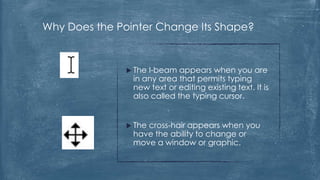
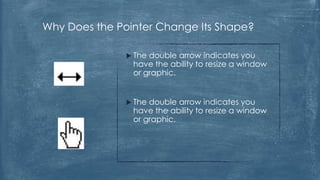
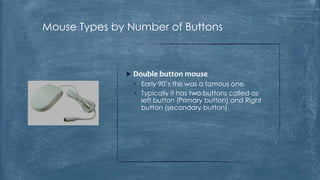
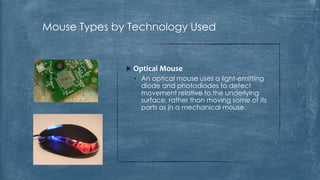
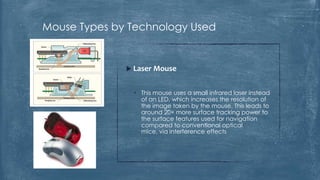
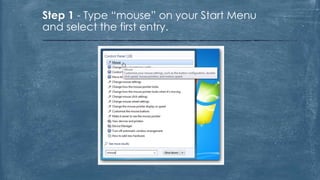
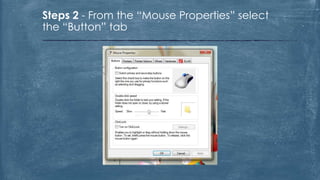
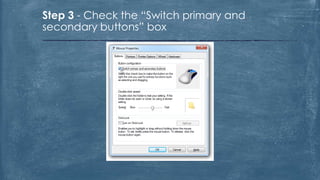
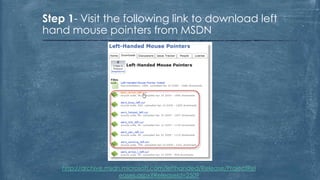
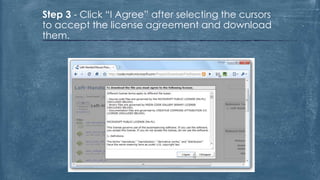
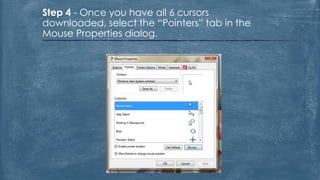
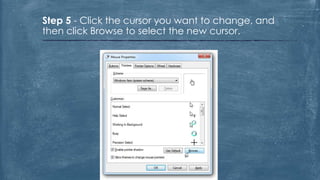
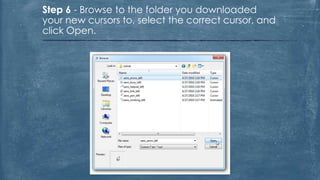
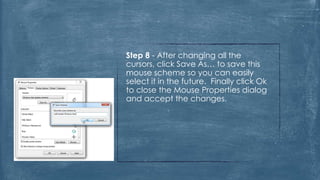
The document discusses the history and functionality of the computer mouse. It describes how Douglas Engelbart invented the first mouse in 1963. It explains the basic functions and actions of a mouse like pointing, clicking, scrolling. It also discusses different types of mice based on available features like cordless, footmouse, and technology used like mechanical, optical. The document is a thorough overview of the computer mouse.