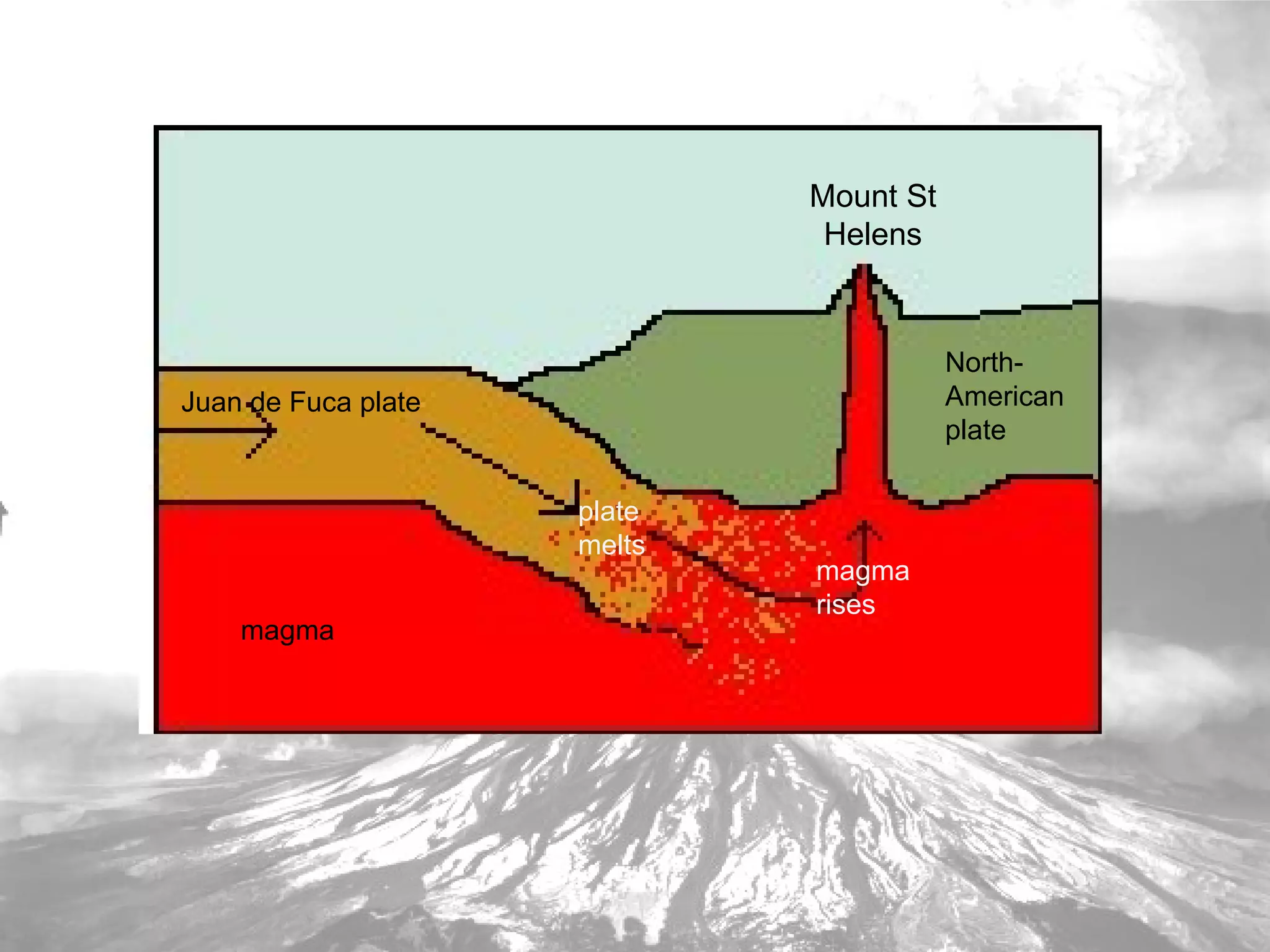
On May 18, 1980, Mount St. Helens erupted, destroying over 15 cubic kilometers of timber and killing 57 people. Mount St. Helens is an active volcano located in Washington state on the boundary between the North American and Juan de Fuca tectonic plates. As the Juan de Fuca plate slid under the North American plate, it melted and caused magma to rise and build up in Mount St. Helens, resulting in earthquakes until the top of the volcano was blown off in the eruption. The eruption covered over 60,000 square kilometers with volcanic debris and ash and caused extensive economic and environmental damage to the surrounding area.