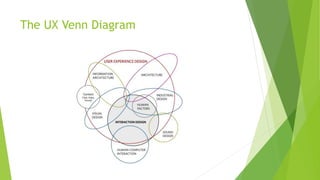
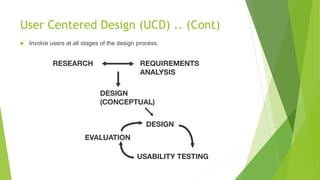
This document discusses the science behind good user experiences (UX) and user interfaces (UI). It defines UX as involving a person's behaviors, attitudes, and emotions about using a product, while defining UI as the space where interactions between humans and machines occur. The document notes that 95% of websites fail at UX despite good UI. It outlines key aspects of UX like user-centered design, design principles, the hierarchy of user needs, and provides tips for creating good UIs and UXs like planning extensively, knowing the user, and making the experience fun and understandable.