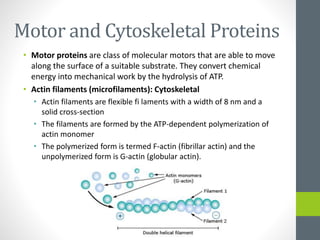
1. Muscle is composed of excitable cells called muscle fibers that contain contractile filaments of actin and myosin which allow the cell to change shape.
2. Muscle fibers are classified as skeletal, smooth, or cardiac muscle depending on their structure and location in the body.
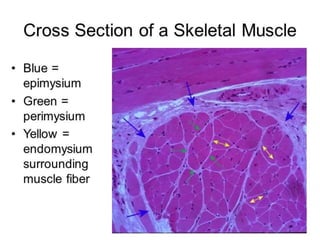
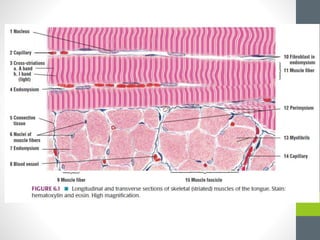
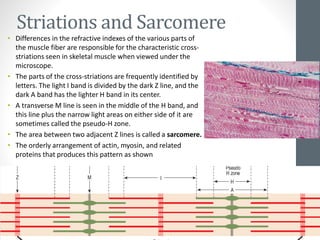
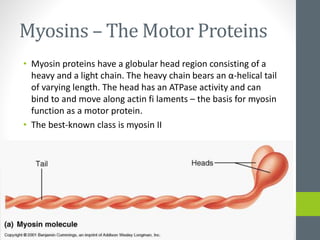
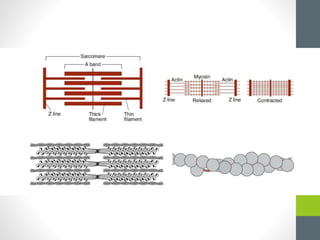
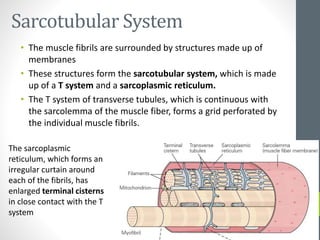
3. Skeletal muscle fibers are long, cylindrical, and multinucleated, containing repetitive contractile units called sarcomeres made up of bands of actin and myosin proteins.