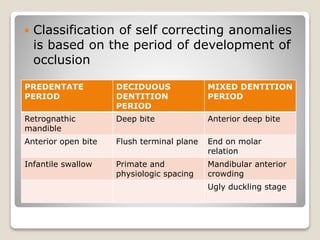
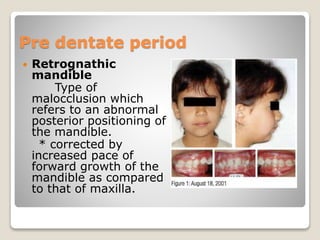
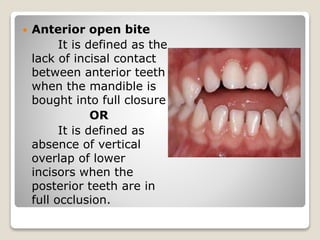
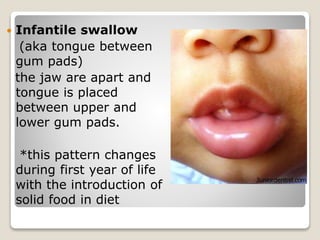
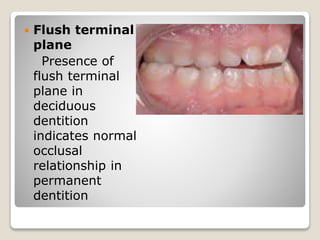
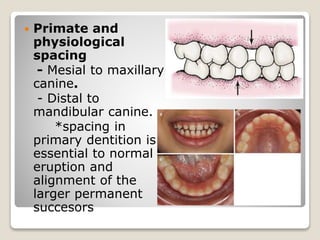
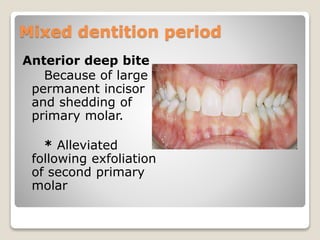
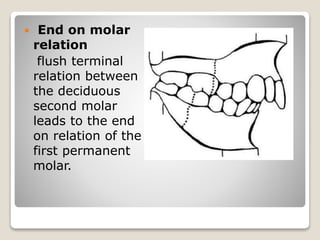
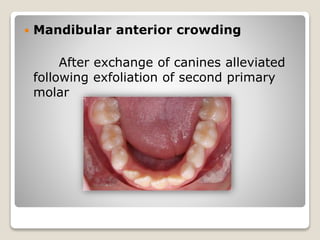
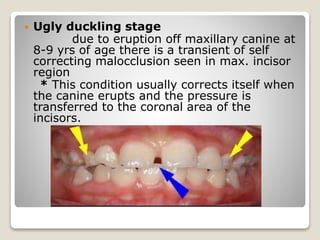
This document discusses self-correcting anomalies that arise during development from the predentate period to the permanent dentition period. It classifies anomalies based on the developmental period and describes several types including retrognathic mandible, anterior open bite, deep bite, flush terminal plane, primate and physiological spacing, anterior deep bite, end on molar relation, mandibular anterior crowding, and the ugly duckling stage. Many of these anomalies correct on their own through continued growth, eruption of teeth, attrition, and movement of jaws without requiring dental treatment.