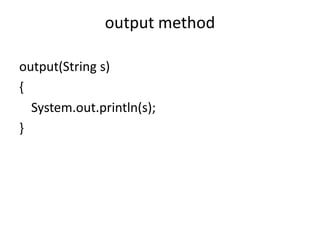
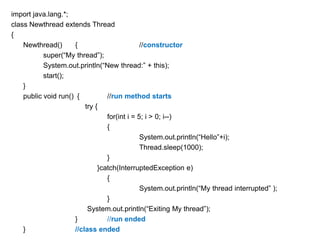
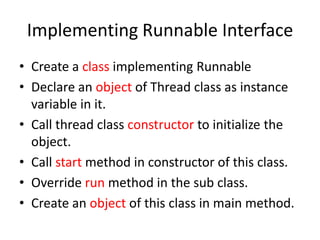
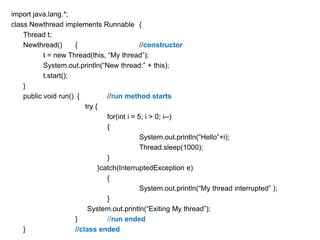
A multithreaded program allows two or more parts of the same program, called threads, to run concurrently. Each thread defines a separate path of execution and threads are lightweight processes that can run independently and share resources such as memory. The document discusses thread creation in Java using the Thread class and Runnable interface, thread life cycle and states, thread priorities, synchronization, and interthread communication using wait(), notify(), and notifyAll() methods.




![class threaddemo {
public static void main(String []args)
{
new Newthread();
// create new thread
try {
for (int i = 1;i<=5;i++)
{
System.out.println(“Main thread “ +i);
Thread.sleep(1000);
}
} cacth(InterruptedException e)
{
System.out.println(“Main thread
interrupted”);
}
System.out.println(“Main thread exiting”);
}
// main ends
} // class ends](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/multithreadedprogramming-140116080930-phpapp01/85/Multithreaded-programming-9-320.jpg)
![class threaddemo {
public static void main(String []args)
{
new Newthread();
// create new thread
try {
for (int i = 1;i<=5;i++)
{
System.out.println(“Main thread “ +i);
Thread.sleep(1000);
}
} cacth(InterruptedException e)
{
System.out.println(“Main thread
interrupted”);
}
System.out.println(“Main thread exiting”);
}
// main ends
} // class ends](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/multithreadedprogramming-140116080930-phpapp01/85/Multithreaded-programming-12-320.jpg)


![class Callme {
// prints [msg] if not interrupted
void call(String msg)
{
print(“*“ + msg);
try
{
Thread.sleep(1000);
}catch(InterruptedException e)
{
println(“Interrupted”);
}
println(“+”);
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/multithreadedprogramming-140116080930-phpapp01/85/Multithreaded-programming-15-320.jpg)

![class synchdemo {
public static void main(String [] args)
{
Callme target = new Callme();
Caller ob1 = new Caller(target, “Hello”);
Caller ob2 = new Caller(target, “New”);
Caller ob3 = new Caller(target, “Day”);
try {
ob1.t.join();
ob2.t.join();
ob3.t.join();
}catch(InterruptedException e)
{
System.out.println(“Interrupted”); }
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/multithreadedprogramming-140116080930-phpapp01/85/Multithreaded-programming-17-320.jpg)







![Main class
class synchpro {
public static void main(String [] args)
{
Que q = new Que();
new producer(q);
new consumer(q);
output(“Press Ctrl + S to stop”);
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/multithreadedprogramming-140116080930-phpapp01/85/Multithreaded-programming-25-320.jpg)