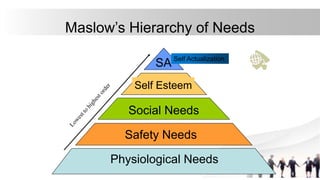
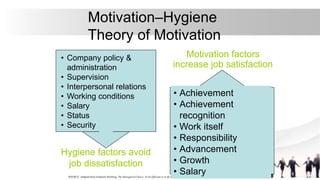
This document discusses various theories of motivation and their application to employee performance. It aims to identify different motivation theories, understand motivation's role in performance, classify employee needs, and apply theories to analyze performance issues. Theories covered include Maslow's hierarchy of needs, Herzberg's two-factor theory, McClelland's need theory, McGregor's Theory X and Y, and Ouchi's Theory Z. Each theory's key aspects and limitations are explained.