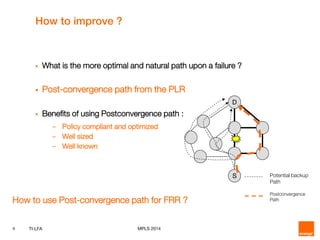
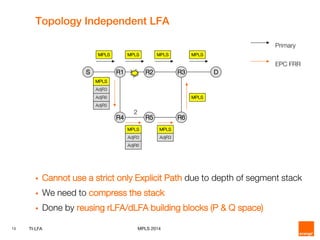
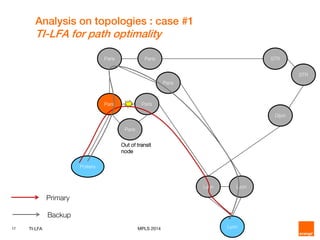
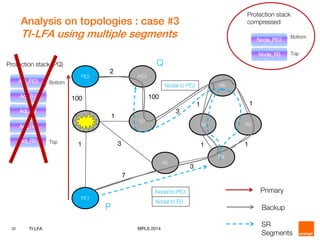
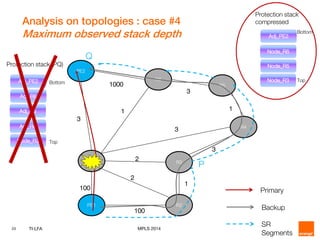
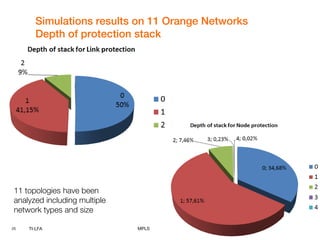
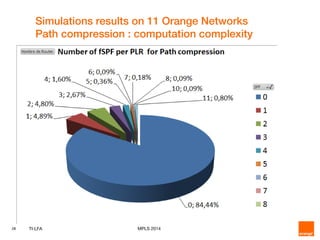
This document discusses Topology Independent LFA (TI-LFA), a fast reroute technique that provides 100% node and link protection using Segment Routing. It begins by outlining requirements for fast reroute, then introduces TI-LFA which computes the post-convergence path and encodes it as a loop-free Segment Routing path. The document analyzes applicability on Orange network topologies and presents simulation results showing TI-LFA achieves low stack depth and path compression. It concludes that TI-LFA is a scalable solution that meets requirements by providing optimal fast reroute paths without side effects.