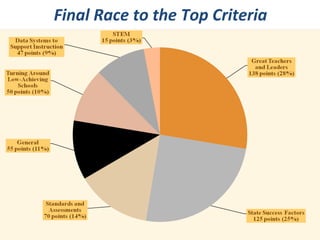
The document discusses STEM education in Maryland. It outlines the governor's STEM taskforce which aims to: 1) align K-12 STEM curriculum with college and career requirements; 2) triple the number of STEM teachers and increase their retention rate; 3) ensure all math and science teachers have skills to teach college-ready curriculum. It also discusses previous STEM initiatives in Maryland and components of effective STEM activities like problem-based learning.