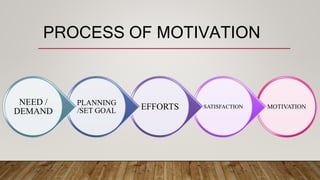
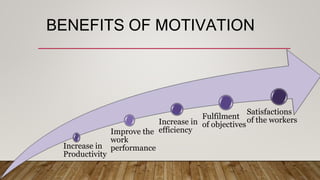
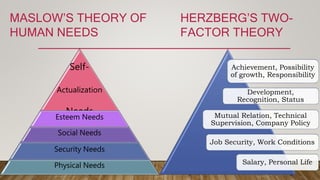
The document discusses motivation in the workplace. It defines motivation as an internal energy that drives people to achieve goals and meet expectations. Motivation comes from the Latin word "movere" meaning to move or energize. The document outlines factors that motivate employees like work environment, pay, benefits and appreciation. It also discusses theories of motivation from Maslow's hierarchy of needs to Herzberg's two-factor theory. The document notes that while motivation can increase productivity and performance, motivating individuals is challenging and excessive motivation can be harmful. Lastly, it states that the most lasting motivation comes from self-motivation.