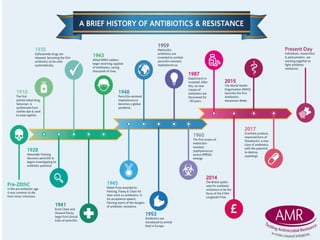
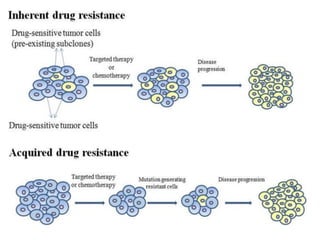
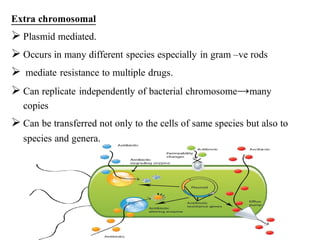
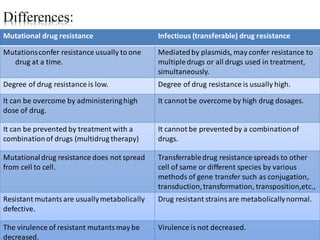
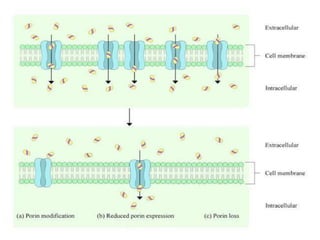
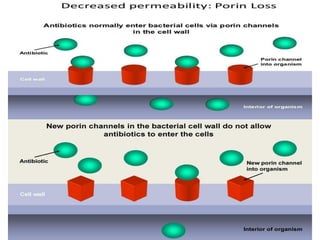
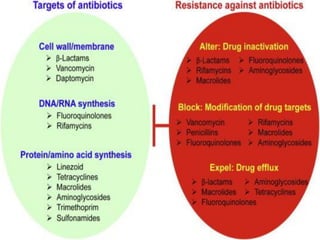
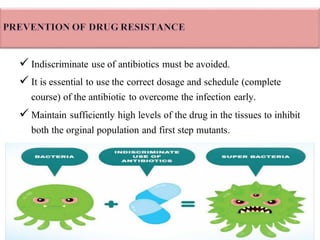
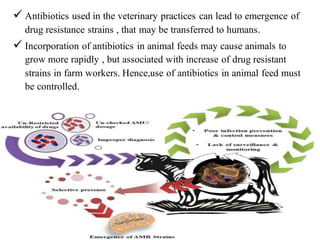
Drug resistance occurs when microbes evolve mechanisms to protect themselves from antimicrobials like antibiotics. There are several mechanisms by which bacteria develop resistance, including limiting drug uptake, modifying drug targets, inactivating drugs, and actively effluxing drugs out of the cell. Resistance can be intrinsic or acquired through genetic mutations or mobile genetic elements that allow resistance genes to spread between bacteria. Prudent antibiotic use and combination therapies can help prevent the emergence and spread of drug-resistant bacteria.