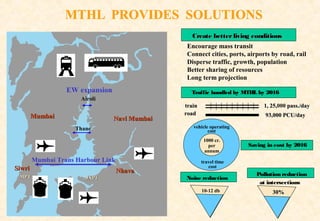
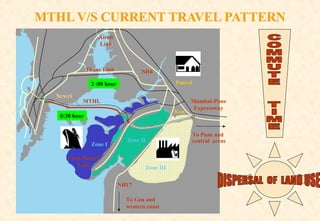
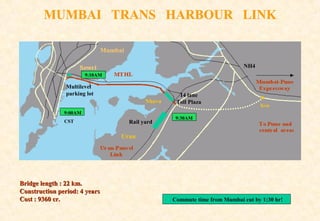
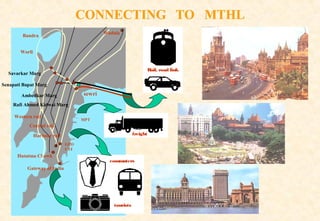
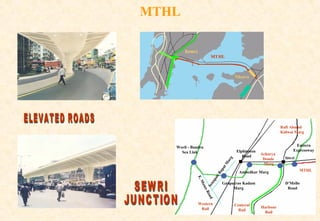
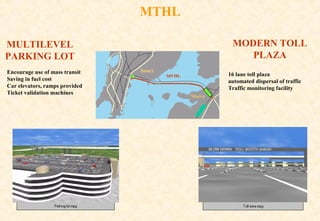
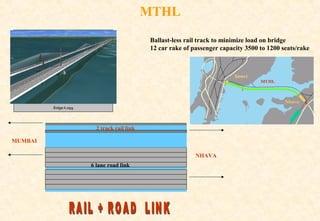
The document provides information on the Mumbai Trans-Harbour Link project, which will be a 22km bridge connecting Mumbai to Navi Mumbai. It will reduce commute times between the two cities. Key points:
- The bridge will carry six highway lanes and connect major ports, airports and cities to boost economic growth.
- Construction is estimated to cost 9360 crore rupees and take 4 years. It is expected to open in 2019.
- The project was first proposed in the 1970s but has faced delays. It received environmental clearance in 2012.
- It aims to improve transportation, disperse traffic, and encourage development across the region.