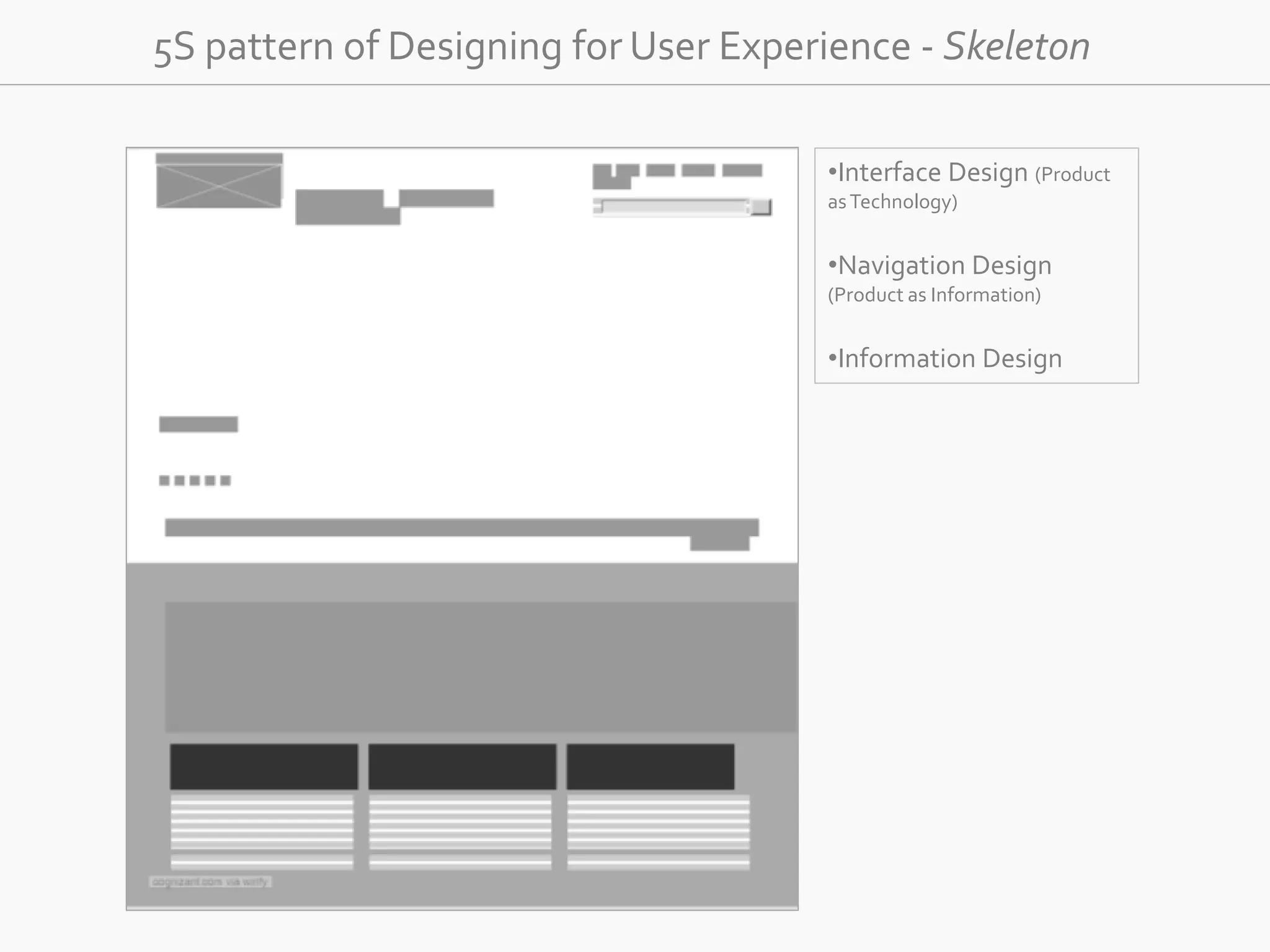
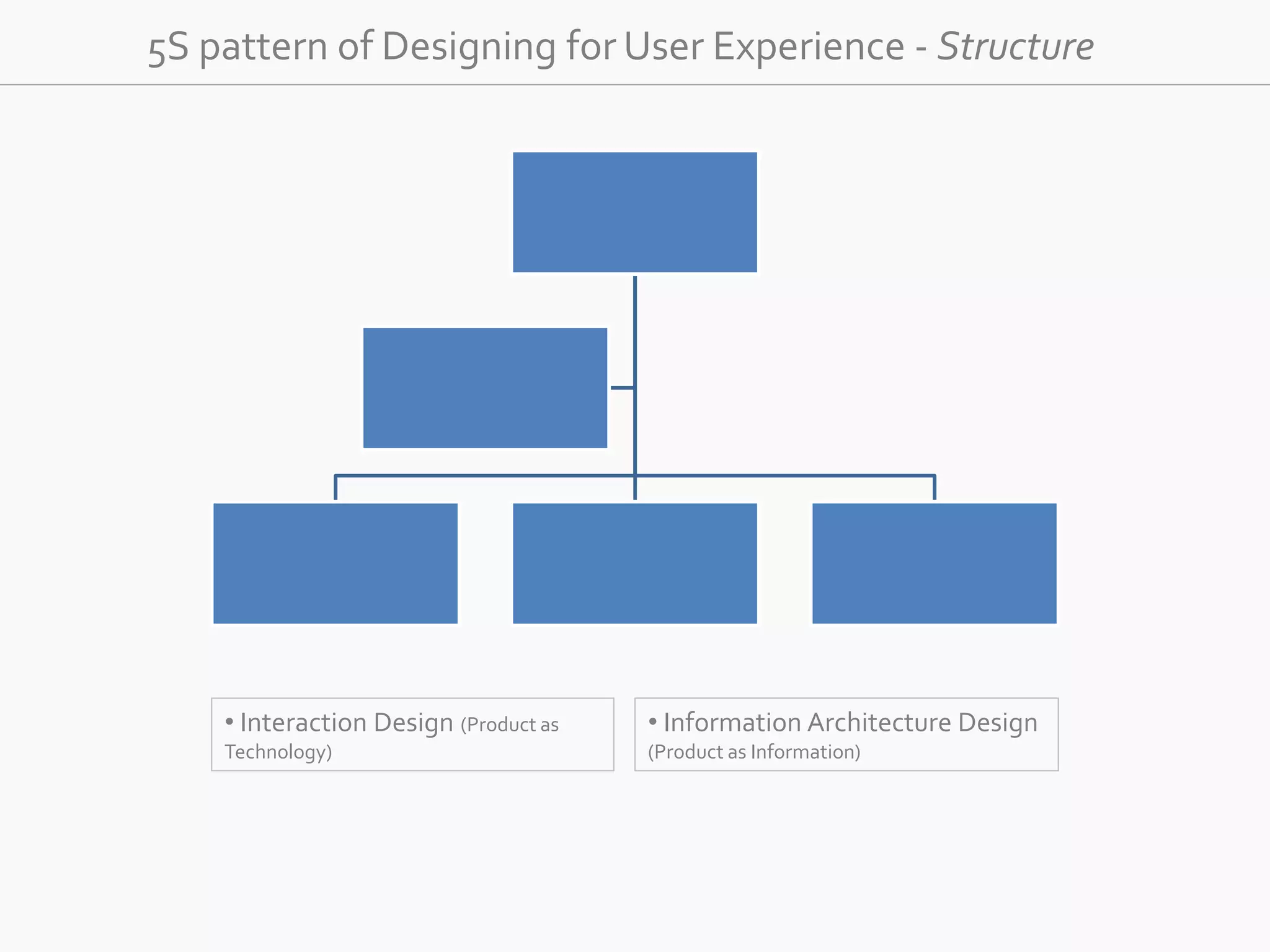
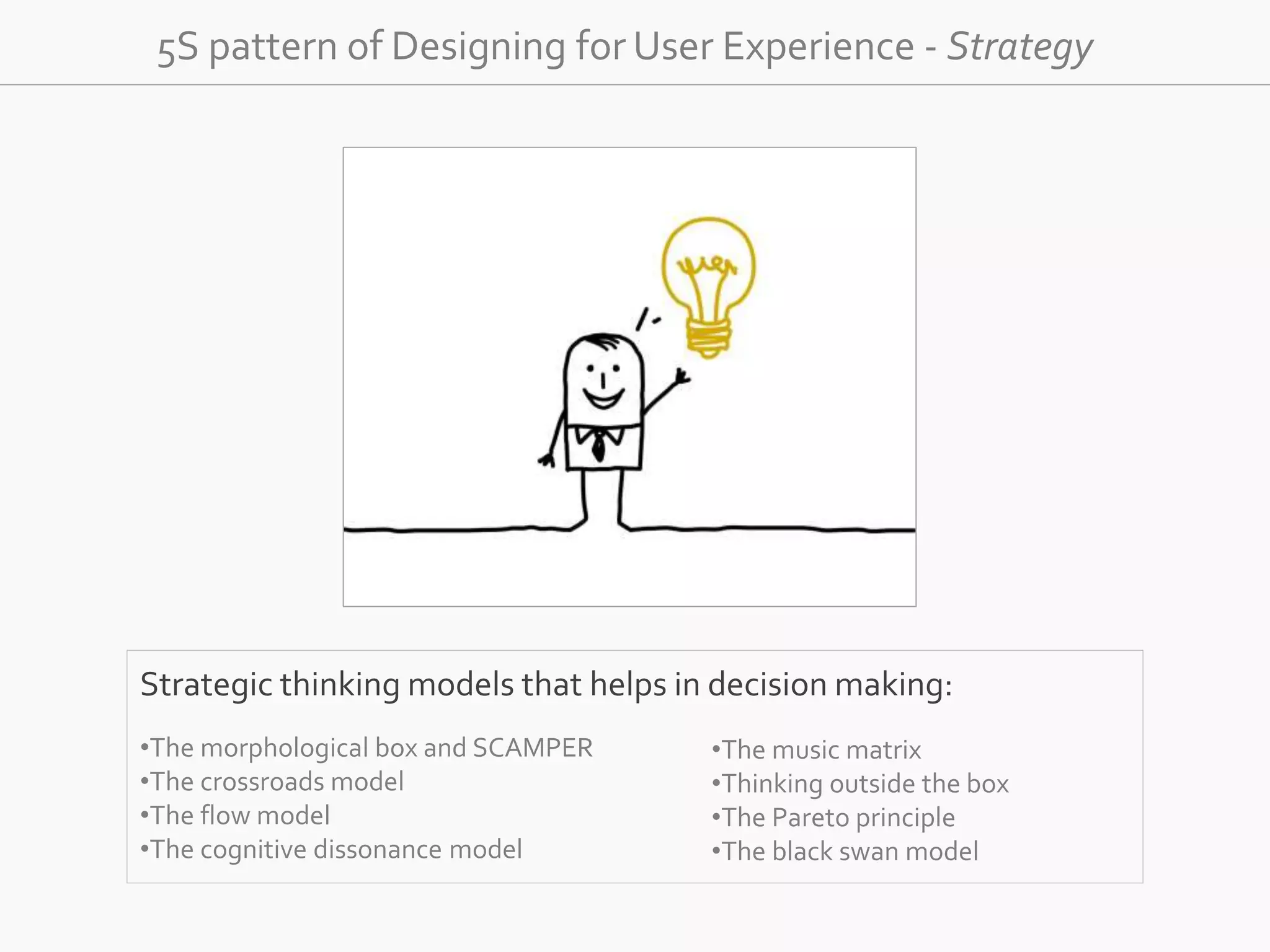
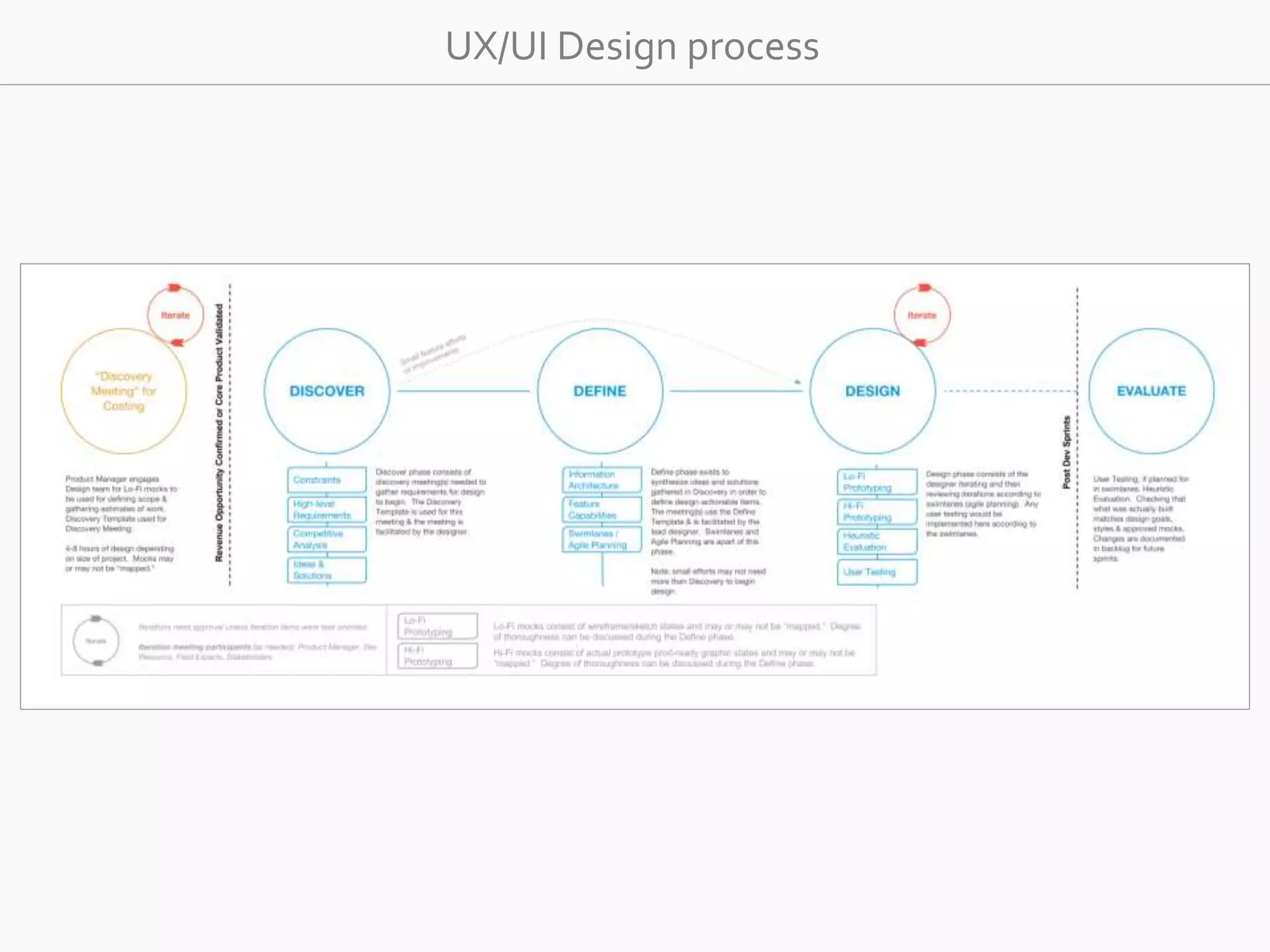
The document discusses the evolution of user experience design (UXD), emphasizing that it encompasses more than just aesthetics—it includes the user's interactions, emotions, and context. It highlights the difference between designing for UX versus designing UX itself, focusing on various factors that affect user engagement and satisfaction. The document outlines key principles and processes involved in UXD, advocating for a user-centered approach that aligns product design with human needs and experiences.