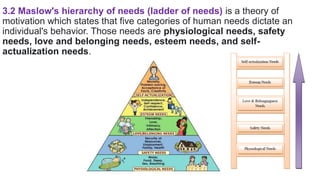
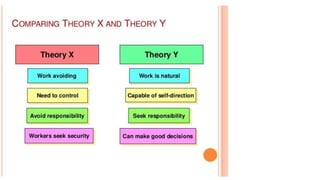
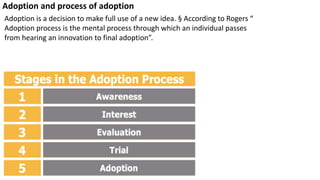
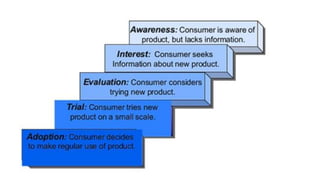
This document outlines theories of motivation including Maslow's hierarchy of needs and McGregor's X and Y theory. It also discusses contingency theory, Herzberg's two-factor theory, and Rogers' model of the adoption process. Maslow's hierarchy proposes that physiological, safety, love, esteem and self-actualization needs motivate behavior. McGregor's X theory assumes people dislike work while Y theory assumes they find it fulfilling. Contingency theory focuses on long-term employment. Herzberg's two factors distinguish between job satisfaction and dissatisfaction. Rogers identified innovators, early adopters, early majority, late majority and laggards in the adoption of new ideas.