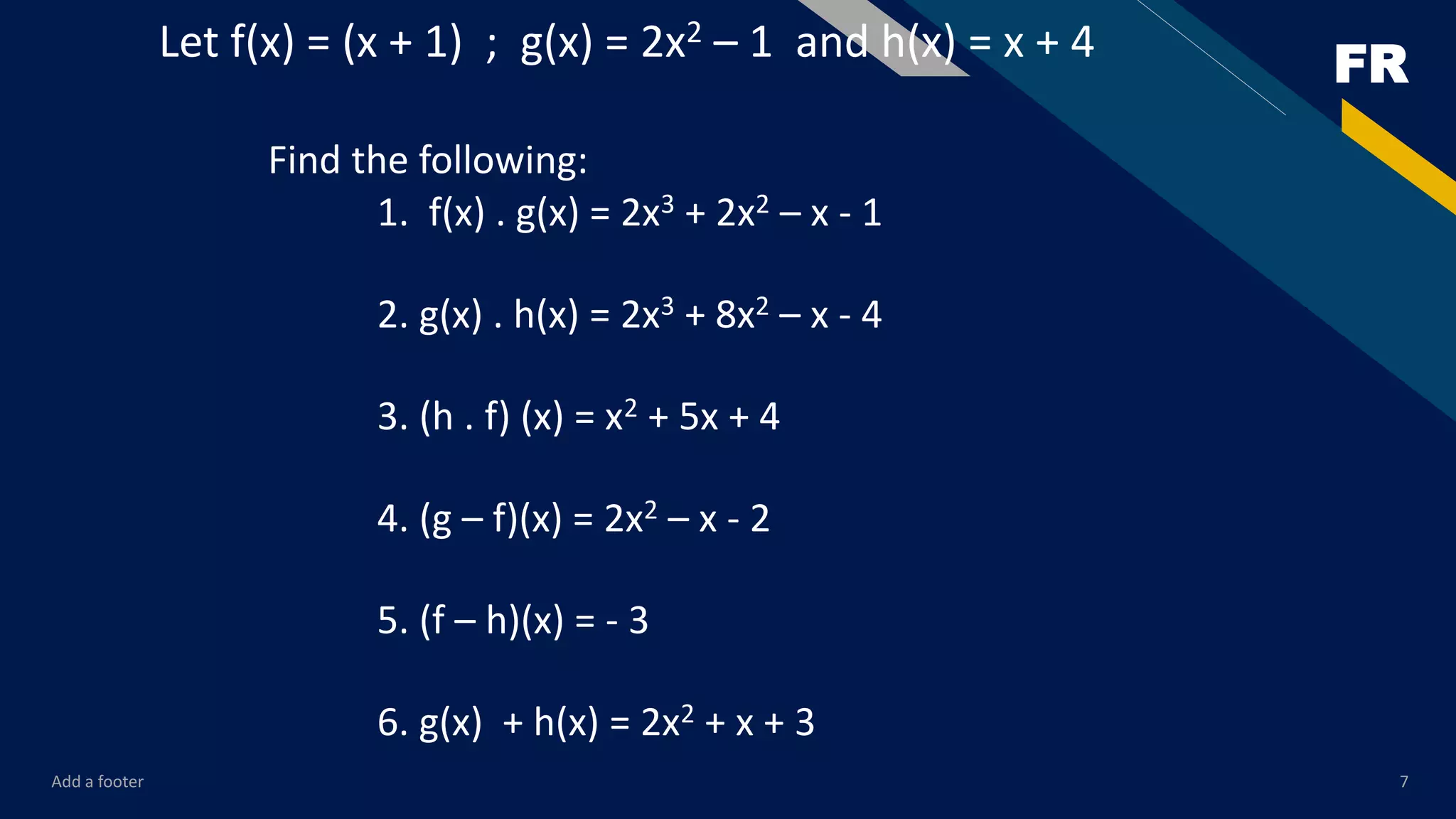Embed presentation
Download to read offline






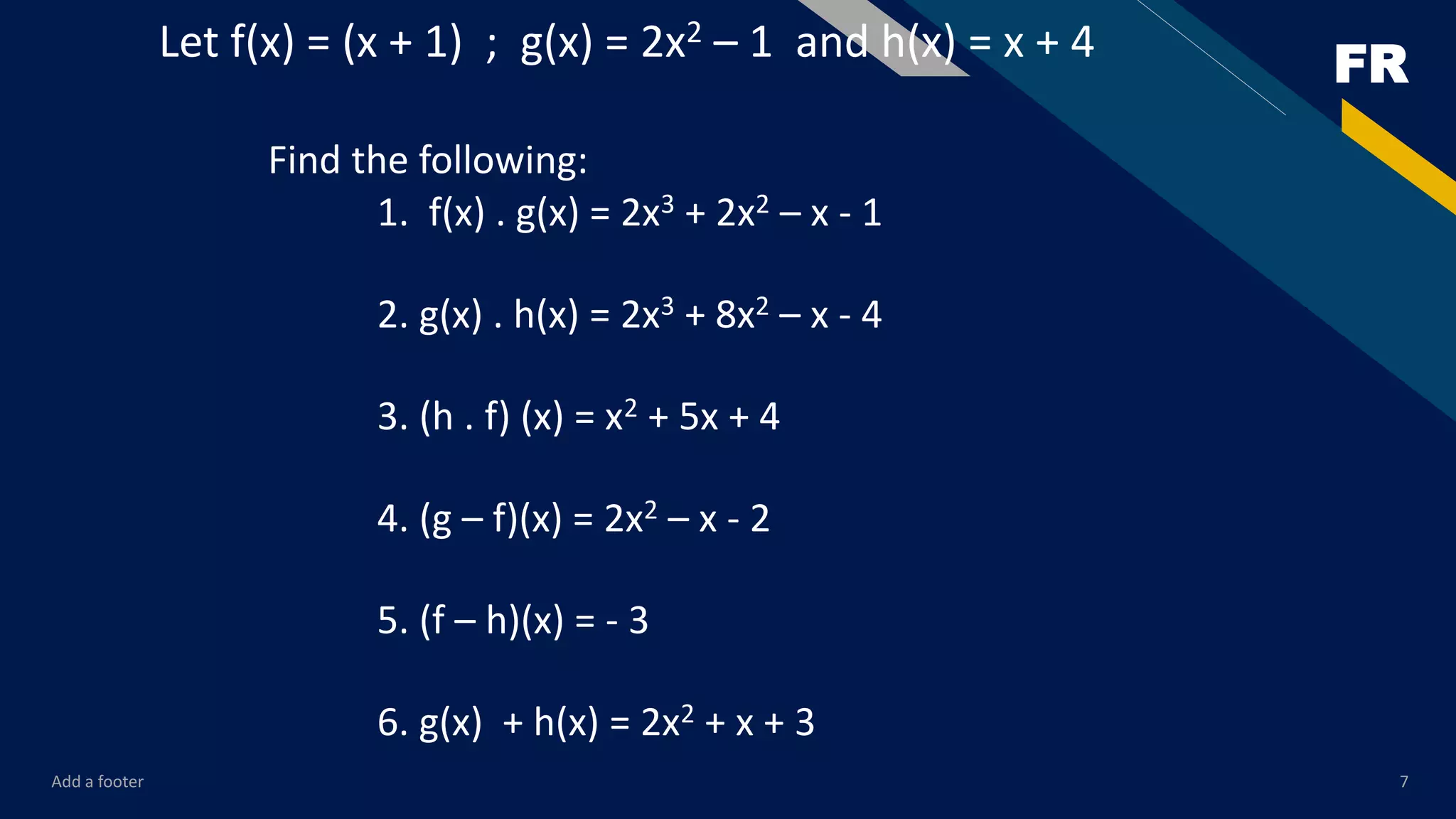


To multiply polynomial functions f and g: 1. Multiply the first term of f with each term of g to get partial products 2. Add the partial products For the given polynomials f(x) = 7x + 1, g(x) = 4x - 7, h(x) = 2x^2 - 3x + 5: (f·g)(x) = 28x^2 - 45x - 7 (h·g)(x) = 8x^3 - 26x^2 + 41x - 35 (f·h)(x) = 14x^3 - 19x^2 + 32x + 5