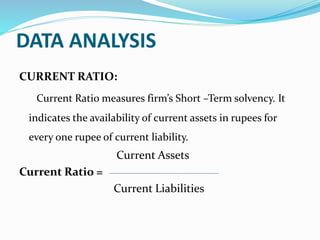
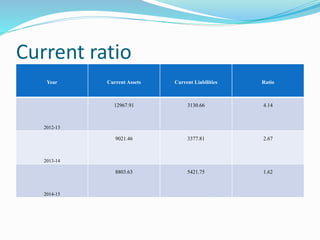
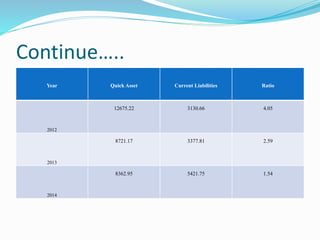
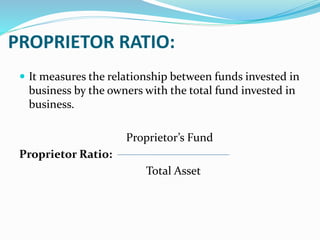
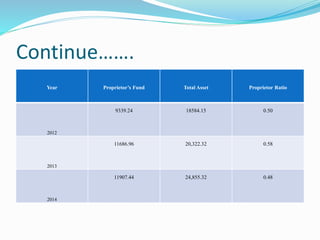
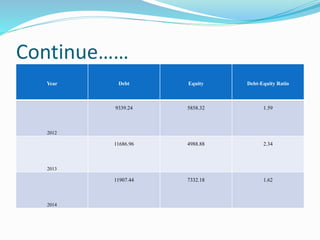
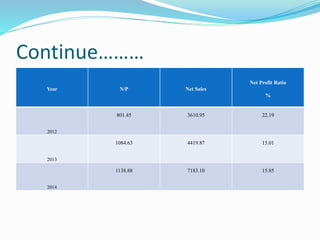
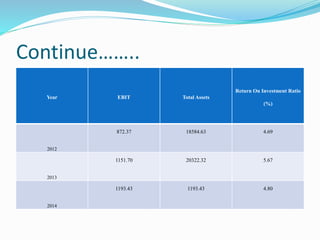
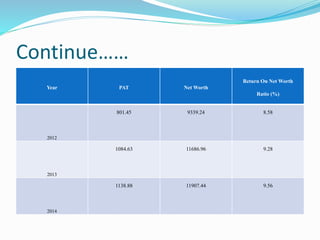
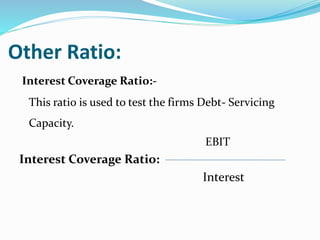
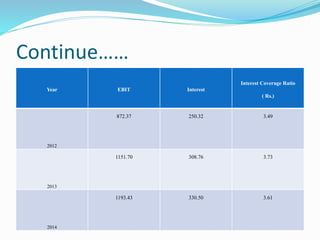
This document analyzes financial ratios for Reliance Infrastructure Limited over three fiscal years. It calculates and interprets ratios related to liquidity, leverage, activity and profitability. Key findings include a declining current ratio, increasing operating expenses, fluctuating proprietary ratio, and adequate interest coverage. Overall, the analysis concludes Reliance Infrastructure's financial condition is good, though it could diversify funds across sectors for stability in changing markets.