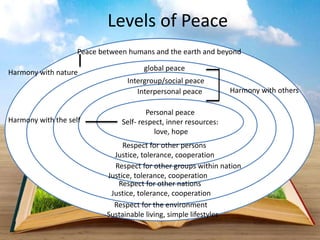
This document discusses the importance of peace education. It defines peace both as the absence of violence and the presence of just relationships. Peace can be analyzed at different levels from personal to global. Peace education aims to develop knowledge about conflict and nonviolent alternatives, as well as attitudes like respect, tolerance and compassion. It also builds skills for reflection, communication and conflict resolution. Overall, the document argues that peace education is an ethical and practical way to promote peace at all levels.