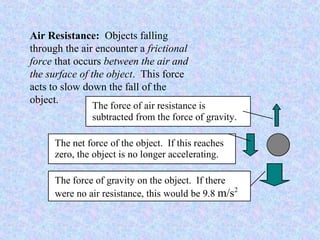
This document discusses gravity and the factors that affect how objects fall. It explains that gravity is a force that pulls all objects towards Earth. The greater the mass of an object, the stronger the gravitational pull, and objects that are closer together experience a stronger gravitational attraction. When only gravity is acting on an object, its acceleration is 9.8 m/s2, so all objects in free fall accelerate at the same rate regardless of their mass. Air resistance acts to slow falling objects based on their size and shape, but two objects in a vacuum would hit the ground simultaneously according to Galileo's experiments.