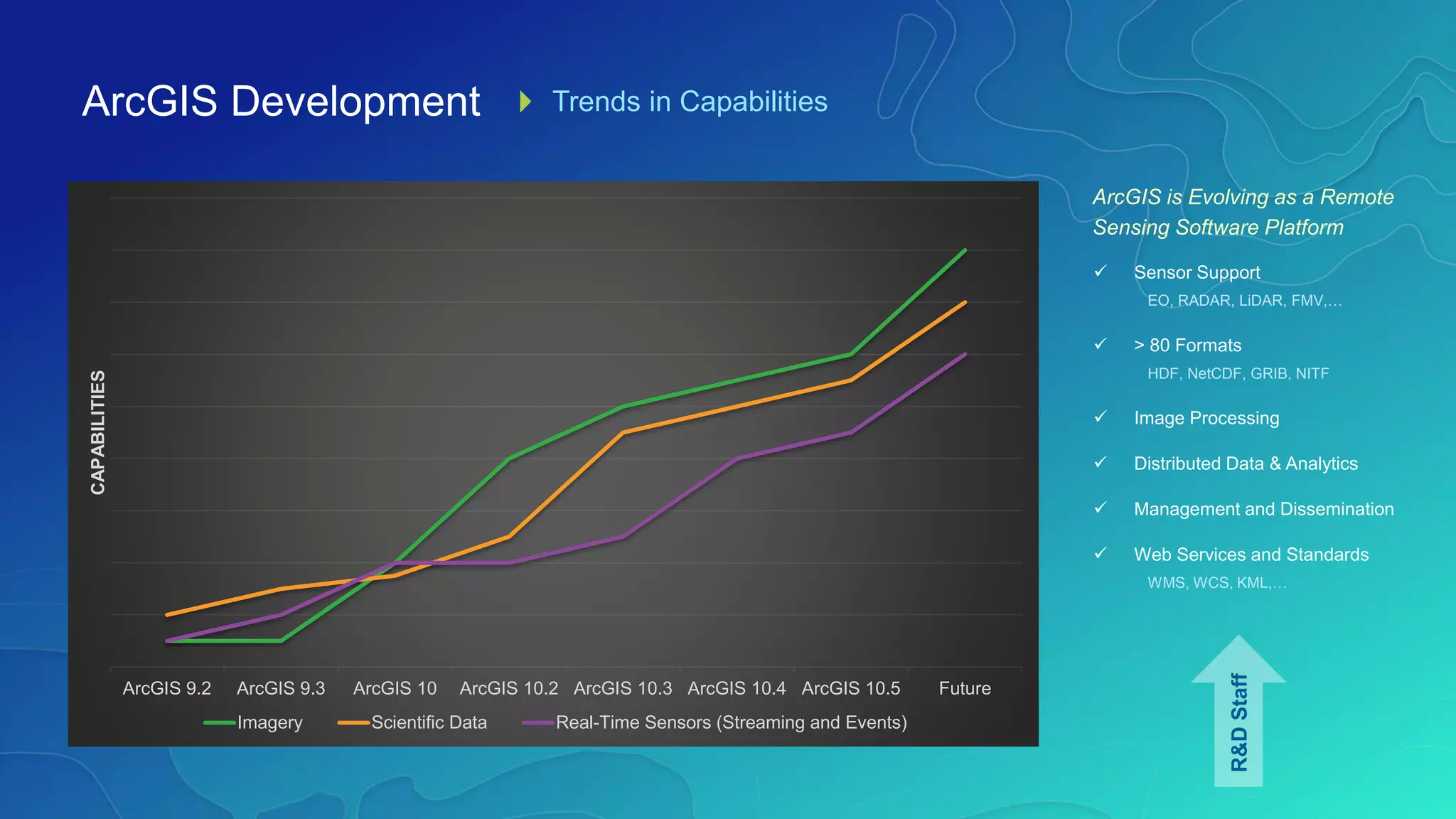
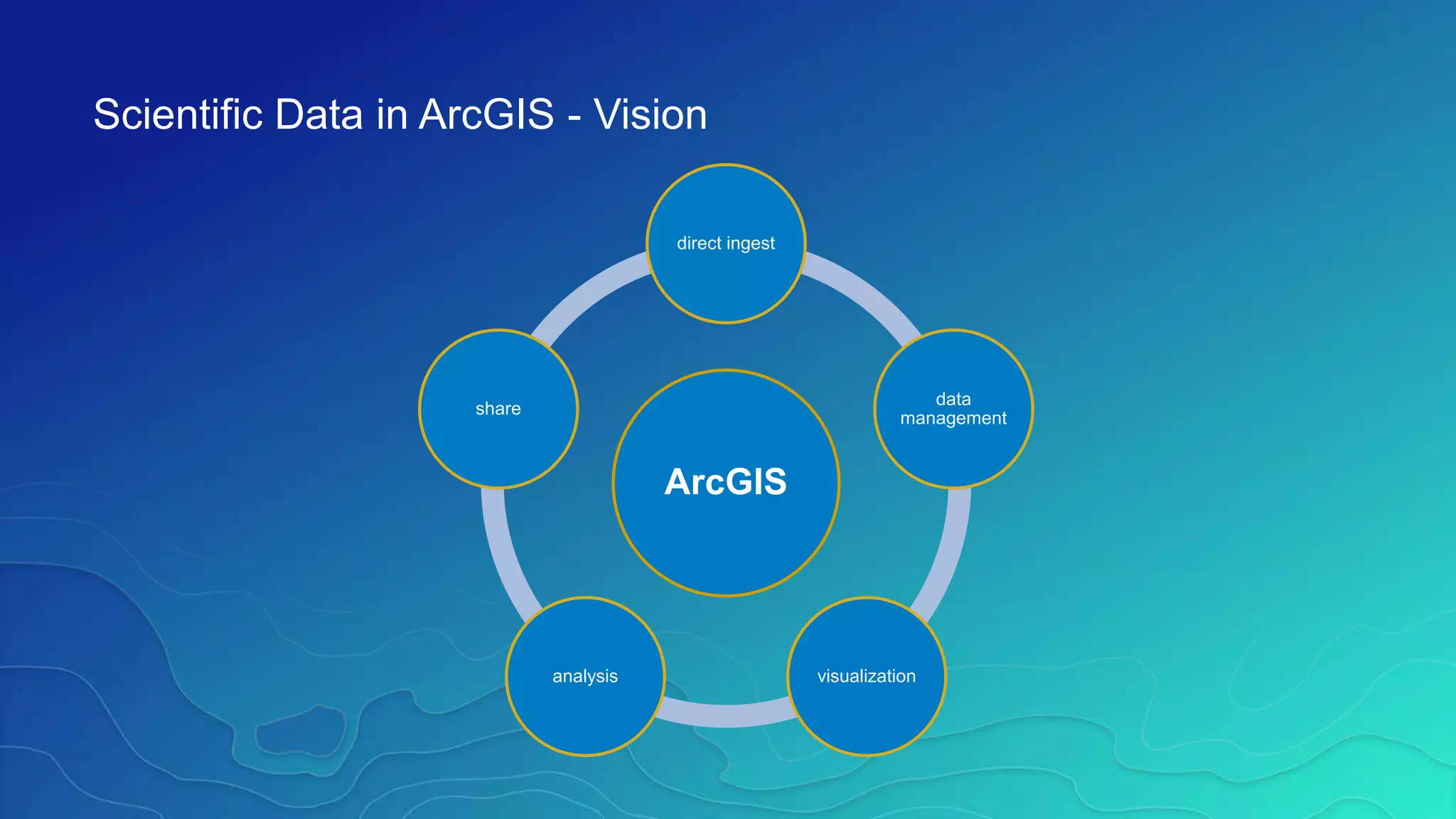
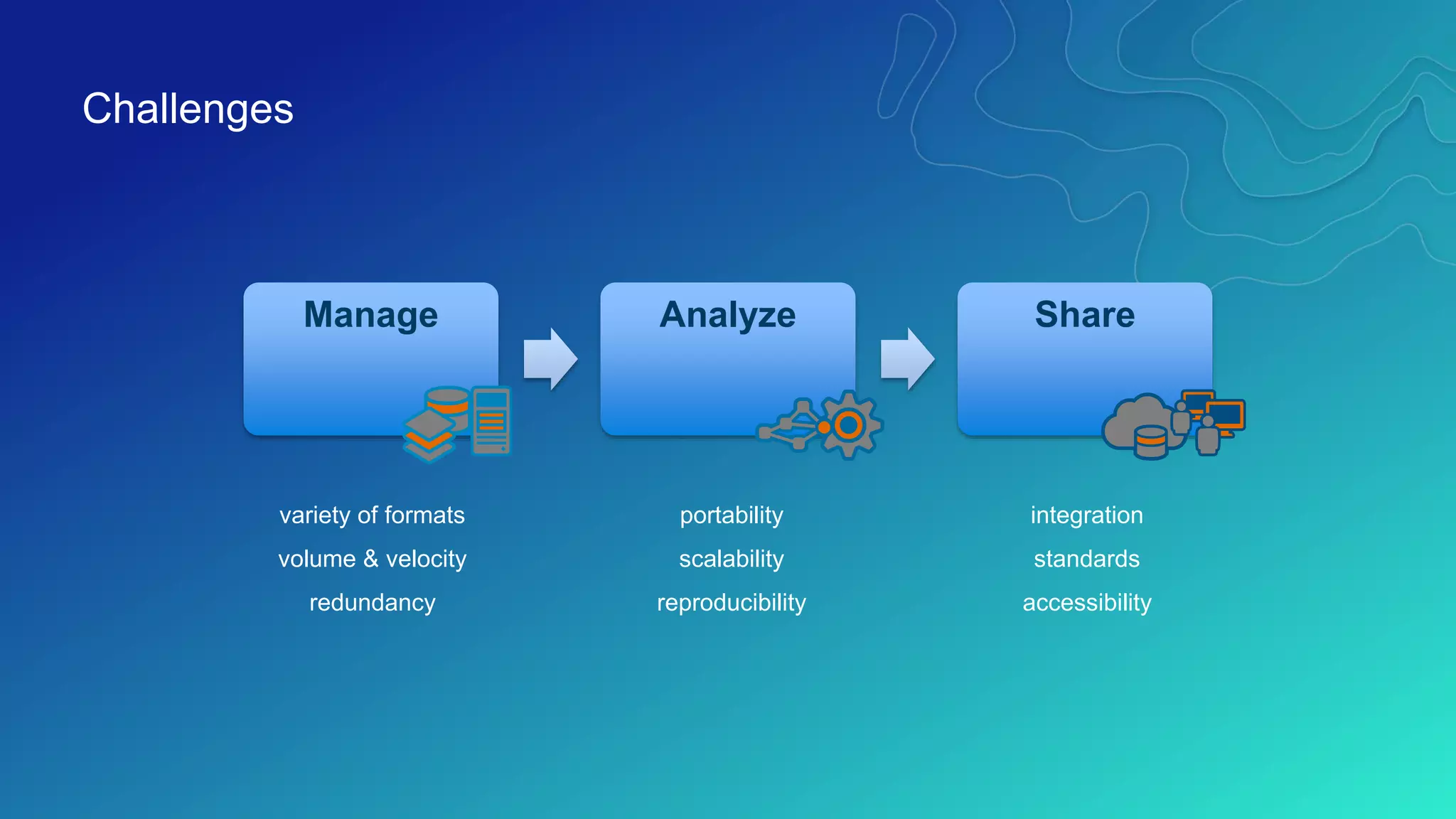
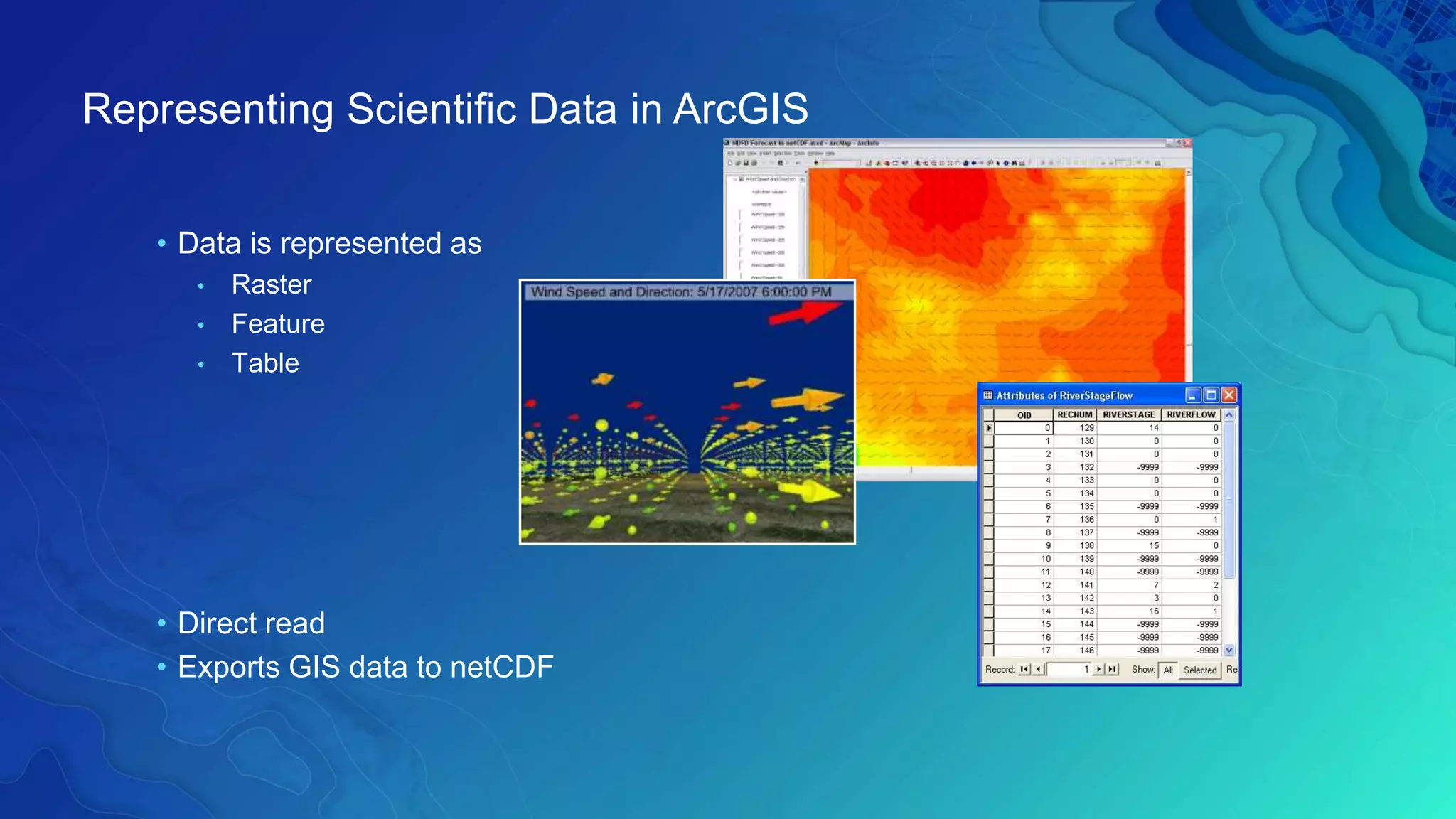
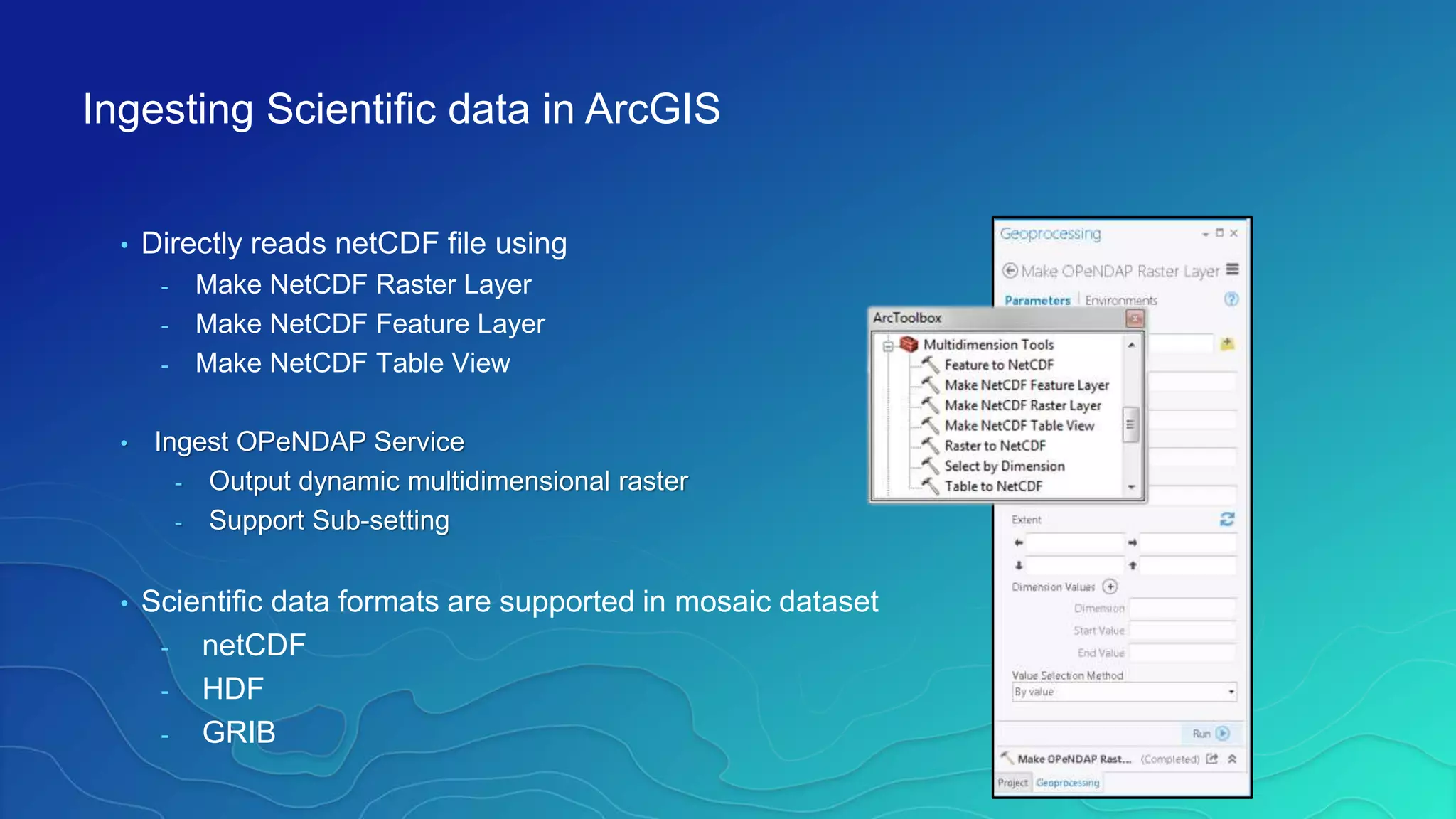
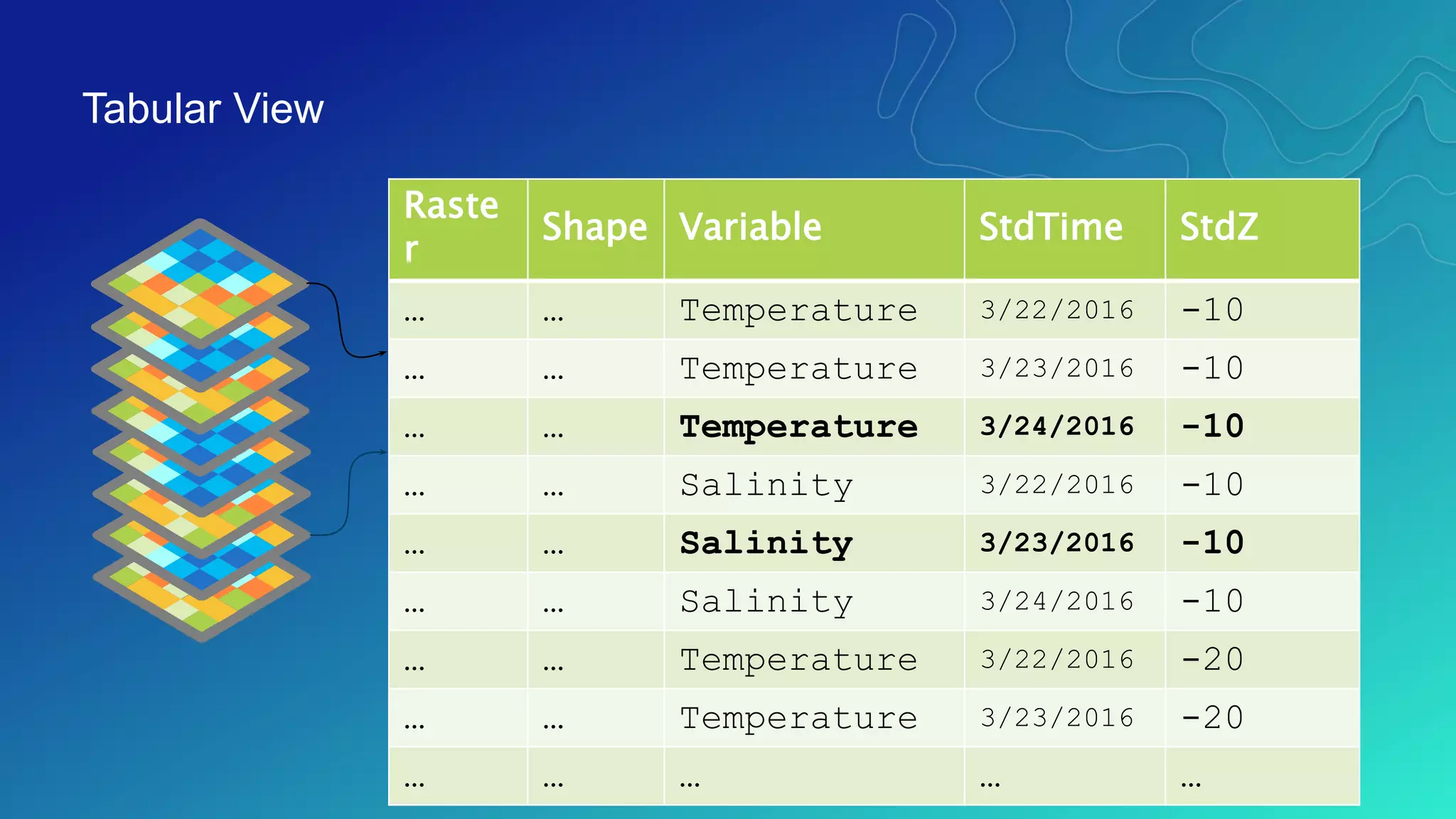
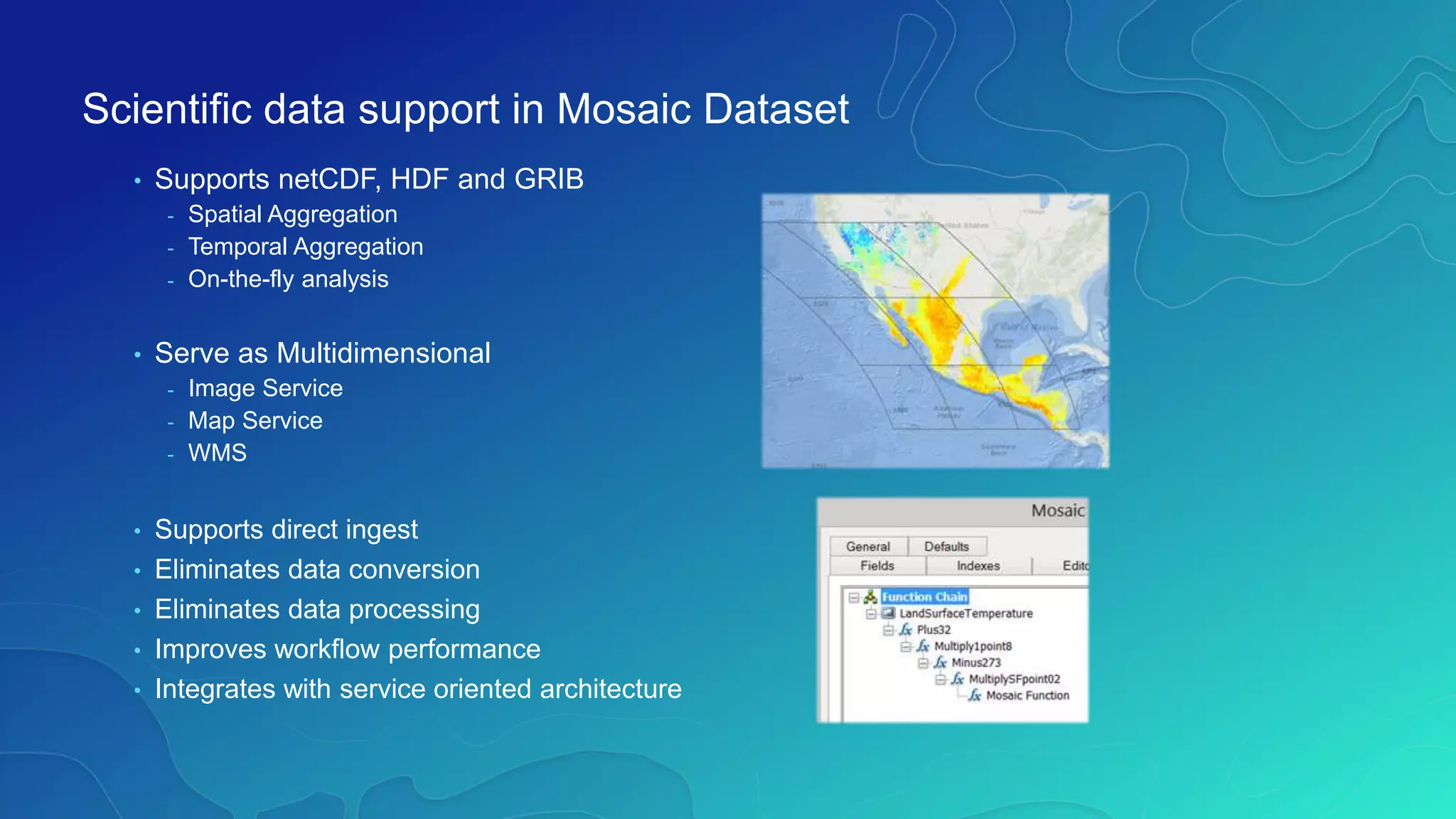
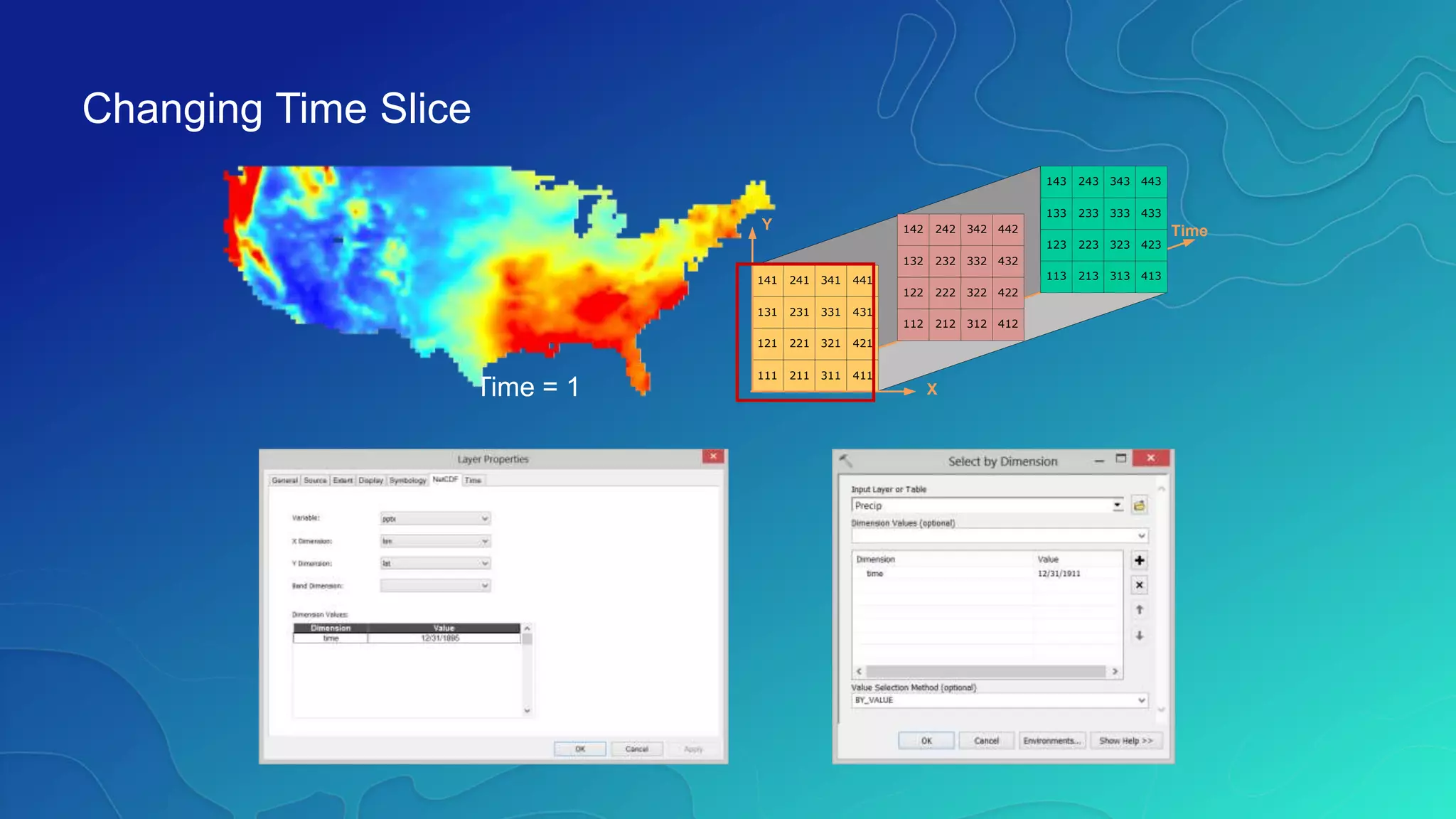
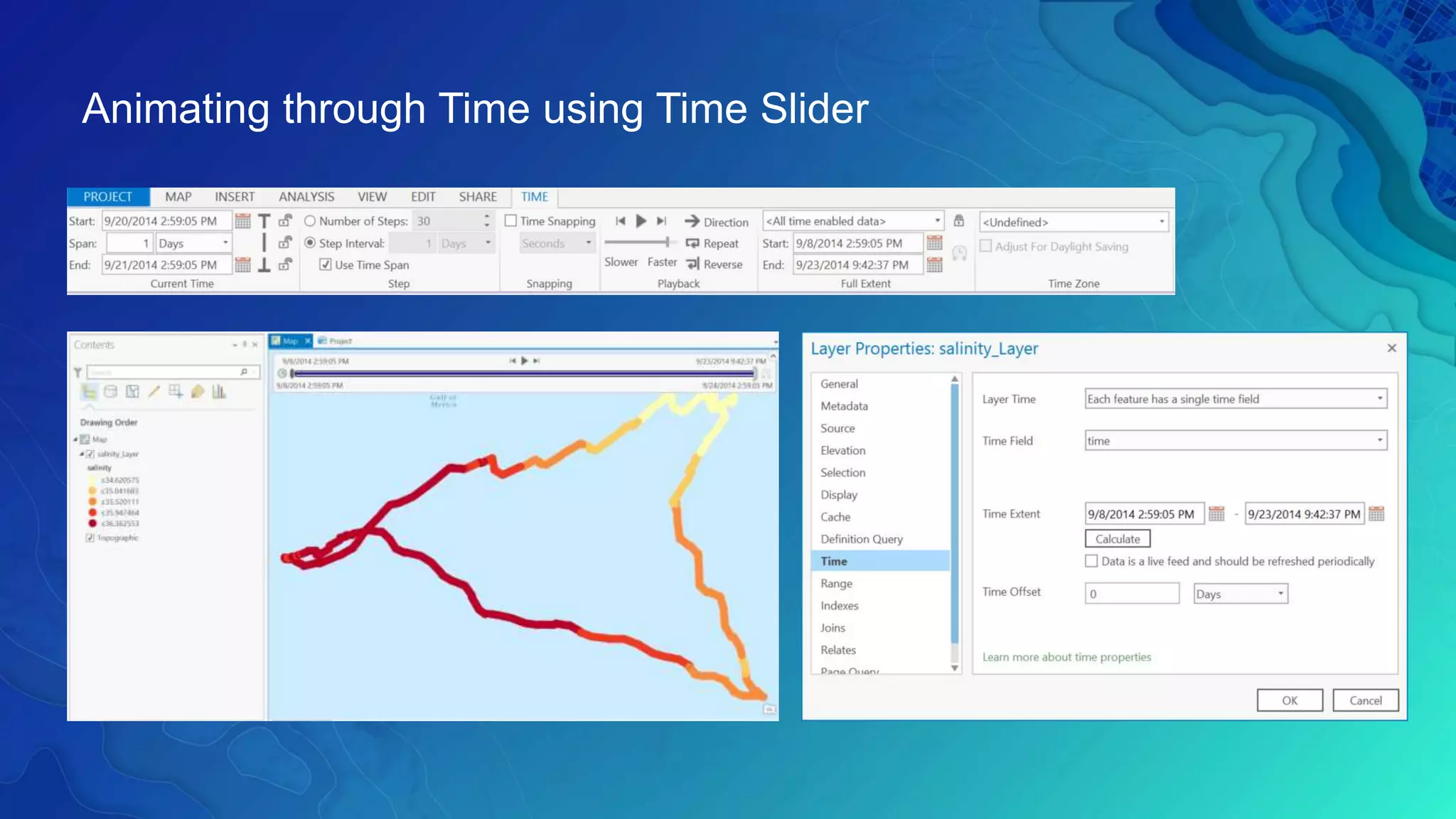
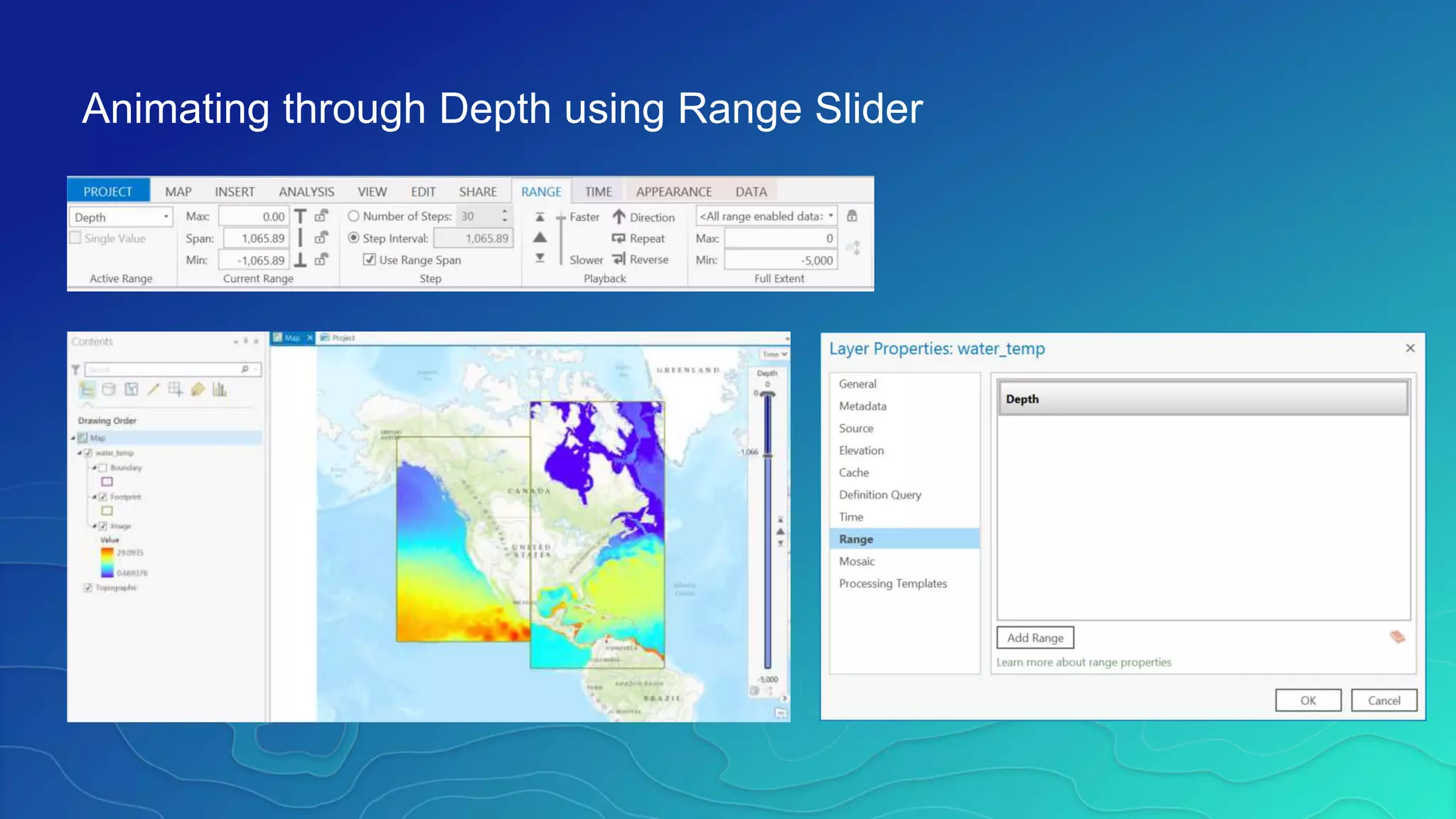
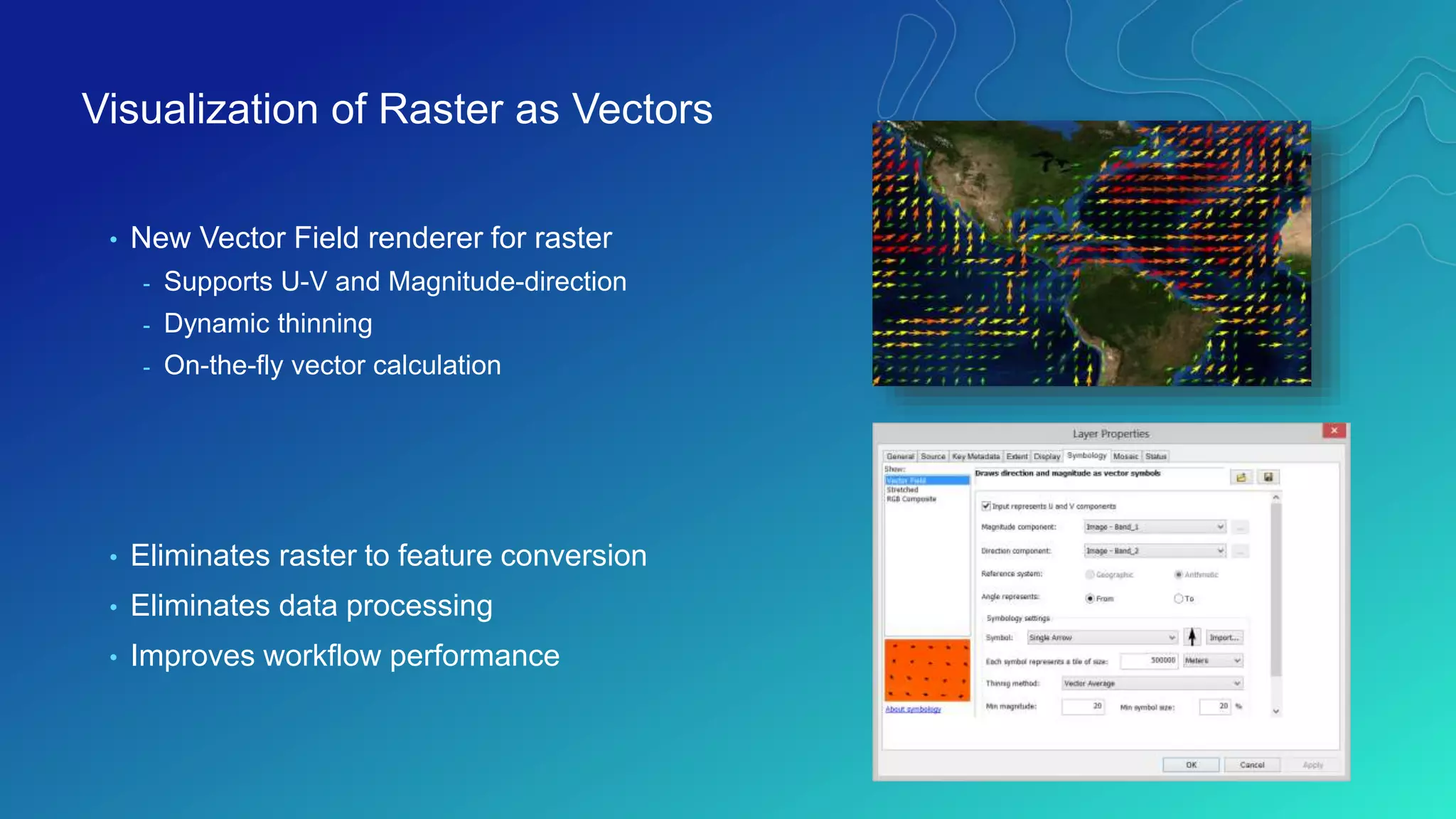
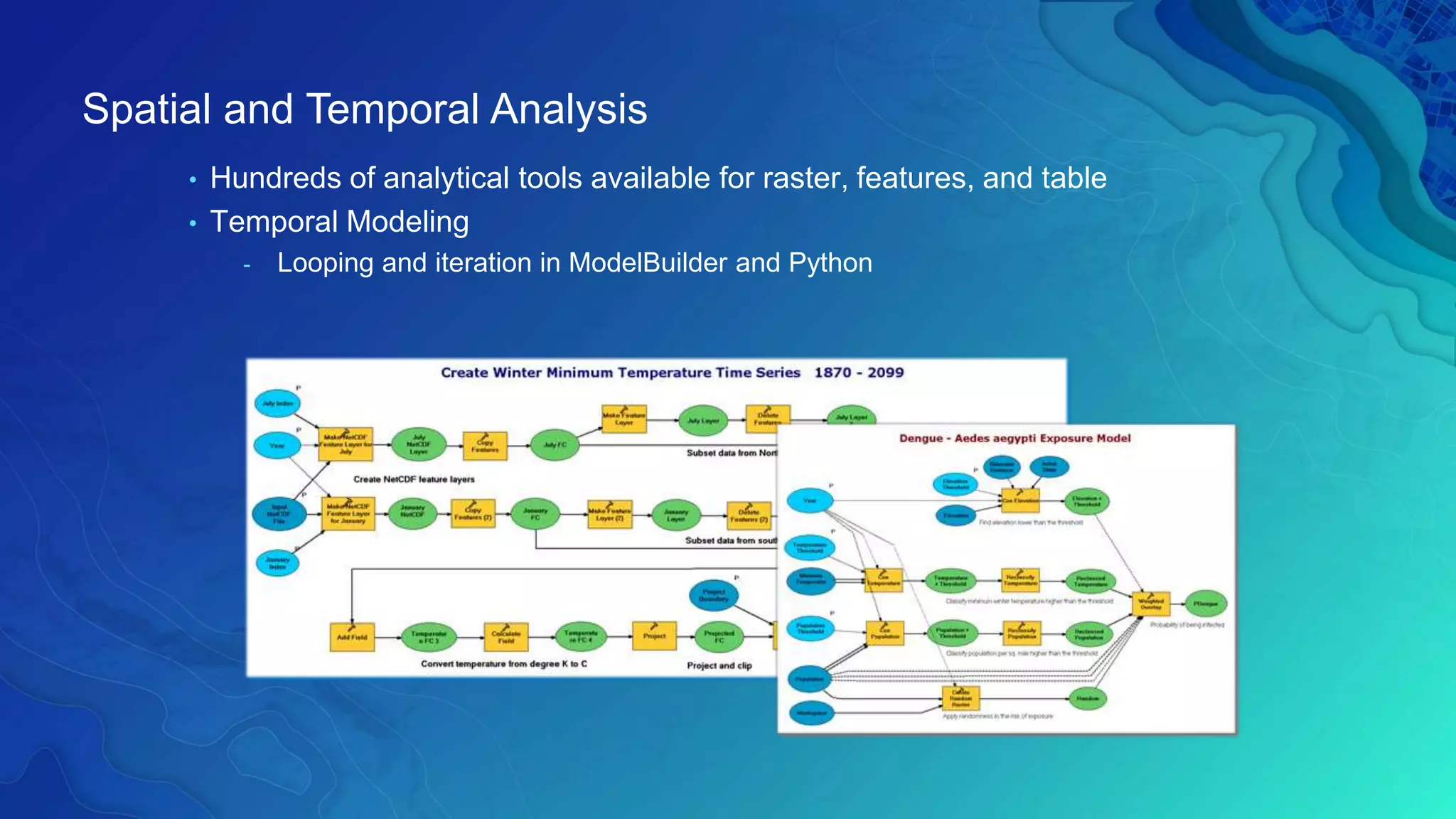
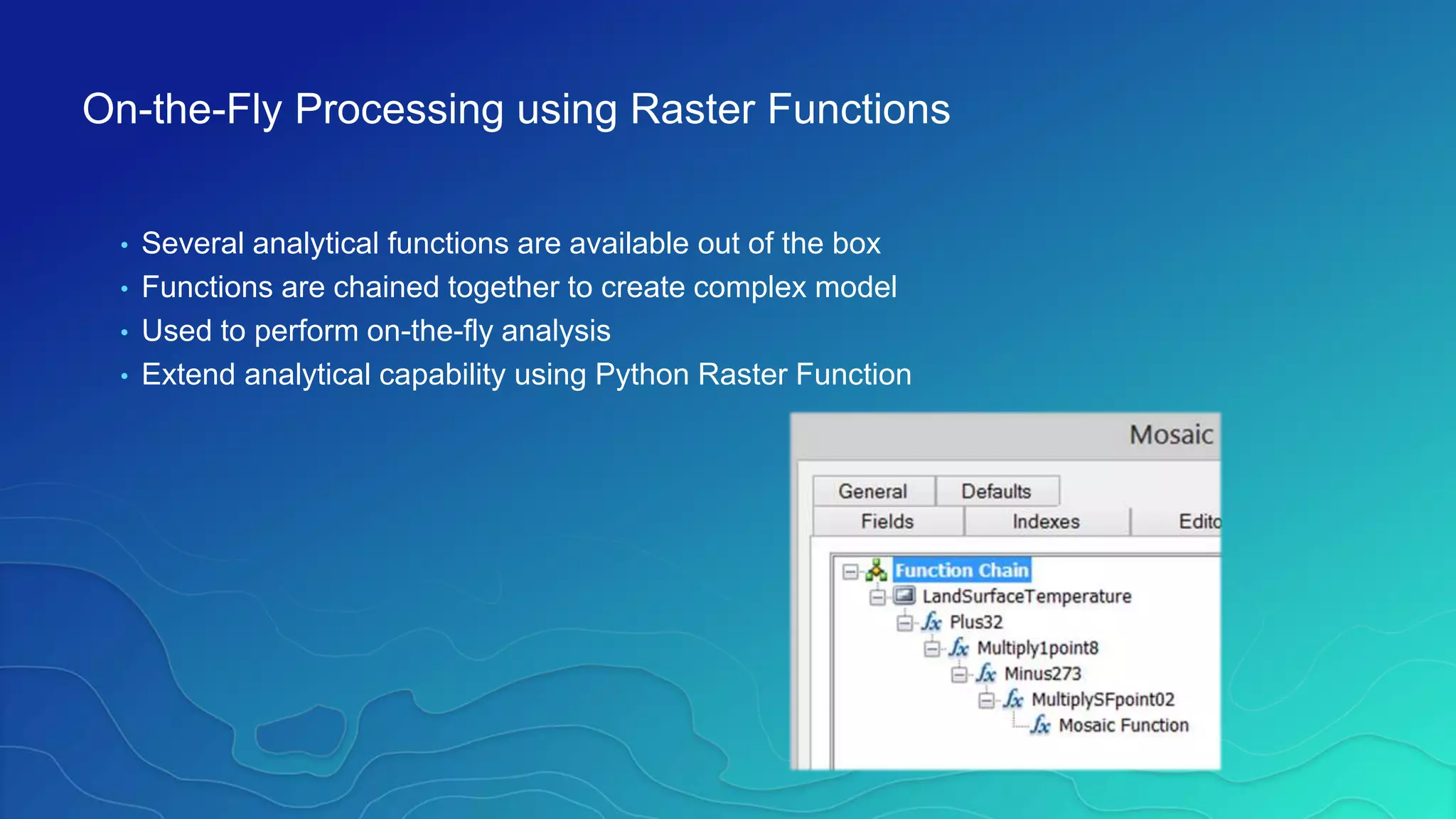
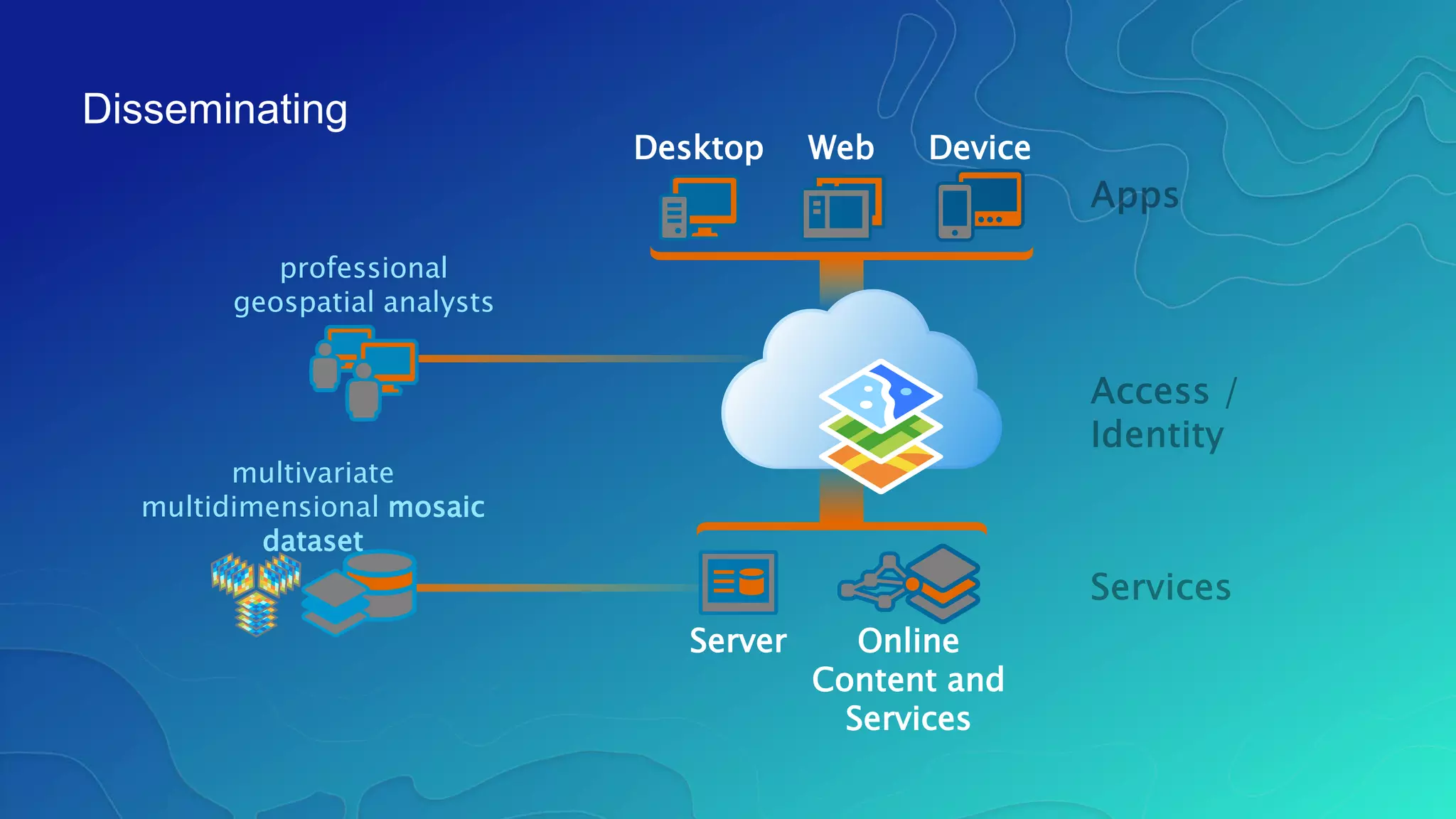
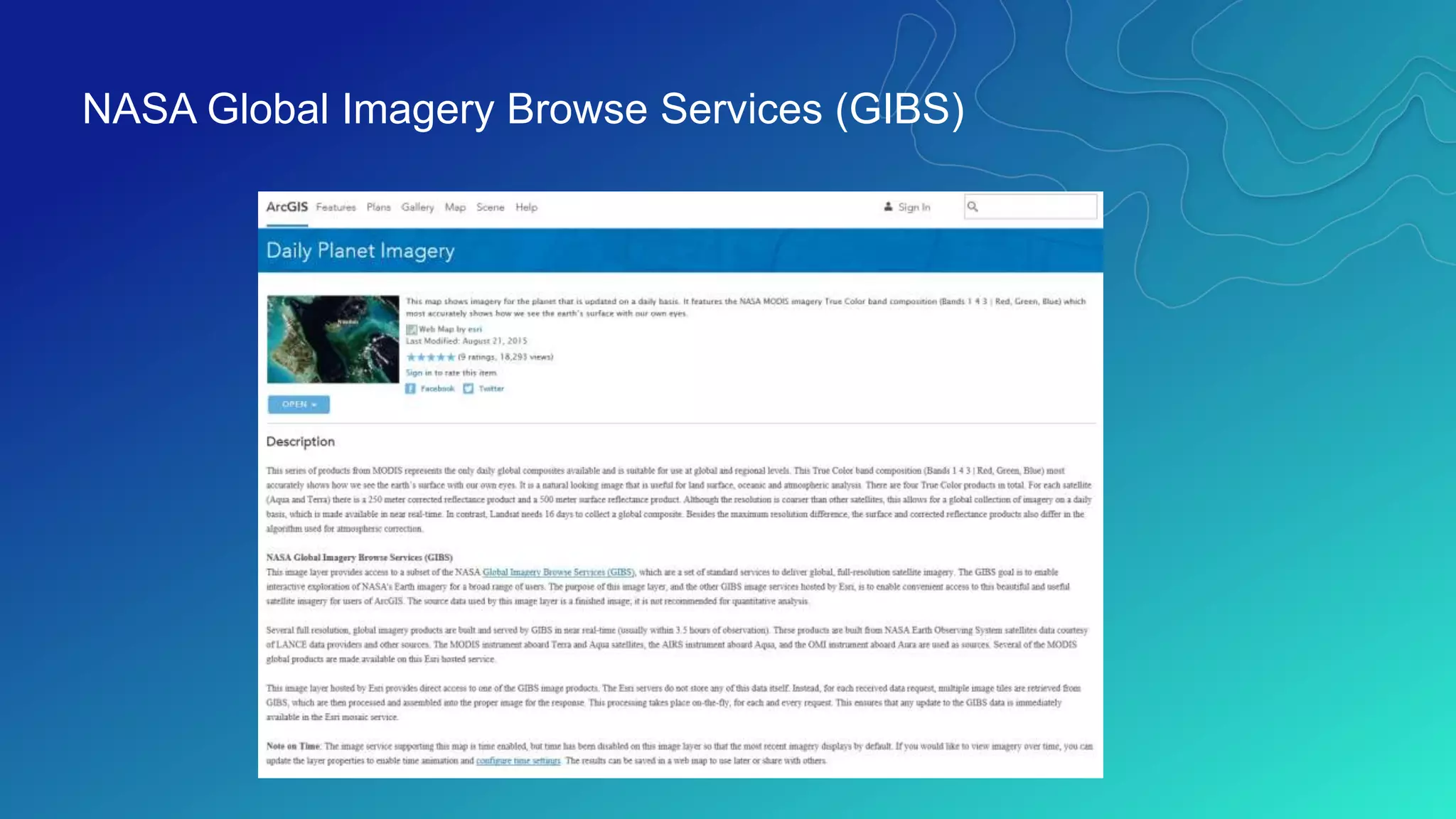
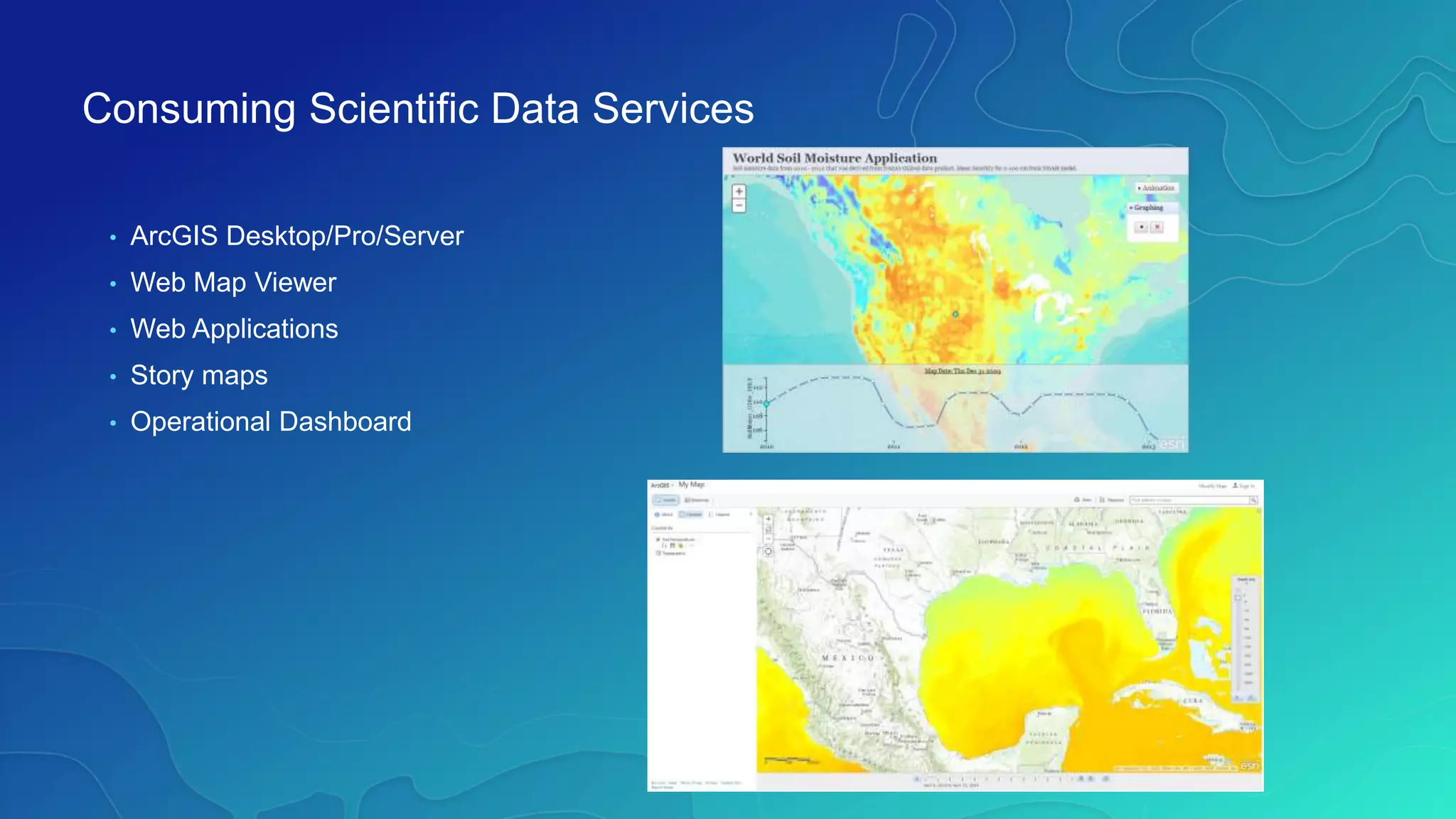
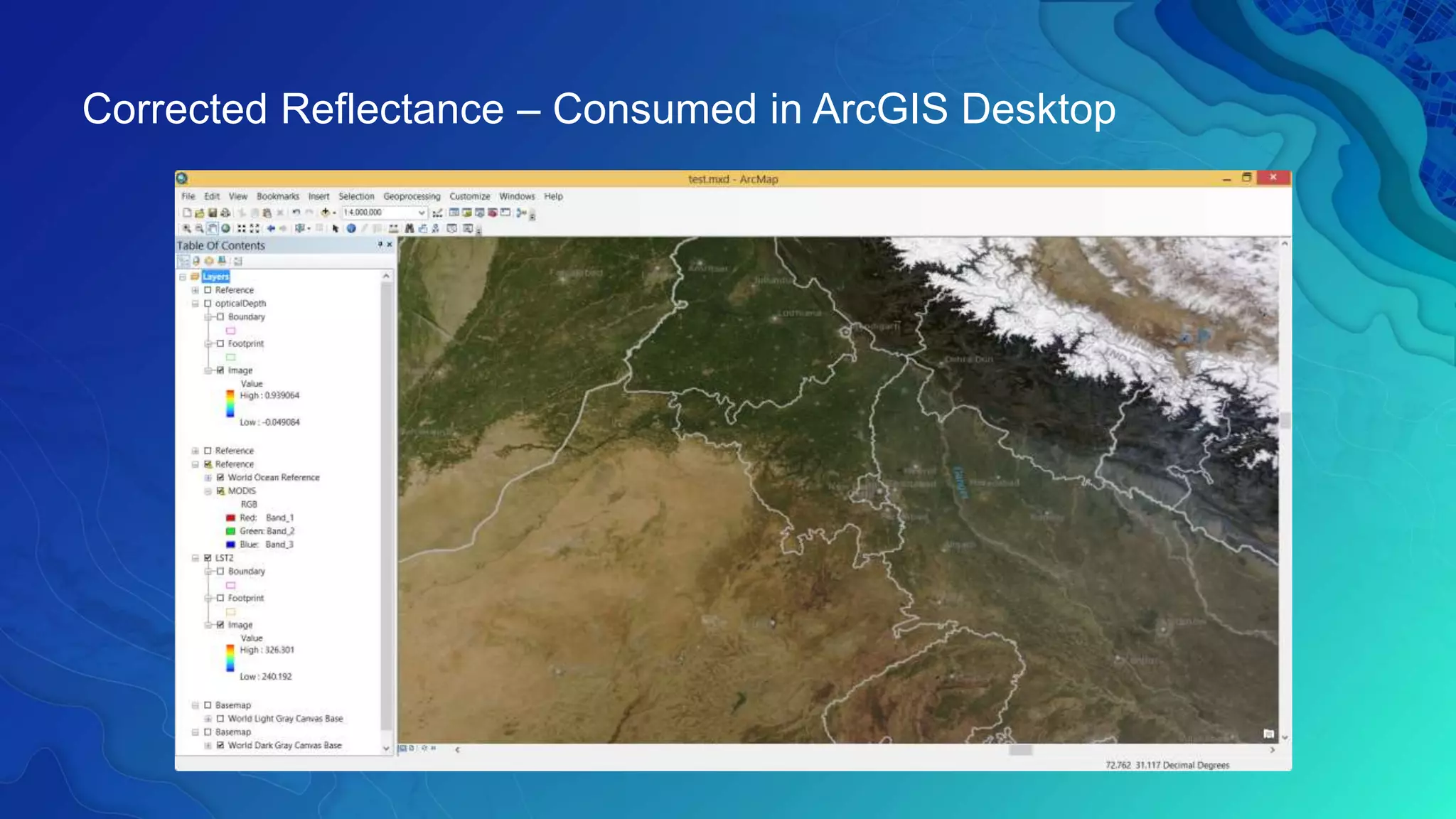
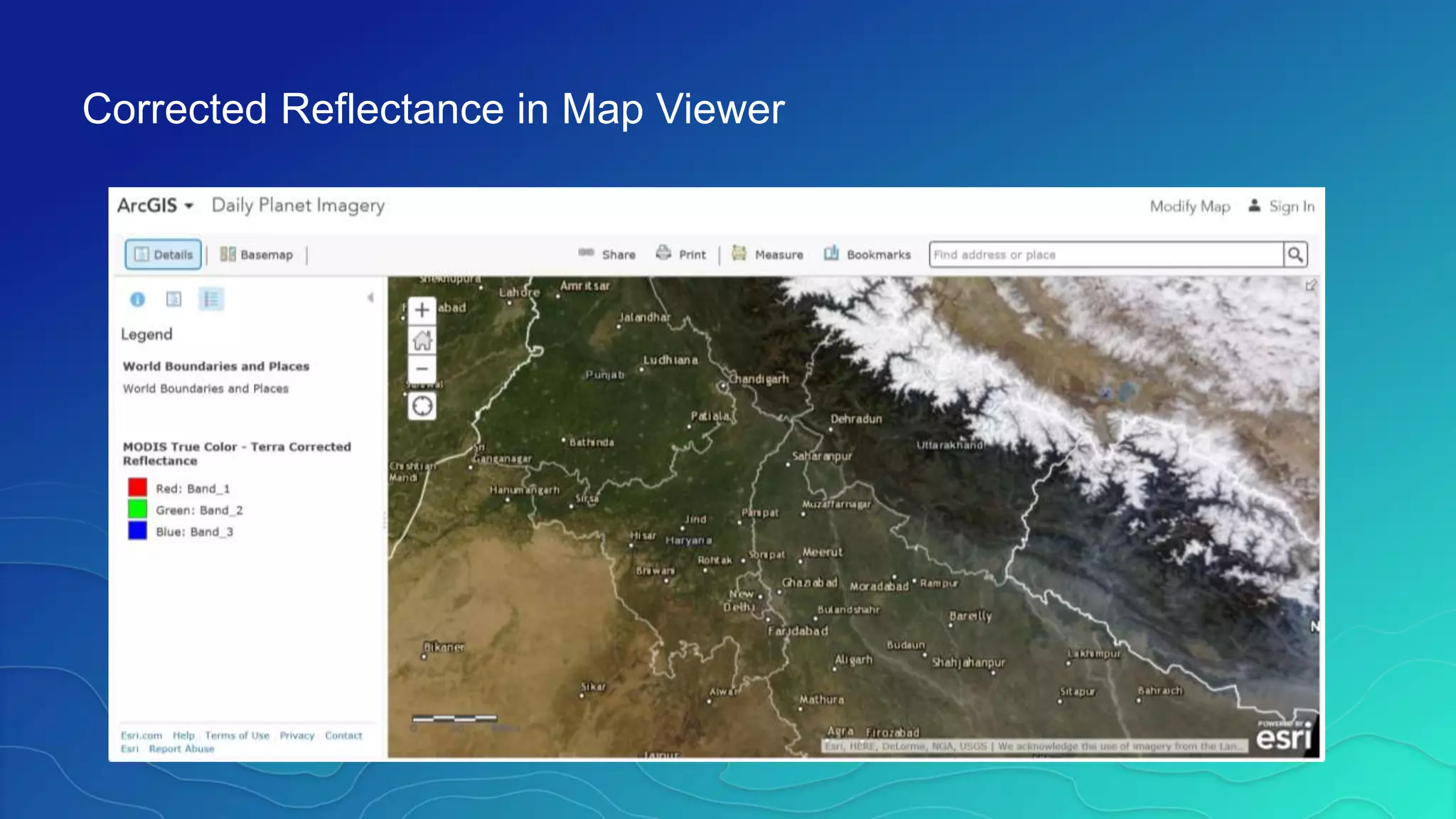
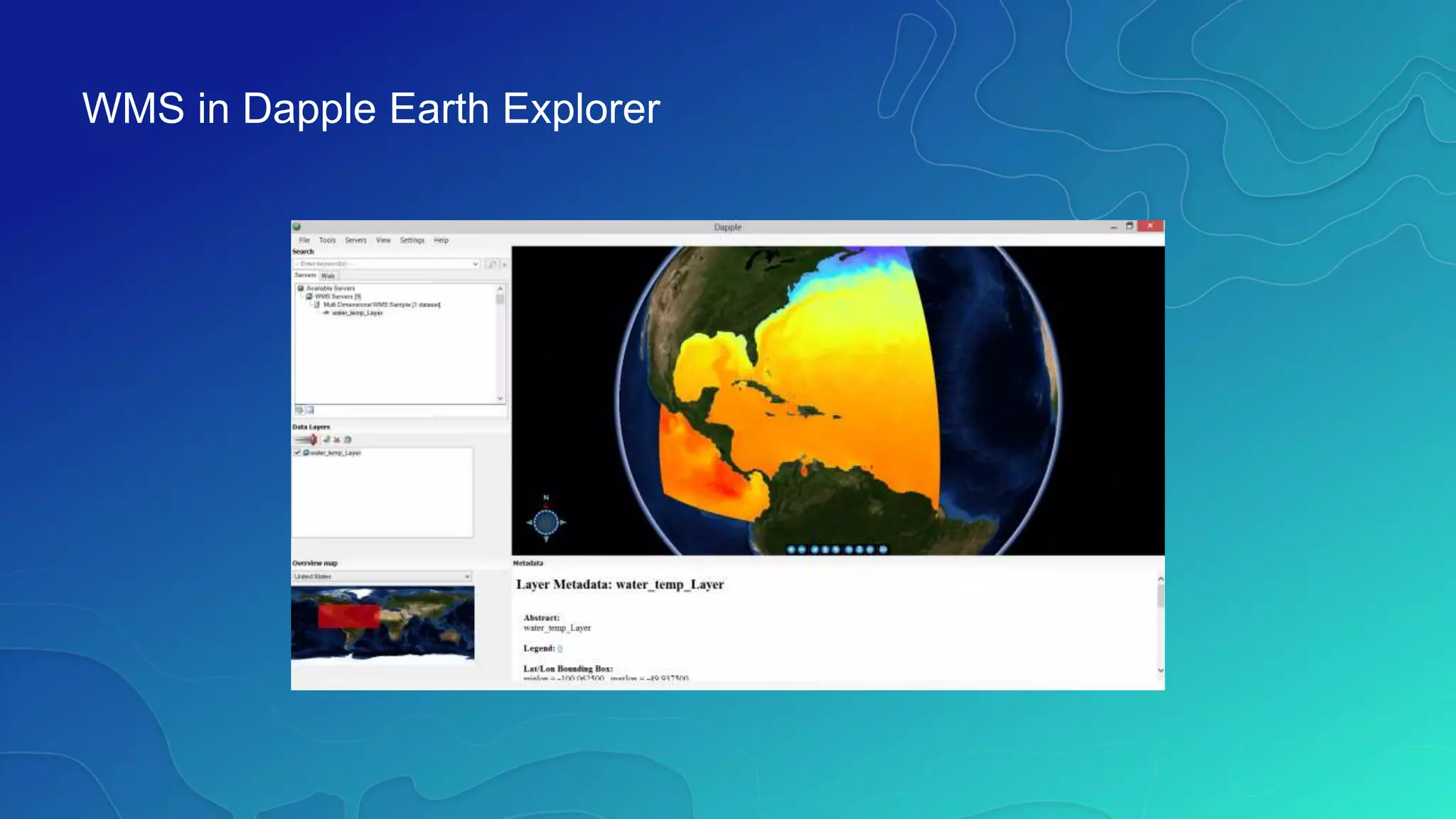
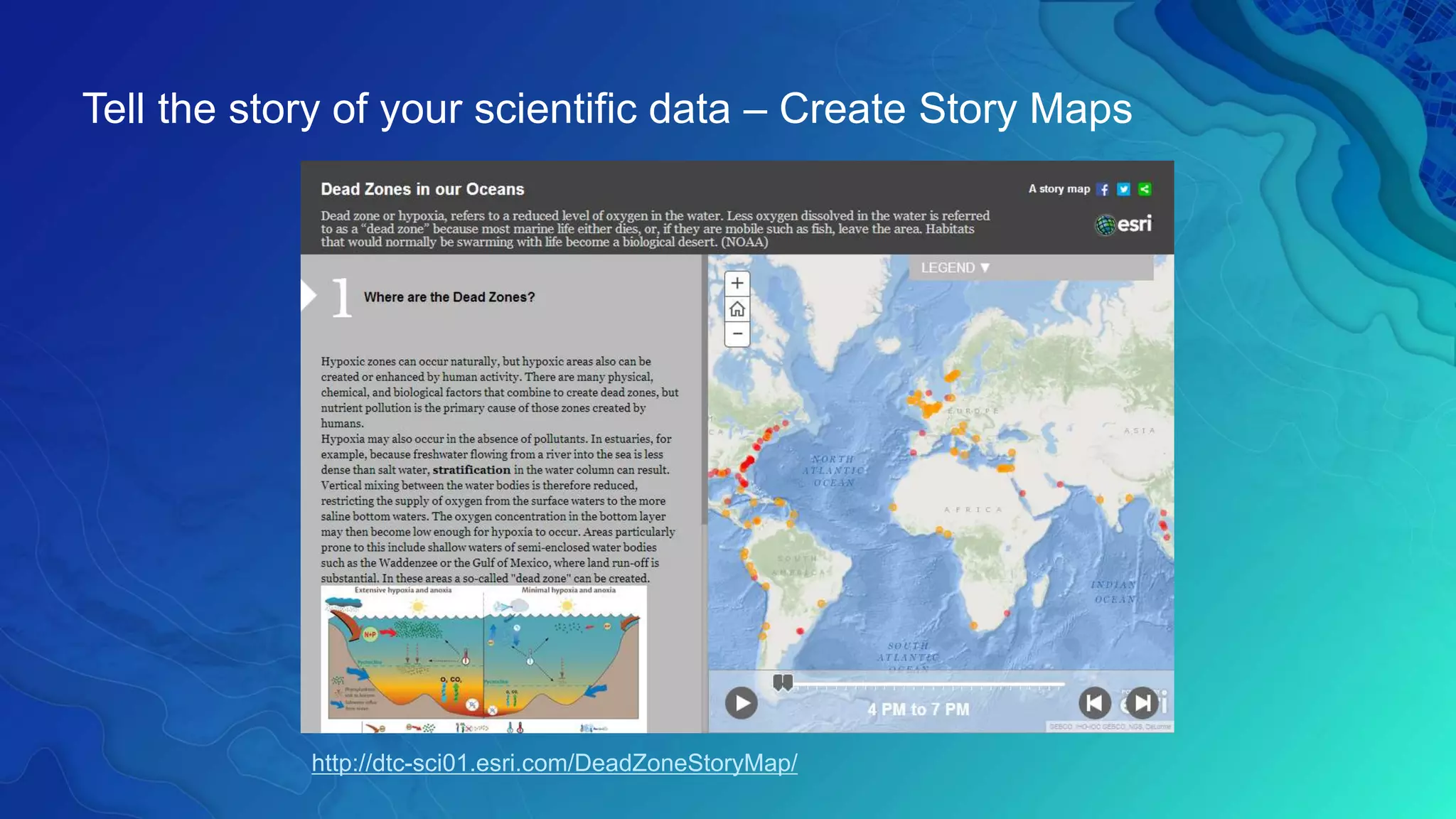
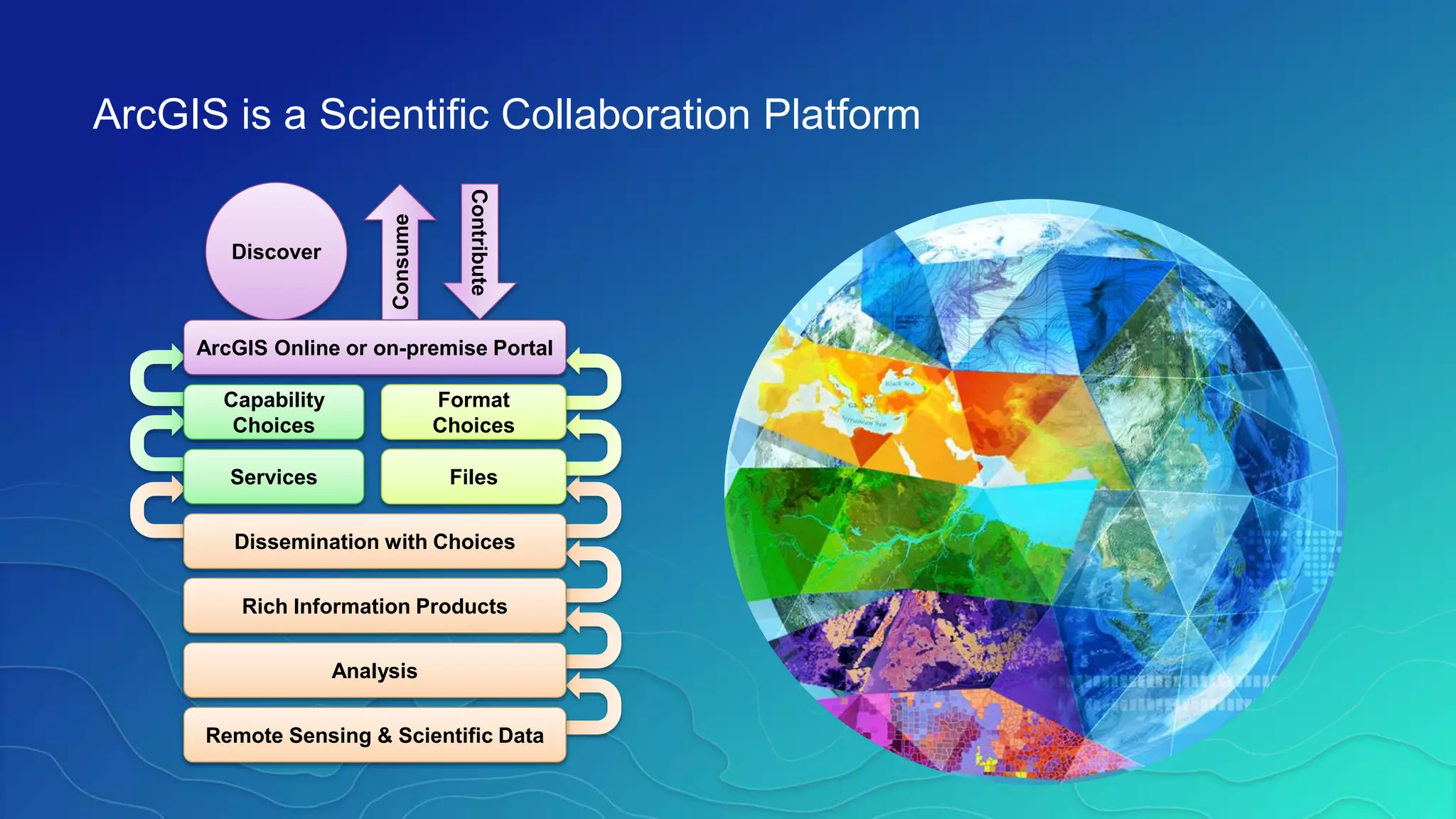
This document discusses how ArcGIS supports scientific multidimensional data. It can directly ingest data in formats like netCDF, HDF, and GRIB, and represent the data as raster layers, feature layers, or tables. Users can visualize, analyze, and share the data through tools in ArcGIS Desktop and services. Python can also be used to extend analytical capabilities. ArcGIS is evolving to better support scientific data through capabilities like multidimensional raster and feature layers, on-the-fly processing, and disseminating content as web services.